J. Bruce Ismay facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
J. Bruce Ismay
|
|
|---|---|

Ismay in 1912
|
|
| Born |
Joseph Bruce Ismay
12 December 1862 Crosby, Lancashire, England
|
| Died | 17 October 1937 (aged 74) |
| Resting place | Putney Vale Cemetery |
| Occupation | Chairman and managing director of White Star Line |
| Title | Ship-owner |
| Spouse(s) |
Julia Florence Schieffelin
(m. 1888) |
| Parent(s) |
|
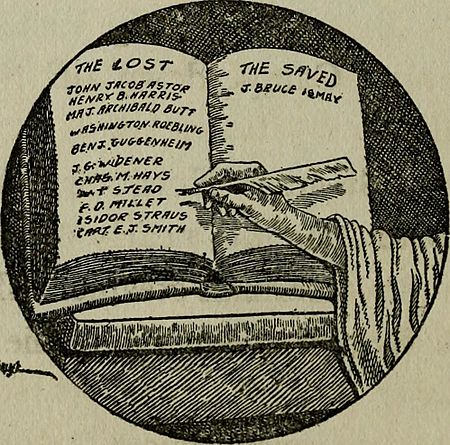
Joseph Bruce Ismay (born December 12, 1862 – died October 17, 1937) was an English businessman. He was the chairman and managing director of the White Star Line, a famous shipping company. In 1912, he became well-known around the world. This happened because he was the highest-ranking White Star official to survive the sinking of the company's new ship, the RMS Titanic. He faced a lot of criticism for surviving the disaster.
Contents
Early Life and Family
Bruce Ismay was born in Crosby, England. His father, Thomas Henry Ismay, was a senior partner in a company called Ismay, Imrie and Company. He also founded the White Star Line. Bruce's mother was Margaret Bruce.
Bruce went to Elstree School and Harrow. After school, he studied in France for a year. Then, he worked in his father's office for four years. He later traveled the world. He then moved to New York City to represent his father's company. He eventually became an agent for the company. Bruce also helped start the Liverpool Ramblers football club in 1882.
In 1888, Bruce Ismay married Julia Florence Schieffelin from New York. They had five children together:
- Margaret Bruce Ismay (born 1889)
- Henry Bruce Ismay (born and died 1891)
- Thomas Bruce Ismay (born 1894)
- Evelyn Constance Ismay (born 1897)
- George Bruce Ismay (born 1902)
In 1891, Ismay and his family moved back to the United Kingdom. He became a partner in his father's company. When his father died in 1899, Bruce Ismay took over the family business. He was a very good businessman, and the White Star Line grew a lot under his leadership.
Leading the White Star Line
After his father passed away in 1899, Bruce Ismay became the chairman of the White Star Line. He decided to build four huge ocean liners. These ships were meant to be even bigger and better than the RMS Oceanic that his father had built. These new ships were called the "Big Four": the RMS Celtic, RMS Cedric, RMS Baltic, and RMS Adriatic. They were designed to be very large and luxurious, rather than super fast.
In 1902, Ismay oversaw the sale of the White Star Line to J.P. Morgan & Co.. This company was forming a large shipping group called the International Mercantile Marine Company (IMM). IMM bought several major American and British shipping lines. White Star Line became one of IMM's companies. In 1904, Ismay became the president of IMM.
The RMS Titanic
In 1907, Ismay met with Lord Pirrie from the Harland & Wolff shipyard. They talked about building new ships to compete with the RMS Lusitania and the RMS Mauretania. These were two very fast ships owned by White Star's main competitor, the Cunard Line.
Ismay's idea was to build ships that were not as fast. Instead, they would be incredibly large and luxurious. They would have huge spaces for passengers traveling in steerage (the cheapest class). They would also offer luxury like no other ship had before. This was meant to attract wealthy people and the middle class. Three ships of this new design were planned: the RMS Olympic, the RMS Titanic, and the Britannic.
During the building of the first two ships, Ismay made a controversial decision. He approved reducing the number of lifeboats from 48 to 16. This was the minimum number allowed by the Board of Trade based on the ship's size.
Ismay often traveled on his ships' first voyages. This was true for the Titanic. During the voyage, Ismay spoke with the ship's chief engineer, Joseph Bell, or Captain Edward J. Smith. They discussed possibly testing the ship's speed if there was time.
On the night of April 14, 1912, the Titanic hit an iceberg. It was clear the ship would sink before any rescue ships could arrive. Ismay got into Collapsible C, a lifeboat that was launched less than 20 minutes before the ship went down. He later said that he turned away, unable to watch, as the ship sank. The Carpathia rescued Collapsible C about 3-4 hours later.
After being rescued, Ismay stayed in the ship's doctor's cabin. He did not leave the cabin for the rest of the journey. He also did not eat any solid food. Another survivor, 17-year-old Jack Thayer, tried to comfort Ismay, even though Thayer had just lost his own father in the sinking.
When he arrived in New York, Ismay stayed with Philip Franklin, a company vice president. He was called to testify before a Senate committee hearing the day after the sinking. A few weeks later, Ismay also testified at the British inquiry.
Public Reaction and Criticism
After the disaster, Ismay was heavily criticized by newspapers in both America and Britain. People were angry that he had left the ship while women and children were still on board. Some newspapers called him the "Coward of the Titanic" or "J. Brute Ismay." They even suggested changing the White Star flag to a yellow color, which was a sign of cowardice. Some cartoons showed him abandoning the ship.
However, some people argued that Ismay followed the "women and children first" rule. They said he helped many women and children himself. The official British inquiry into the disaster also defended Ismay's actions. The inquiry stated that "Mr. Ismay, after rendering assistance to many passengers, found "C" collapsible, the last boat on the starboard side, actually being lowered. No other people were there at the time. There was room for him and he jumped in. Had he not jumped in he would merely have added one more life—namely, his own—to the number of those lost."
Ismay boarded Collapsible C with another first-class passenger, William Carter. Both said they got into the lifeboat only after there were no more women and children nearby. Despite the official findings, many people in London society avoided Ismay and called him a coward. On June 30, 1913, Ismay resigned as president of International Mercantile Marine and chairman of the White Star Line. Harold Sanderson took his place.
During the United States Inquiry, Ismay announced that all ships of the International Mercantile Marine Company would have enough lifeboats for everyone on board. After the inquiry, Ismay and the surviving officers returned to England on the RMS Adriatic.
Later Life
Even though the official British inquiry cleared him, Ismay never fully recovered from the Titanic disaster. He was already a private person, and the tragedy made him very depressed. He lived a quiet life afterward. He spent part of the year in a large cottage in Connemara, Ireland. He bought this cottage less than a year after the sinking.
Paul Louden-Brown, who wrote a history of the White Star Line, says that Ismay continued to be active in business. Much of his work was for an insurance company founded by his father. This company paid out a lot of money to the families of the Titanic victims. Ismay and his directors handled this difficult task with courage.
Ismay remained interested in maritime affairs. He helped start a cadet ship called Mersey to train officers for Britain's Merchant Navy. He also donated money to help lost sailors and to recognize the efforts of merchant mariners in the First World War.
After the tragedy, Ismay's wife, Florence, made sure that the Titanic was never discussed in their family.
In his personal life, Ismay became very solitary. He spent his summers fishing for trout and salmon in Ireland. When he was in Liverpool, he would go to concerts or the cinema by himself. He would also walk in parks and talk to strangers. A family friend said that the Titanic was always on Ismay's mind. He constantly wondered how the disaster could have been avoided. At a family gathering in 1936, one of his grandsons asked if his grandfather had ever been shipwrecked. Ismay finally spoke about the tragedy, saying: "Yes, I was once in a ship which was believed to be unsinkable."
Death
Ismay's health got worse in the 1930s. He had diabetes, and in 1936, he had to have his right leg amputated. He then mostly used a wheelchair. On October 14, 1937, he collapsed in his bedroom after having a major stroke. He became unconscious, blind, and unable to speak. Three days later, on October 17, J. Bruce Ismay died at the age of 74.
Ismay's funeral was held on October 21, 1937. He is buried in Putney Vale Cemetery, London. He left a large personal estate. In 1939, his wife Florence gave their property in Ireland to their son George. After Ismay's death, Florence gave up her British citizenship to become an American citizen again in 1949.
Julia Florence Ismay died on December 31, 1963, at the age of 96.
Portrayals in Media
J. Bruce Ismay has been shown in many films, TV shows, and plays about the Titanic. Here are some of the actors who have played him:
- Ernst Fritz Fürbringer (1943) in Titanic
- Lowell Gilmore (1955) in You Are There: The Sinking of the Titanic (TV episode)
- Frank Lawton (1958) in A Night to Remember
- Ian Holm (1979) in S.O.S. Titanic (TV film)
- Jonathan Hyde (1997) in Titanic (Film)
- David Garrison (1997) in Titanic (Broadway musical)
- James Wilby (2012) in Titanic (TV series)
See also
 In Spanish: J. Bruce Ismay para niños
In Spanish: J. Bruce Ismay para niños
- Passengers of the RMS Titanic
 | Isaac Myers |
 | D. Hamilton Jackson |
 | A. Philip Randolph |