Josiah Henson facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Josiah Henson
|
|
|---|---|
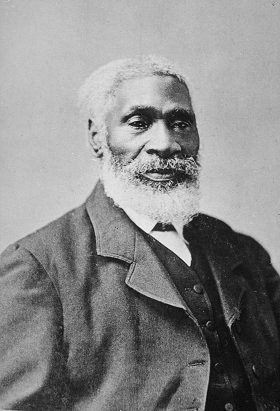
Josiah Henson in 1877
|
|
| Born | June 15, 1789 Charles County, Maryland, United States
|
| Died | May 5, 1883 (aged 93) Dresden, Ontario, Canada
|
| Nationality | American, Canadian |
| Other names | Uncle Tom |
| Occupation |
|
| Spouse(s) | Nancy Henson |
| Relatives | Matthew Henson |
| Signature | |
Josiah Henson (born June 15, 1789 – died May 5, 1883) was an amazing person who was an author, a minister, and an abolitionist. An abolitionist is someone who worked to end slavery. Josiah was born into slavery in Charles County, Maryland, in the United States.
In 1830, he bravely escaped to Upper Canada (which is now Ontario). There, he started a special community and school for other people who had escaped slavery. This settlement was called Dawn, and it was near Dresden, Ontario.
Josiah Henson wrote a book about his life called The Life of Josiah Henson, Formerly a Slave, Now an Inhabitant of Canada, as Narrated by Himself (1849). Many people believe his story helped inspire the main character in Harriet Beecher Stowe's famous 1852 novel, Uncle Tom's Cabin. Because of the book's success, Josiah wrote more versions of his own story, sharing his experiences with even more people.
Contents
Early Life and Escape to Freedom

Josiah Henson was born on a farm in Maryland. His family was enslaved, meaning they were forced to work without pay and were not free. When Josiah was a young boy, his father was severely punished for trying to protect his family. After this, his father was sold away to a different place.
Josiah also faced many difficulties and was injured while enslaved. He was separated from his mother and siblings when they were sold at an auction. Luckily, his mother was able to convince her new owner, Isaac Riley, to buy Josiah so they could be together.
Josiah worked hard and gained the trust of his owner, Isaac Riley. He even became a supervisor on the farm in Montgomery County, Maryland. In 1825, Mr. Riley faced money problems. He asked Josiah to take eighteen enslaved people to his brother's farm in Kentucky. Josiah led them on a long journey by foot.
Later, Josiah tried to buy his freedom from Mr. Riley. He had saved up money, but Mr. Riley cheated him by changing the price. Josiah returned to Kentucky. He then learned that Mr. Riley planned to sell him again, which would separate him from his wife and four children. This made Josiah determined to escape to Canada.
The Journey to Canada
Josiah convinced his wife to escape with him. She made a special bag to carry their two smallest children, while the older children walked with her. The Henson family traveled at night and hid in the woods during the day to avoid being caught.
They crossed into Indiana and then Ohio. Along the way, they met some Native Americans who helped them with food and a place to rest. After crossing a lake in Ohio, Josiah met a ship captain named Captain Burnham. The captain agreed to take the Henson family to Buffalo, New York. From there, they crossed the river into Canada.
On October 28, 1830, Josiah Henson and his family finally set foot in Canada. Josiah felt incredibly free and happy. He described throwing himself onto the ground and celebrating with his family. He was finally a free man!
Slavery Laws in Canada
Upper Canada (now Ontario) became a safe place for people escaping slavery from the United States. In 1793, a law was passed that stopped more enslaved people from being brought into the province. This law didn't end slavery right away, but it meant that any enslaved person who reached what would become Ontario was free.
Life in Canada and His Legacy
After gaining his freedom, Josiah Henson worked on farms in different parts of Ontario. He eventually moved to Colchester, Ontario in 1834 to help start a Black settlement. When he earned enough money, he sent his oldest son, Tom, to school. Tom then taught Josiah how to read.
Josiah became a leader in the growing community of people who had escaped slavery in Canada. With help from others, he bought 200 acres (about 0.8 square kilometers) of land in Dawn Township. Here, he created his dream of a self-sufficient community called the Dawn Settlement. At its busiest, the Dawn Settlement had about 500 residents. They even exported wood to the United States and Britain.
Josiah also became a Methodist preacher and spoke out against slavery. He traveled to the United States and Great Britain to share his story and raise money for his community. He even met Queen Victoria in Britain!
Josiah Henson also served as a military officer in the Canadian Militia. He led a Black militia unit during the Canadian Rebellion of 1837. In 1838, his unit successfully captured a rebel ship, which helped stop the rebellion.
Even after slavery ended in the United States, Josiah and his wife continued to live in Dawn for the rest of their lives. Josiah became a spiritual leader in the community and helped many other enslaved people find freedom in Canada.
His Published Works
Josiah Henson's books helped share his incredible life story with the world:
- The Life of Josiah Henson, Formerly a Slave, Now an Inhabitant of Canada, as Narrated by Himself. 1849
- Truth Stranger Than Fiction. Father Henson's Story of His Own Life. 1858
- Uncle Tom's Story of His Life: An Autobiography of the Rev. Josiah Henson. 1876
Honors and Recognition
Josiah Henson was the first Black man to be featured on a Canadian stamp, which is a great honor! In 1999, he was recognized as a National Historic Person by the Historic Sites and Monuments Board of Canada. There is a special plaque for him in the Henson family cemetery, near the Uncle Tom's Cabin Historic Site.
A documentary film about his life, called Redeeming Uncle Tom: The Josiah Henson Story, was released in 2018.
Historic Sites to Visit
Josiah Henson Museum & Park – Maryland
The original cabin where Josiah Henson and other enslaved people lived no longer exists. However, the Riley family house, where his owner lived, is still standing in Rockville, Maryland. This house and the land around it were bought by the Montgomery Planning Board in 2006 to preserve its history.
The Josiah Henson Museum & Park in North Bethesda, Maryland, reopened to the public in 2021 after renovations. It now has new exhibits and a visitor center. Archaeologists are still working there to find out more about where Josiah Henson might have lived on the site.
The Josiah Henson Museum of African-Canadian History – Ontario

Located near Dresden, Ontario, in Canada, this site was formerly known as Uncle Tom's Cabin Historic Site. It is now called the Josiah Henson Museum of African-Canadian History. This museum includes the actual cabin where Josiah Henson lived from 1841 until his death in 1883.
The museum complex covers about 5 acres (2 hectares). It features Henson's cabin, a center that explains his life and the Dawn settlement, an exhibit about the Underground Railroad, old buildings, a 19th-century historic house, a cemetery, and a gift shop. It's a great place to learn about Josiah Henson's incredible journey and legacy.
See also
 In Spanish: Josiah Henson para niños
In Spanish: Josiah Henson para niños
- List of enslaved people
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |


