Long-legged bat facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Long-legged bat |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Phyllostomidae |
| Genus: | Macrophyllum Gray, 1838 |
| Species: |
M. macrophyllum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Macrophyllum macrophyllum (Schinz, 1821)
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The long-legged bat (Macrophyllum macrophyllum) is a small bat known for its unusually long legs and big feet. It belongs to the Phyllostomidae family, a group of bats found in Central and South America. Both male and female long-legged bats are quite small. Their wings can spread up to 80 millimeters wide. They usually weigh between 6 and 9 grams, which is about the same as a few paperclips.
These bats have a short snout and a noticeable noseleaf on their face. But their most special feature is their long back legs. These legs are longer than those of most other bats in their family. At the end of these long legs, they have very large feet with strong claws.
Contents
Where Long-Legged Bats Live
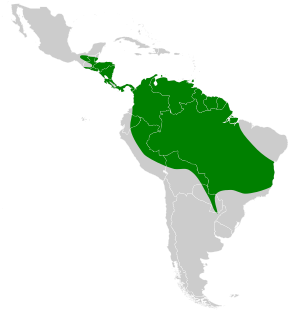
The first long-legged bat was discovered in Brazil in 1855. Since then, these bats have been seen in many places. They live across parts of South America and Central America.
In northern South America, you can find them in Peru, Ecuador, Bolivia, and Venezuela. In Central America, they have been spotted in Costa Rica, Honduras, Guatemala, and Nicaragua. These bats also live in southern Mexico. Even though they are small, long-legged bats can travel far. They have a large home area that can be up to 150 hectares. Female bats tend to have slightly larger home ranges than males.
Long-Legged Bat Habitats
Long-legged bats usually live in areas just north of the equator. They prefer rainforests and tropical dry forests. Most of the time, these bats are found near water. This includes lakes, streams, or sea caves along the Pacific coast. Scientists think they live near water because there are lots of insects there. Besides natural water sources, these bats also roost in human-made places. They have been found in water pipes, modern buildings, and even old Panama ruins.
What Long-Legged Bats Eat
Long-legged bats are insectivorous. This means they mostly eat insects. Scientists have studied the contents of their stomachs. They found that these bats mainly eat flying insects. This shows that most of their food comes from insects caught in the air. While flying insects are their main food, long-legged bats have also been known to drink animal blood. However, they do not eat fruit.
How Long-Legged Bats Find Food
The most common way long-legged bats find food is called "gleaning." A bat will hover over water and use its big feet and long legs to pick up insects from the surface. This way of hunting is different from most other bats in their family. However, these bats can hunt in other ways too. Studies in labs show that long-legged bats can also catch insects in mid-air. This is called "aerial hawking." They are good at both hunting methods. Being able to hunt in different ways helps them catch many types of insects. They can catch insects sitting on the water or flying above it.
How Long-Legged Bats Use Echolocation
Like many bats, the long-legged bat uses echolocation. This helps them move around and find their prey. They send out sound waves. These waves bounce off objects and return to the bat. As the bat gets closer to something, its echolocation signals get faster. This helps them create a clearer picture of their surroundings.
Unlike many bats in the Phyllostomidae family, long-legged bats make loud echolocation calls. Many other bats in this family use quiet, "whispering" echoes. Long-legged bats change how loud their calls are depending on their environment. In noisy areas, they make quieter calls. In open areas, they make louder calls. Making louder calls in open spaces helps them find food from farther away. For example, their calls can be 4 times louder in open areas compared to closed spaces.
See also
 In Spanish: Murciélago de patas largas para niños
In Spanish: Murciélago de patas largas para niños
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |


