Asian badger facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Asian badger |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Female | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Mustelidae |
| Genus: | Meles |
| Species: |
M. leucurus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Meles leucurus Hodgson, 1847
|
|
 |
|
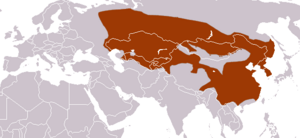
| Asian badger range | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Asian badger (Meles leucurus), sometimes called the sand badger, is a type of badger that lives in parts of Asia. You can find them in countries like Mongolia, China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, the Korean Peninsula, and Russia.
Characteristics
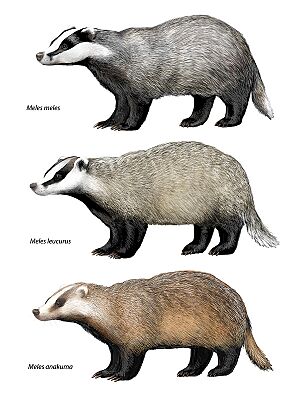
Asian badgers usually have lighter fur than their cousins, the European badgers. Some can be darker, with shades of brown and yellow. Their sides are often lighter than their backs. The stripes on their faces are usually brown, not black, and they get narrower behind the eyes, going above the ears. The white parts of their heads are often a bit dirty-looking compared to European badgers. The light stripe on top of their head, between the two facial stripes, is quite short and thin.
Asian badgers are generally smaller than European badgers. They also have longer upper teeth used for grinding food. Even though their size can change depending on where they live, they seem to be the smallest of the three Meles badger types. The biggest Asian badgers are found in Siberia.
These badgers typically weigh between 3.5 to 9 kilograms (about 8 to 20 pounds). They are about 50 to 70 centimeters (about 20 to 28 inches) long. For example, three adult male badgers from Sobaeksan National Park weighed about 6 kilograms (13 pounds) on average.
Taxonomy
Scientists recognize five different types, or subspecies, of the Asian badger. These types are found in different areas and have slight differences in their looks or size. For example, the Amur badger, found near the Ussuri River and in the Korean Peninsula, is known for being the darkest and smallest type. The Siberian badger, found across Siberia, is a medium-sized type with light grey fur and a dense undercoat.
Distribution and habitat
The Asian badger lives across a large area. This includes the southern parts of Russia, east of the Volga River and the Ural Mountains. They also live in Kazakhstan, Mongolia, China, and Korea. You can find them in high places, even up to 4,000 meters (about 13,000 feet) in mountain ranges like the Ural Mountains, the Tian Shan mountains, and the Tibetan Plateau.
Asian badgers prefer open forests with trees that lose their leaves (like deciduous woodlands) and nearby grassy areas (pastureland). However, they can also live in forests with cone-bearing trees (like coniferous woodlands), mixed forests, areas with shrubs, and open grasslands (steppes). Sometimes, they even come into areas near towns and cities.
Behaviour and ecology
Asian badgers usually live in burrows underground. These burrows are called setts. However, they can also climb trees sometimes! Camera footage in South Korea has shown them climbing Korean oak trees.
Threats
Asian badgers are hunted legally in countries like China, Russia, and Mongolia. Sadly, they are also hunted illegally in South Korea and even in protected areas in China. In Russia, the hunting season for badgers usually runs from August to November.
In traditional Mongolian medicine, a balm made from badger fat oil is used. People believe it helps with various health problems, such as lung issues, stomach problems, and colds.
In South Korea, Asian badgers are also used in traditional medicine. Sometimes, they are even used as a replacement for the Asian black bear in certain remedies. People also eat badger meat and use badger-derived products in some cosmetics. Because of this, badger farms have been around in South Korea since the 1990s. In 2009, there were about 5,000 Asian badgers on these farms in South Korea.
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |



