Kalinga (region) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Kalinga
|
|
|---|---|
|
Region
|
|
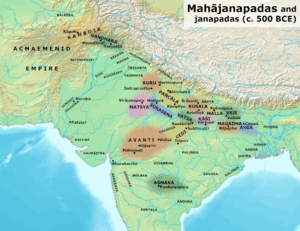
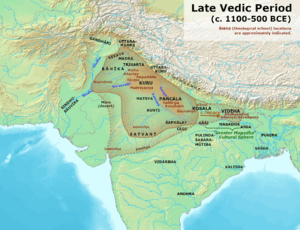
Kalinga Janapada and neighbours among the Mahajanapadas During Vedic period.
|
|
| Country | India |
| State |
|
| Founded by | King Kalinga of Mahabharata |
| Languages | |
| • Spoken | Odia, Telugu (only in parts of Northern AP) |
| Time zone | UTC+5:30 (IST) |
| Ancient and Medieval Capitals | Tosali, Sisupalgarh, Dantapuram, Prishtapura, Kalinganagara, Cuttack, Jajpur |
Kalinga is an ancient region in India with a rich history. It's located on the eastern coast, mainly between the Ganges and Godavari rivers. Today, this area covers most of Odisha and parts of northern Andhra Pradesh. Over time, Kalinga's borders changed as different rulers took control.
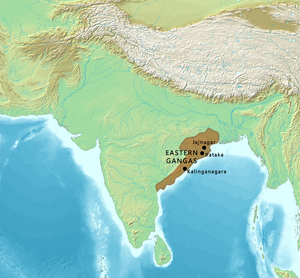
Long ago, the people of Kalinga were mentioned in the famous Indian story, the Mahabharata. Around 261 BCE, the powerful Mauryan Empire took over Kalinga after a huge battle called the Kalinga War. After the Mauryans, many different kingdoms ruled Kalinga. Their leaders often used the title Kalingādhipati, which means "Lord of Kalinga." Important dynasties included the Mahameghavahanas and the Eastern Gangas. Later, the Gajapatis also ruled this historic land.
Contents
Where Was Kalinga Located?
Kalinga was a coastal region in eastern India. It was mainly located between the Ganges and Godavari rivers. However, its exact size and borders changed a lot throughout history. At its largest, Kalinga stretched north to the Ganges and west to the Amarkantak hills. The Bay of Bengal formed its eastern border. Sometimes, it also included the Utkala region, which is now part of northern Odisha.
Ancient writings often mention the Mahendragiri mountain in Odisha as being part of Kalinga. The term "Trikalinga" also appears in old records. Some believe it meant the largest area Kalinga ever covered. Others think Trikalinga was a separate hilly region to Kalinga's west.
Kalinga's Long History
Early Beginnings
Kalinga gets its name from an ancient tribe. According to the Mahabharata, the Kalinga people were related to other tribes in the area. Their land stretched from the Baitarani River in Odisha to the Varahanandi in the Visakhapatnam district.
One of Kalinga's earliest capitals was a city called Dantapura. Ancient texts show that Kalinga was an important kingdom even in very old times. Its kings were known to other rulers across India.
Ancient Kalinga Kingdom (c. 1100 – 261 BCE)
The Kalinga kingdom was founded by a prince named Kalinga, according to ancient texts like the Mahabharata. This kingdom was located in the coastal area of what is now Odisha. The Mahabharata also mentions King Srutayudha of Kalinga.
Over centuries, different royal families ruled Kalinga. These included the first and second Kalinga dynasties. Later, the Suryavamsha dynasty ruled Kalinga. King Ananta Padmanabha was a ruler of Kalinga around the time of the famous Kalinga War.
Kalinga Before the Classical Era
Nanda Empire's Influence
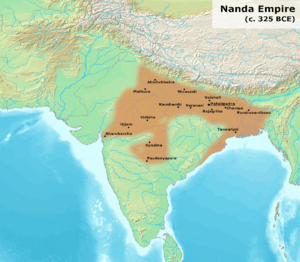
Around 345 BCE, the powerful Nanda dynasty briefly took control of Kalinga. This is known from the Hathigumpha inscription, an important ancient record. The Nanda Empire was very large, stretching across much of northern India.
However, Kalinga became independent again around 322 BCE. This happened when Chandragupta Maurya challenged the Nanda rulers.
The Kalinga War
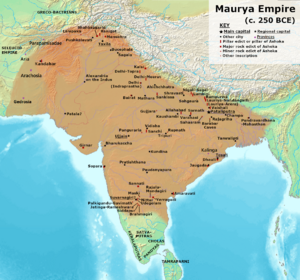
The most famous event in Kalinga's ancient history is the Kalinga War. In 261 BCE, Emperor Ashoka of the Mauryan Empire invaded Kalinga. This was a very bloody war. After the battle, Kalinga became part of the Mauryan Empire. Its capital, Tosali, became a Mauryan center.
Kalinga later broke away from the Mauryan Empire around 224 BCE.
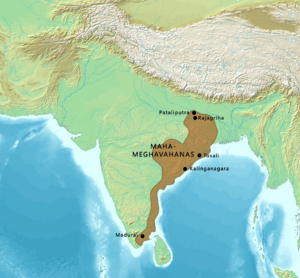
The Mahameghavahana Dynasty
After the Mauryans, the Mahameghavahana dynasty took over Kalinga. Their greatest ruler was King Kharavela, who lived around the 2nd or 1st century BCE. He called himself the "supreme Lord of Kalinga."
We learn a lot about Kharavela from the Hathigumpha inscription. This inscription tells us about his many achievements. He built public projects, helped his people, supported arts, and won many battles. He also respected different religions, including Jainism.
Kalinga After Ancient Times
Gupta Empire's Influence
In the 4th century CE, Kalinga came under the influence of the powerful Gupta Empire. However, after the Guptas withdrew, Kalinga was ruled by several smaller kingdoms. Their rulers continued to use the title Kalingadhipati, meaning "Lord of Kalinga."
These dynasties included the Matharas, Pitrbhaktas, and Nalas. Later, the Shailodbhavas and early Eastern Gangas also ruled parts of Kalinga.
Shailodbhava and Somavamshi Dynasties
The Shailodbhavas ruled parts of eastern India in the 7th century. Their king, Madhavaraja II, called himself "the lord of the entire Kalinga." Later, the Bhauma-Kara dynasty ruled the region, calling their kingdom "Tosala."
From the 9th to the 12th centuries, the Somavamshis ruled parts of Odisha. They conquered Kalinga and Utkala, calling themselves the "lord of Kalinga, Kosala, and Utkala." They also brought new styles of art and buildings to Odisha.
Kalinga in the Middle Ages
Eastern Ganga Dynasty's Rule
From the 11th to the 15th century, the Eastern Gangas became the most powerful rulers in Kalinga. They also used the title Kalingadhipati. They sometimes called themselves "Lord of three Kalingas" or "Lord of all Kalingas."
Their capital moved from Mukhalingam to Cuttack in the 12th century. King Anantavarman Chodaganga built the famous Jagannath Temple in Puri. Another important king, Narasimhadeva I, built the amazing Sun Temple at Konark. He was also the first to use the title Gajapati, meaning "Lord of war elephants."
The Gajapati Empire
The Eastern Ganga dynasty ended in 1434. The Suryavamsi Gajapatis then took over. They ruled over both northern and southern Odisha. Prataparudra Deva was the last great king of this empire.
After the Gajapatis, the Bhoi dynasty briefly ruled parts of the Odisha coast. Later, Mukunda Deva declared himself an independent ruler. However, the region became fragmented into many smaller states.
Kalinga's Impact on Other Regions
Kalinga had a big influence on many other parts of the world, especially in Southeast Asia.
Connections with Southeast Asia
A merchant named Kaundinya I from Kalinga helped found the Funan kingdom in what is now Cambodia. He married a local princess, Queen Soma.
Some historians believe that the Shailendra dynasty of Java (in modern Indonesia) also came from Kalinga. This dynasty was very powerful and ruled over many islands and coastal areas. They were known for their strong navies.
There is also evidence of Kalinga's influence in Myanmar (formerly Burma). Ancient records mention a region called Kalinga-rattha. Traders and Buddhist missionaries from Kalinga settled there very early on. Old ship remains found in Myanmar suggest trade with Kalinga.
Influence in Maldives and Philippines
According to the history of the Maldives, the first kingdom there was founded by a prince from Kalinga. This shows how far Kalinga's influence reached.
In the Philippines, some historians suggest that a king of Butuan might have had Indian origins, possibly from Kalinga.
The Term "Keling"
The word "Keling" or "Kling" is still used in parts of Southeast Asia. It refers to people from the Indian subcontinent. While it has sometimes been used in a negative way, it originally came from the name Kalinga. This shows the long history of Indian traders from Kalinga in the region.
A ruler from Sri Lanka, Nissanka Malla, who ruled from 1187 to 1196, said he was from a royal family of Kalinga.
See also
 In Spanish: Kalinga para niños
In Spanish: Kalinga para niños
- History of Odisha
- List of rulers of Odisha
- Kalinga script, derived from Brahmi script
- Keling
- Kalingga kingdom
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |