Nernst equation facts for kids
The Nernst Equation is a scientific rule used to figure out the reduction potential, or voltage, of an electrochemical cell. Think of an electrochemical cell as a tiny battery! This equation is super important in understanding how our bodies work (physiology) and how our brains work (neurobiology). It was named after Walther Nernst, a German chemist who created it.
This equation helps scientists choose the right chemicals to build powerful electric cells.
What the Nernst Equation Looks Like
The Nernst Equation helps us calculate the voltage of a battery. Here's what it looks like:
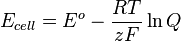
Let's break down what each part means:
- Ecell is the actual voltage or "power" of your electrochemical cell (battery).
- Eo is the standard voltage of the cell. This is the voltage under perfect, normal conditions. These conditions usually mean a temperature of 298 Kelvin and a pressure of 1 bar.
- R is the Gas constant. It's a fixed number used in thermodynamics, which is the study of heat and energy. Its value is 8.314 J.K-1.mol-1.
- T is the Temperature of the electrochemical cell. It's measured in Kelvin.
- z is the number of moles of electrons that move during the chemical reaction. Electrons are tiny particles that carry electricity.
- F is the Faraday constant. This number tells us the total electric charge carried by one mole of electrons. Its value is about 96,485 s Ampere/mole.
- Q is the Reaction quotient. This number shows how much of the chemicals are reacting at any given moment.
When the Cell is Balanced
When the voltage of a cell (Ecell) becomes 0 V, it means the cell has reached a balanced state. We call this state "equilibrium." At this point, the reaction quotient (Q) becomes equal to the equilibrium constant (Keq). This means the chemical reaction inside the cell has stopped producing a net flow of electricity.
Images for kids
-
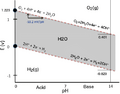
Pourbaix diagram for water. It shows where water, oxygen, and hydrogen are stable at normal temperature and pressure. The vertical line shows the electrode potential, and the horizontal line shows the pH of the liquid.
See also
 In Spanish: Ecuación de Nernst para niños
In Spanish: Ecuación de Nernst para niños