Kyshtym disaster facts for kids
|
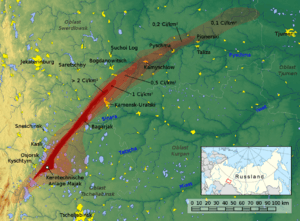
Map (in German) of the East Urals Radioactive Trace (EURT): area contaminated by the Kyshtym disaster.
|
|
| Date | 29 September 1957 |
|---|---|
| Location | Mayak, Ozyorsk, Chelyabinsk Oblast, |
| Coordinates | 55°42′45″N 60°50′53″E / 55.71250°N 60.84806°E |
| Type | Nuclear Accident |
| Outcome | INES Level 6 (serious accident) |
| Casualties | |
| 66 diagnosed cases of chronic radiation syndrome | |
| Estimated 200 additional cases of cancer | |
| 10,000 evacuated | |
The Kyshtym disaster was a serious accident involving radioactive contamination. It happened on September 29, 1957, at a place called Mayak in the Soviet Union (now Russia). Mayak was a secret site where plutonium was made for nuclear weapons. It also processed used nuclear fuel.
The accident took place in Ozyorsk, Chelyabinsk Oblast, a closed city built around the Mayak plant. This means it was a secret city not shown on maps. The disaster was rated as a Level 6 on the International Nuclear Event Scale (INES). This makes it the third-worst nuclear accident ever recorded. Only the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster and the Chernobyl disaster were worse (both Level 7).
At least 22 villages were affected by radiation from the disaster. About 10,000 people living there had to leave their homes. Some people were moved within a week. However, it took almost two years for others to be evacuated.
The disaster spread tiny radioactive particles over more than 52,000 square kilometers (20,000 square miles). About 270,000 people lived in this large area. Since Ozyorsk/Mayak was a secret city, the disaster was named after Kyshtym. This was the closest known town.
Why the Accident Happened
After World War II, the Soviet Union wanted to catch up to the U.S. in making nuclear weapons. So, they quickly started a program to produce uranium and plutonium.
The Mayak plant was built very fast between 1945 and 1948. At that time, scientists did not know as much about nuclear safety. This made it hard to make safe choices. People also did not worry much about the environment during the early building stages.
At first, Mayak dumped highly radioactive waste into a nearby river. This river flowed into the Ob River, which then went to the Arctic Ocean. All six nuclear reactors at Mayak were on Lake Kyzyltash. They used a cooling system that sent contaminated water right back into the lake.
Lake Kyzyltash quickly became very polluted. So, Lake Karachay was then used to store waste in the open air. This kept the pollution a bit further from the reactors. But soon, Lake Karachay became one of the most polluted places on Earth.
Around 1953, a special storage place for liquid nuclear waste was added. It had steel tanks set in concrete, about 8.2 meters (27 feet) underground. This waste was very radioactive and heated itself up. This is called decay heat. To stop it from getting too hot, a cooling system was built around each group of 20 tanks.
However, the equipment used to check the coolers and the tanks was not good enough.
The Explosion
In 1957, the cooling system in one of the tanks stopped working. This tank held about 70 to 80 tons of liquid radioactive waste. The problem was not fixed. The temperature inside the tank started to rise. This caused the liquid to evaporate and the dried waste to explode. The dried waste was mostly made of chemicals like ammonium nitrate.
The explosion happened on September 29, 1957. It was as powerful as about 70 to 100 tons of TNT. The blast threw the 160-ton concrete lid of the tank into the air. No one died right away from the explosion. But it released a huge amount of radioactivity into the air.
Most of this contamination fell close to the accident site. It added to the pollution of the Techa River. This river was already polluted because waste had been dumped there on purpose before. A cloud of radiation also spread out over hundreds of kilometers.
Over the next 10 to 11 hours, the radioactive cloud moved northeast. It traveled about 300 to 350 kilometers (186 to 217 miles) from the accident. The fallout from this cloud caused long-term contamination over a huge area. This area was between 800 and 20,000 square kilometers (300 to 7,700 square miles). This contaminated region is known as the East-Ural Radioactive Trace (EURT).
Images for kids
Related pages
See also
 In Spanish: Accidente de Kyshtym para niños
In Spanish: Accidente de Kyshtym para niños
 | Laphonza Butler |
 | Daisy Bates |
 | Elizabeth Piper Ensley |