Denisovan facts for kids
The Denisovans were an ancient group of humans, much like the Neanderthals. They lived across Asia for a very long time, from about 285,000 to 30,000 years ago. Most of what we know about Denisovans comes from studying their DNA, which is like a genetic blueprint. For many years, scientists only had a few small bone pieces from them. However, a skull found in Harbin, China, was recently identified as Denisovan. This important discovery gives us a much clearer idea of what these ancient people looked like.
Contents
What are Denisovans?
For a long time, scientists weren't sure if Denisovans were a completely new species of human or a type of modern human. This was because they only had a few small bone fragments. It was hard to give them a proper scientific name.
However, in June 2025, scientists studied the Harbin cranium (a skull found in China). They looked at its mitochondrial DNA and proteins. They found that this skull, which belongs to a species called Homo longi, is definitely from a Denisovan. This discovery helped scientists understand more about these ancient people.
Some other older human fossils found in East Asia, like the Dali skull and the Jinniushan human, might also be related to Denisovans. Scientists are still studying these connections.
How Were Denisovans Discovered?
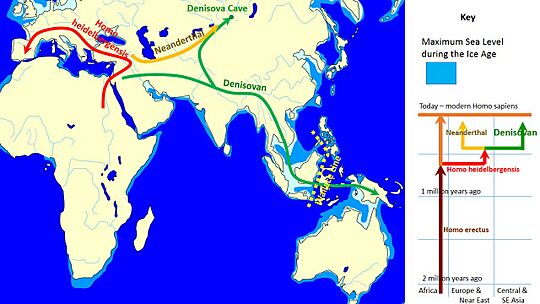
The first clue about Denisovans came from a place called Denisova Cave in Siberia, Russia. This cave is named after a hermit who lived there long ago. In the 1970s, a paleontologist named Nikolai Ovodov explored the cave, looking for animal fossils.
Then, in 2008, Russian archaeologists found a tiny finger bone from a young girl. This bone was very old, dating back between 76,200 and 51,600 years ago. When scientists studied the mitochondrial DNA from this bone, they realized it belonged to a new type of ancient human. This ancient human was different from both modern humans and Neanderthals. They called this new group "Denisovans."
Later, in 2019, scientists used special dating methods to find even older Denisovan remains in the cave. Some DNA from the cave's soil showed Denisovans were there as far back as 217,000 years ago. Neanderthals also lived in this cave at different times, sometimes even at the same time as Denisovans.
Important Denisovan Fossils
Scientists have found several important Denisovan fossils. Each discovery helps us learn more about these ancient humans.
| Name | What was found | Age | Where it was found | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Denisova 3 | Finger bone | 76,200–51,600 years old | Denisova Cave (Russia) | |
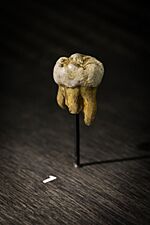
| Denisova 4 | Upper molar (tooth) | 84,100–55,200 years old | Denisova Cave (Russia) | |
| Denisova 8 | Upper molar (tooth) | 136,400–105,600 years old | Denisova Cave (Russia) | |
| Denisova 2 | Lower molar (baby tooth) | 194,400–122,700 years old | Denisova Cave (Russia) | |
| Xiahe mandible | Part of a jawbone | More than 160,000 years old | Baishiya Karst Cave (China) |  |
| Penghu 1 | Part of a jawbone | 130,000 to 190,000 years old | Penghu Channel (Taiwan) | |
| Denisova 11 | Arm or leg bone fragment | 118,100–79,300 years old | Denisova Cave (Russia) |  |
| TNH2-1 | Lower molar (tooth) | 164,000–131,000 years old | Tam Ngu Hao 2 Cave (Laos) | 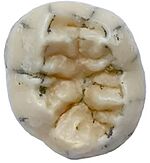 |
| BSY-19-B896-1 (Xiahe 2) | Rib fragment | About 42,000 years old | Baishiya Karst Cave (China) |  |
| Harbin cranium | Complete skull | More than 146,000 years old | Harbin (China) |  |
How Denisovans Evolved
By studying their DNA, scientists learned that Denisovans and Neanderthals were more closely related to each other than they were to modern humans. It's like they were cousins.
Scientists believe that the ancestors of Denisovans and Neanderthals separated from the ancestors of modern humans about 804,000 years ago. Then, Denisovans and Neanderthals themselves separated from each other around 640,000 years ago.
The cool climate of Denisova Cave helped preserve the DNA. Scientists found that Denisovan mitochondrial DNA (a special type of DNA passed down from mothers) is quite different from that of modern humans and Neanderthals. This suggests that Denisovans branched off from our shared family tree a very long time ago.
Where Did Denisovans Live?
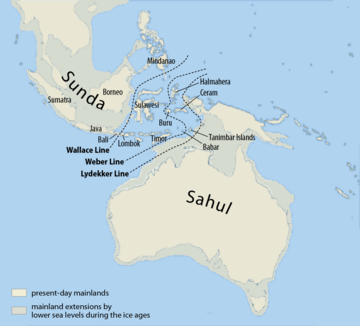
We know Denisovans lived in places like Siberia, Tibet, Laos, Taiwan, and Manchuria. The jawbone found in Baishiya Karst Cave in Tibet shows they were the first humans known to live on the high Tibetan Plateau.
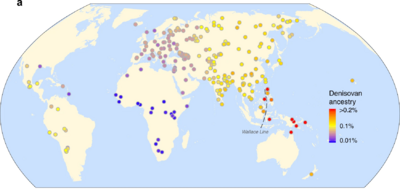
Even though we've only found their bones in a few spots, their DNA in modern people suggests they spread out across much of East Asia and even into Oceania. Scientists think there might have been different groups of Denisovans living in different areas.
Some studies suggest that Denisovans were able to cross the Wallace Line, which is a deep-water boundary that separates Asian wildlife from Australian wildlife. This means they might have traveled across large bodies of water, possibly using simple boats. If so, they would be one of the few ancient human groups to do this.
Denisovans were very adaptable! They lived in many different environments. In Denisova Cave, the climate changed a lot, from warm forests to cold, open lands. In Baishiya Karst Cave, they lived high up in the mountains, where it's cold and there's less oxygen. They also seemed to live in the warm, humid jungles of Southeast Asia.
What Did Denisovans Look Like?
The Harbin cranium shows Denisovans had a long, low skull with a sloping forehead. They had very wide faces, large eye sockets, and thick brow ridges. Their noses were large, possibly to help with cold air. They also had flat cheekbones and a wide mouth. The Harbin skull is the longest ancient human skull found.
Denisovans had large brains, similar to modern humans and Neanderthals. Their faces were flatter than Neanderthals, but like Neanderthals, Denisovans did not have a chin. This is seen in the Penghu 1 jawbone.
Their molars (back teeth) were very large, much bigger than those of modern humans or Neanderthals. These large teeth are more like those of much older human ancestors.
From the Jinniushan human fossil, thought to be Denisovan, we know they could be quite tall. This female fossil was about 168 cm (5 feet 6 inches) tall and weighed around 78 kg (172 pounds).
Denisovan DNA suggests they likely had dark skin, dark hair, and brown eyes. Their DNA also shows special genes that helped them adapt to living in high places with less oxygen, like the Tibetan Plateau.
How Did Denisovans Live?
Tools and Ornaments
In Denisova Cave, archaeologists found many stone tools for scraping and cutting. Some are very old, dating back about 287,000 years. This shows Denisovans developed new ways to make and use tools over time.
Beautiful ornaments were also found, like marble and ivory rings, and pendants made from animal teeth. However, scientists are not sure if Denisovans or later modern humans made these items.
Life in Different Environments
At Baishiya Karst Cave in Tibet, Denisovans hunted large animals like goat antelopes and woolly rhinoceroses. They also hunted smaller animals and used their bones to make tools.
In 2025, archaeologists in Yunnan, China, found 35 wooden tools near an ancient lake. These tools, like digging sticks, were used to find and prepare plant foods. This shows Denisovans were smart about using resources in their environment.
Ancient Handprints
In Tibet, scientists found five hand and footprints made by children between 226,000 and 169,000 years ago. These might have been made by Denisovan children. Some scientists think these could be the oldest examples of rock art in the world. The prints suggest they were made by children around 7 to 12 years old.
Denisovans and Other Humans
Scientists have found that ancient humans, including Denisovans, Neanderthals, and early modern humans, sometimes had children together. This means their genes mixed, and some of these ancient genes are still present in people today!
Mixing with Neanderthals
Denisovans and Neanderthals often met and had families. A famous example is "Denny" (Denisova 11), a girl who lived about 118,000 to 79,000 years ago. Scientists discovered she had a Denisovan father and a Neanderthal mother! This shows that mixing between these groups was not uncommon.
Scientists also found that about 4% of the Denisovan genome came from an even older, unknown type of human. This shows the complex story of human evolution.
Mixing with Modern Humans
Denisovan DNA is found in many modern human populations, especially in people from Melanesia, Aboriginal Australians, and Filipino Negritos. In these groups, about 5% of their DNA comes from Denisovans. This suggests that early modern humans who moved into these regions had children with Denisovans.
Denisovan genes have been very helpful to modern humans. For example, a special Denisovan gene helps Tibetans live comfortably at high altitudes with less oxygen. Other Denisovan genes might affect how our bodies handle fat or how our immune systems work. In August 2025, a study showed that a Denisovan gene related to mucus production is common in many Indigenous American populations.
Scientists also reported in December 2023 that genes from Neanderthals and Denisovans might even affect our daily routines today!
See also
 In Spanish: Hombre de Denísova para niños
In Spanish: Hombre de Denísova para niños
- Red Deer Cave people
- Homo longi
- Homo naledi
- Nesher Ramla Homo
- Solo Man
- Timeline of human evolution