Miramar Peninsula facts for kids
|
Native name:
Te Motu Kairangi
|
|
|---|---|

Wellington Airport in centre, with Miramar Peninsula beyond.
|
|
| Etymology | Spanish for "sea view" |
| Geography | |
| Coordinates | 41°19′12″S 174°49′23″E / 41.320°S 174.823°E |
| Area | 21.2 km2 (8.2 sq mi) |
| Length | 7 km (4.3 mi) |
| Width | 2.5 km (1.55 mi) |
| Coastline | 19.8 km (12.3 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 163 m (535 ft) |
| Highest point | Mount Crawford |
| Administration | |
| Region | Wellington Region |
| City | Wellington |
| Suburbs | Miramar, Maupuia, Strathmore, Seatoun |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 19,230 (2022) |
| Pop. density | 907 /km2 (2,349 /sq mi) |
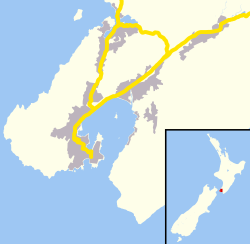
Te Motu Kairangi / Miramar Peninsula is a large piece of land that sticks out into the sea. It's located on the southeastern side of Wellington, New Zealand. This peninsula sits right at the entrance to Wellington Harbour.
According to an old Māori legend, the peninsula was formed when a giant water monster, a taniwha named Whaitaitai, got stuck trying to leave the harbour. Today, the peninsula is home to several suburbs like Miramar, Seatoun, Strathmore Park, and Karaka Bays.
Contents
Exploring Miramar Peninsula's Location

If you look at the peninsula from above, it looks a bit like a shark! To the north, it reaches into Wellington Harbour, which Māori call Te Whanganui-a-Tara (the Great Harbour of Tara). To the south, you'll find Cook Strait and the vast Pacific Ocean.
West of the peninsula are Wellington suburbs like Kilbirnie and Lyall Bay. To the east, a narrow channel connects Wellington Harbour to the open sea. From high points on the peninsula, you can see far-off places like the Hutt Valley and the Tararua Ranges. On clear days, you might even spot the snowy Kaikōura Ranges across Cook Strait.
What Miramar Peninsula Looks Like
This peninsula covers about 21 square kilometres. Its coastline is mostly rocky, with many hidden coves, tall cliffs, and small caves. But you'll also find beautiful sandy beaches at places like Breaker Bay, Worser Bay, and Scorching Bay.
A high ridge runs down the middle of the peninsula, like its spine. The highest points are Mount Crawford in the north and Beacon Hill in the south. There are also large flat areas, known as the Miramar flats and a smaller one at Seatoun. These flat areas are mostly covered with houses.
The peninsula is quite busy with towns and cities. You'll find homes, shops, schools, and even Wellington International Airport. There are also areas with native bush, pine forests, and gardens. A narrow road circles the entire peninsula, offering amazing views of the bays and headlands.
Near the entrance to Wellington Harbour, you'll see the rocks of Barrett Reef. In 1968, a ferry called the TEV Wahine had a serious accident near these rocks. This was a very sad event for New Zealand.
Weather on the Peninsula
Miramar Peninsula gets a lot of wind! It's open to Wellington's common northwest wind and the strong southerly wind. During big southerly storms, huge waves crash against the southern shore. However, the peninsula's hills and bays offer some shelter from the wind in many spots.
Snowfall is very rare at sea level in Wellington. But on August 15, 2011, snow actually fell across the peninsula. It settled lightly on trees, streets, and fields, which was a very unusual sight!
Cool Places to See
- Seatoun Tunnel: This tunnel was built between 1906 and 1907. It made it much easier to get to the suburb of Seatoun, which used to be only reachable by boat or a rough path.
Getting Around Miramar Peninsula
Cobham Drive is the main road that connects Miramar to the rest of Wellington city. Buses run often between Miramar and the city centre. You can also catch a harbour ferry to places like Queens Wharf and Matiu / Somes Island. There's even a cycle path that goes all the way from Miramar to the central city.
Sports and Community Groups
The peninsula is home to several sports clubs. These include Miramar Rangers, a semi-professional football club started in 1907, and Seatoun AFC, an amateur football club from 1909. There's also the Oriental Rongotai Football Club, a rugby club formed in 1888. Young and older cricketers can join the Eastern Suburbs Cricket Club in nearby Kilbirnie.
Miramar's Film Industry Connection
Did you know that famous film director Peter Jackson has his film studios right here in Miramar? This is where many of his movies are made, including The Lord of the Rings trilogy, King Kong, and The Hobbit. Weta Workshop, which creates amazing special effects and props for these films, is also located in Miramar.
A Look Back at Miramar Peninsula's History
The Māori name for this area, when it was still an island, was Te Motu Kairangi. This means "esteemed" or "precious" island. It was separated from the main land by a sea channel where Kilbirnie is today. Later, the island became known as Hataitai or Whataitai.
Early Māori Settlements and Life
The island of Te Motu Kairangi was first settled around 950 AD by the explorer Kupe. Kupe first landed near Seatoun. A large rock near the shore is still named Te Ure-o-Kupe or Te Aroaro-o-Kupe, meaning "Kupe's presence."
Over many centuries, different Māori tribes (iwi) lived here. These included Ngai Tara, Rangitane, Ngati Kahungungu, and Te Ati Awa.
Ngai Tara were the first to settle on the island. They built the first fortified village, called a pā, named "Whetu Kairangi" (bountiful stars). This pā was on a hill overlooking Worser Bay. Wellington Harbour itself, Te Whanganui-a-Tara, is named after Tara.
Around 1460 AD, a big earthquake called "Haowhenua" (earth swallower) lifted the land. This earthquake removed the shallow channel, connecting the island to the mainland. It created a flat plain and a freshwater lake in the middle of the peninsula. This lake was first called "Te Rotokura" (red lagoon) and later "Para." When European settlers arrived, they named it "Burnham Water."
Many pā and kāinga (homes) existed on the peninsula over hundreds of years. These included:
- Rangitatau Pa: This was the largest pā on the peninsula, located above Seatoun. It was a very strong fortress used by people from nearby villages for safety during attacks.
European Arrival and Changes
Captain Cook sailed near Miramar on his first visit to New Zealand. He mapped the coastline but didn't enter Wellington Harbour. On his second trip, he tried to enter the harbour but couldn't because of the winds and tides.
Musket Wars and the Fall of Rangitatau
In late 1819 or early 1820, the strong Rangitatau pā was attacked and destroyed. About 50 people died in this attack. Even years later, in 1899, people could still see the burned wooden fences of the pā.
By 1840, when the Treaty of Waitangi was signed, the land of Miramar was held by the Te Āti Awa tribe.
Farming on the Peninsula
In 1839, James Coutts Crawford bought a large area of land, including the Miramar peninsula. At that time, it was known as "Watt's Peninsula." Crawford started a cattle farm and named his house "Miramar," which means "sea view" in Spanish.
The large lake, Rotokura/Burnham Waters, was drained by James Coutts Crawford in 1847. He built a tunnel to do this, which was one of New Zealand's first tunnels! This tunnel is still there today. When the farmland was sold for housing in 1901, the area was named "Miramar Estate," and that's how the suburb got its name.
New Zealand's first permanent racecourse was created in Miramar in 1847.
In the 1880s, people worried about a possible invasion by Russia. So, New Zealand built fortifications to protect itself. Miramar Peninsula was a perfect spot for big guns to stop enemy ships from entering Wellington Harbour. Fortifications were built at Fort Ballance in 1885 and Fort Dorset from 1908.
Miramar Becomes a Borough
In the early 1900s, Miramar was part of a larger area called "Hutt County." Locals were unhappy because they paid high taxes but didn't see much money spent on their area. After a lot of discussion, Miramar became its own town, called a "Borough," on November 10, 1904. Mr. C.J. Crawford was elected its first Mayor. Miramar Borough joined Wellington City on January 31, 1921.
Key Events in the 1900s
- 1907: The Miramar Gas Works opened.
- 1907: Shelly Bay Naval base opened. It grew bigger during World War Two and was used by the Air Force for seaplanes.
- 1907: Wonderland amusement park opened in Miramar. It had fun attractions like a Japanese Tea-House and a helter-skelter. It closed in 1912.
- 1929: Rongotai Aerodrome opened, which was an early airport.
- 1937: New Zealand's first state house (a house built by the government) was built at 7 Fife Lane Miramar. The Prime Minister, Michael Joseph Savage, even helped move furniture in!
- 1940s: During World War Two, the peninsula was still important for defence. A lookout post was built at Palmer Head in 1938. However, with new aircraft carriers, these coastal forts became less important.
- 1950s: The hill west of Miramar was flattened to create land for a new airport runway. Houses on Rongotai Terrace were removed.
- 1959: Wellington Airport opened in its current location, replacing the older Rongotai Aerodrome.
Miramar Peninsula Today
In November 2023, Miramar Peninsula was officially declared pest-free! This amazing achievement was thanks to the hard work of many people and the use of bait stations and cameras. As a result, birdlife on the peninsula has increased by 71% since the project began.
Images for kids
 | Anna J. Cooper |
 | Mary McLeod Bethune |
 | Lillie Mae Bradford |