Indigenous people of New Guinea facts for kids
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 14,800,000 | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| Papua New Guinea and Western New Guinea, Indonesia | |
| Languages | |
| Languages of Papua In Papuan New Guinea: Tok Pisin, Hiri Motu, Unserdeutsch and English In Indonesia: Papuan Malay and Indonesian |
|
| Religion | |
| Christianity, Islam, and Traditional Faiths | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Other Melanesians, Ambonese, Moluccans, Aboriginal Australians, Malagasy people |
The Papuans are the original people who live in Western New Guinea (part of Indonesia) and Papua New Guinea. They are part of a larger group called Melanesians.
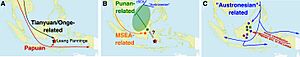
Scientists believe that the first people arrived in New Guinea and nearby islands about 50,000 years ago. Back then, New Guinea and Australia were connected as one big landmass called Sahul. Much later, about 3,500 years ago, another group of people called Austronesians arrived. They brought new languages and pigs, and their genes can still be found in some Papuan people living near the coast today.
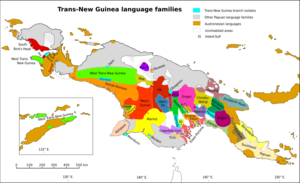
Papuans speak many different languages. Most of these are "non-Austronesian" languages, which are unique to New Guinea and nearby islands. Some Papuans also speak Austronesian languages, especially along the coast. Newer languages like Tok Pisin and Papuan Malay have also developed.
The word "Papuan" is used in different ways. In language studies, "Papuan languages" refers to many different language families that are not related to each other, but are spoken in this region. In anthropology (the study of human societies), "Papuan" often means the diverse groups of people who lived in Melanesia before the Austronesian speakers arrived.
Contents
Papuan Languages
There are over 1,000 different languages spoken in Papua New Guinea and Western New Guinea! This makes it one of the most linguistically diverse places on Earth. These languages are generally split into two main types:
- Austronesian languages: These languages are spoken by people who arrived later, mostly along the coasts.
- Papuan languages: This is a general term for all the other languages. These languages are very diverse and most of them are not related to each other. They are unique to New Guinea and its surrounding islands.
Papuan People Groups
Many different groups of Papuan people live in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea. Some groups speak Austronesian languages, and these are sometimes shown in italic writing.
In Indonesia
Indonesia has several provinces in New Guinea, and each is home to many unique Papuan groups.
West Papua Province
Some of the groups in West Papua include the Arfak, Hatam, Meiah, and Wamesa people.
Southwest Papua Province
In Southwest Papua, you can find groups like the Abun, Biak, Ma'ya, and Tehit people.
Papua Province
The Papua province is home to groups such as the Sentani, Tobati, and Demta people.
Highland Papua Province
In the mountains of Highland Papua, groups like the Dani, Yali, and Lani live.
Central Papua Province
Central Papua has groups like the Amung, Kamoro, and Mee people.
South Papua Province
In South Papua, you'll find groups like the Asmat, Marind, and Korowai people.
In Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea also has many different Papuan groups. Some well-known ones include the Huli, Fore, Iatmul, and Orokaiva people.
Bismarck Archipelago
This group of islands near Papua New Guinea is home to people like the Baining and Tolai.
How Papuans Came to Be
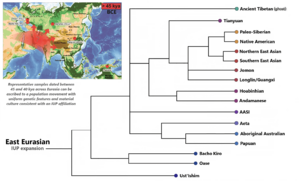
The history of Papuan people is very old! They are thought to be among the first people to settle in the region of Australia and New Guinea. This happened between 50,000 and 37,000 years ago. Back then, Australia and New Guinea were connected as one big continent called Sahul.
About 10,000 years ago, sea levels rose and separated New Guinea from Australia. Even though they were once connected, the ancestors of Aboriginal Australians and Papuans had already become different groups about 40,000 years ago. Papuans are more closely related to other Melanesians than to Aboriginal Australians.
Genetic Clues
Scientists study DNA to learn about human history.
- Y-DNA: Most Papuan men have specific types of Y-DNA (passed down from father to son) called Haplogroup MS and Haplogroup C1b2a.
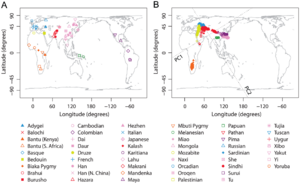
- Autosomal DNA: The main part of Papuan DNA comes from ancient groups in East Eurasia. This connects them to people in East and Southeast Asia. Papuans also have a small amount of DNA from an ancient human group called Denisovans. This suggests that their ancestors mixed with Denisovans long ago.
Scientists believe that the ancestors of Papuans went through a "bottleneck" (a time when their population became very small) before they settled in the region. They also found that Papuan people have a lot of genetic diversity, meaning there are many differences in their DNA. This is because different groups lived separately for a long time. For example, people living in the highlands (mountains) have different DNA from those living in the lowlands.
Ancient Human Mixing
In 2010, scientists discovered an ancient human species called the Denisovan. Research suggests that the ancient ancestors of Papuans mixed with Denisovans in Asia. This means that Papuan people today share about 4% to 7% of their DNA with Denisovans! This ancient DNA might have helped Papuans adapt to their local environment, especially their immune systems.
The ASPM Gene
A study in 2005 looked at a gene called ASPM. This gene is thought to be important for brain development. The study found that Papuan people have a high rate (about 59.4%) of a specific, newer version of the ASPM gene. Scientists believe this gene version might have given an advantage, causing it to become more common over time.
Famous Papuan People
- Archie Thompson, a former Australian soccer player
- Elie Aiboy, a former Indonesian footballer
- Frans Kaisiepo, a former Governor of Papua and a National Hero of Indonesia
- Marlina Flassy, an Indonesian anthropologist and the first woman to be a Dean at Cenderawasih University
- Michael Somare, a former Prime Minister of Papua New Guinea
- Nitya Krishinda Maheswari, an Indonesian badminton player who won a gold medal at the 2014 Asian Games
- Nowela Auparay, a professional singer and winner of Indonesian Idol
- Peter O'Neill, a former Prime Minister of Papua New Guinea
- Raema Lisa Rumbewas, an Indonesian weightlifter who won silver medals at the 2000 and 2004 Summer Olympics
- Boaz Solossa, an Indonesian footballer
- Benny Wenda, a leader for West Papuan independence
See also
- Aboriginal Australians
- Indigenous Australians
- Koteka Tribal Assembly
- List of ethnic groups of West Papua
- Malagasy people (Africa)
- Moluccans (to the west of New Guinea)
- Negrito (Southeast Asia)
- Papua conflict
- Proto-Australoid
- Stéphane Breton (filmmaker)
- Torres Strait Islanders between New Guinea and mainland Australia (including the Meriam people, whose language family is otherwise found in New Guinea)
Images for kids
-
Papuan people in folk dress in Jakarta
-
Newly married Kayu Batu couple in Jayapura, Indonesia