Nguni languages facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Nguni |
|
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution: |
South Africa, Swaziland, Zimbabwe |
| Linguistic classification: | Niger–Congo
|
| Subdivisions: |
Zunda
Tekela
|
The Nguni languages are a group of Bantu languages. People in Southern Africa speak them. You can find these languages mostly in South Africa, Eswatini (formerly Swaziland), and Zimbabwe. Some well-known Nguni languages include Xhosa, Zulu, Swati, and Ndebele.
The name "Nguni" comes from a special cow breed called Nguni cattle. Sometimes, people use "Nguni" to mean all the people who speak these languages. But this is not quite right. Many different tribes speak these languages, not just one group.
Contents
How Nguni Languages Are Organized
 |
 |
|||||||
|
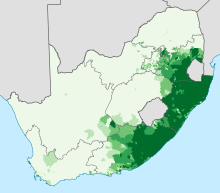
Proportion (percent) of the population that speaks a Nguni language at home.
|
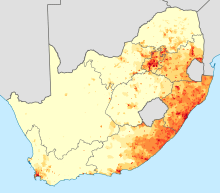
Density of people who speak Nguni languages at home.
|
The Nguni languages are part of the Southern Bantu languages. They are spoken in a fairly small area. These languages are very similar to each other. They often sound alike, too. This means that if you speak one Nguni language, you can usually understand someone speaking another. This is called being mutually intelligible.
Linguists are people who study languages. They divide the Nguni languages into two main groups. These groups are called "Zunda Nguni" and "Tekela Nguni".
What are Zunda Languages?
The Zunda group includes some of the most widely spoken Nguni languages. Here are a few examples:
- Zulu: About 10 million people speak Zulu.
- Xhosa: Around 8 million people speak Xhosa.
- Northern Ndebele: Also known as 'Zimbabwean Ndebele', about 1.6 million people speak it.
What are Tekela Languages?
The Tekela group includes other important Nguni languages. Some of these are:
- Swati: About 3 million people speak Swati.
- Phuthi: Around 20,000 people speak Phuthi.
- Other languages like Bhaca, Hlubi, Cele, and Lala.
See also
 In Spanish: Lenguas nguni para niños
In Spanish: Lenguas nguni para niños

