Interglacial facts for kids
An interglacial period is a time when the Earth's average temperature gets warmer for thousands of years. These warm periods happen in between much colder glacial periods, which are also known as ice ages. Right now, we are living in an interglacial period called the Holocene. It started about 11,700 years ago, after the last big ice age ended.
Contents
Earth's Past: The Pleistocene Ice Age
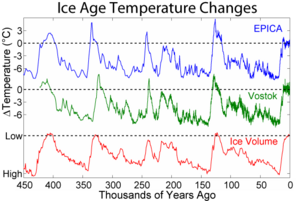
The Pleistocene was a long time, about 2.5 million years ago. During this period, huge sheets of ice covered large parts of places like North America and Europe. These cold, icy times, called glacials, happened every 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long cold periods were separated by shorter, warmer interglacials.
During an interglacial, like the one we are in now, the climate gets warmer. The cold, treeless land called tundra shrinks and moves closer to the poles. Forests then grow back in areas that were once covered by tundra or ice.
Scientists can tell when interglacials happened by looking at old plants and animal remains. For example, they find fossils of animals and plants that prefer warmer climates. They also study pollen and seeds. More recently, scientists use ice cores and ocean sediment cores. These give them very accurate information about past temperatures and how much ice was on Earth.
Why Do Interglacials Happen?
Interglacials and glacials are linked to regular changes in Earth's orbit around the Sun. There are three main ways Earth's orbit changes:
- Eccentricity: This is how stretched out or circular Earth's path around the Sun is.
- Obliquity: This is the tilt of Earth's axis. A bigger tilt means more extreme seasons.
- Precession: This is like a wobble in Earth's axis, similar to a spinning top.
These orbital changes affect how much sunlight reaches different parts of Earth. For example, in the Southern Hemisphere, summers are warmer when Earth is closest to the Sun and tilted towards it. These effects are stronger when Earth's orbit is more stretched out.
Studying the Past
Interglacials are very helpful for scientists who study Earth's history. They use them to map out different layers of rock and soil. They are also important for anthropologists, who study human history. Interglacials help them figure out the age of hominid fossils, which are the remains of early humans.
Sometimes, during a long cold glacial period, there are short times when the climate gets a bit milder. These are called interstadials. Most interstadials are shorter than interglacials. They might not have been super warm, but they were often wetter than the very dry, cold periods around them.
Scientists also study the oxygen levels in seabed sediments. This is like a natural thermometer that tells them about Earth's average temperature in the past.
The Warmest Part of an Interglacial
The warmest part of an interglacial is called the interglacial optimum or climatic optimum. This is when the climate is most "favorable." It usually happens in the middle of an interglacial period. During this time, sea levels often rise to their highest points. Even after the optimum, the climate is still much better than during a glacial period.
Past Interglacial Periods
Here are some of the most recent interglacial periods:
- Marine Isotope Stage 13: This was about 524,000 to 474,000 years ago.
- Hoxnian / Holstein Interglacial: This happened around 424,000 to 374,000 years ago.
- Purfleet Interglacial: This was about 337,000 to 300,000 years ago.
- La Bouchet Interglacial: This occurred roughly 242,000 to 230,000 years ago.
- Last Interglacial / Eemian: This period was about 130,000 to 115,000 years ago. During the Eemian, the climate was at its warmest around 131,000 to 114,000 years ago. At that time, the sea level was 5 to 9.4 meters higher than it is today. The water in the North Sea was also about 2°C warmer.
- Holocene: This is the interglacial period we are in right now. It started about 12,000 years ago and continues to the present day. The warmest part of the Holocene, called the Holocene climatic optimum, happened between roughly 9,000 and 2,500 years ago. After that, the temperature slowly dropped until about 2,000 years ago. There was another warm period called the Medieval Warm Period, followed by a colder time known as the Little Ice Age (from about 1250 to 1850).
See also
 In Spanish: Interglaciar para niños
In Spanish: Interglaciar para niños
- Greenhouse and icehouse Earth
- Milankovitch cycles
- Snowball Earth
- Interstadial periods
- Last glacial maximum
- Timeline of glaciation