No. 103 Squadron RAF facts for kids
Quick facts for kids No. 103 Squadron RAF |
|
|---|---|

No. 103 Squadron badge
|
|
| Active | 1 Sep 1917 - 1 Oct 1919 10 Aug 1936 - 26 Nov 1945 30 Nov 1954 - 1 Aug 1956 1 Aug 1959 - 31 Jul 1963 1 Aug 1963 - 31 Jul 1975 |
| Country | |
| Branch | |
| Nickname(s) | "Swindon's 'own' Squadron" (unofficial) |
| Motto(s) | Latin: Noli me tangere (Translation: "Touch me not" or more modern: "Don't touch me") |
| Battle honours | Western Front, 1918* Hindenburg Line* France & Low Countries, 1939-40* Invasion Ports, 1940* Fortress Europe, 1940-44* Biscay Ports, 1941-43 Berlin, 1941-44* German Ports, 1941-45 Baltic, 1941-45 Ruhr, 1941-45* France & Germany, 1944-45* The honours marked with an asterisk(*) are those emblazoned on the squadron standard. |
| Insignia | |
| Squadron Badge heraldry | A swan, wings elevated and addorsed A swan was chosen because this bird is very strong on the wing and also well able to defend itself |
| Squadron Codes | GV (Apr 1939 - Sep 1939) PM (Sep 1939 - Nov 1945) |
No. 103 Squadron was a special unit of the Royal Air Force (RAF). It flew bomber planes during World War I and World War II. Later, during the Cold War, it switched to flying helicopters. The squadron was finally closed down in 1975.
Contents
History of No. 103 Squadron
Forming in World War I
No. 103 Squadron first started during World War I (also called the Great War). It was formed on September 1, 1917, at RAF Beaulieu in England. Back then, it was part of the Royal Flying Corps (RFC). The squadron used Airco DH.9 aircraft.
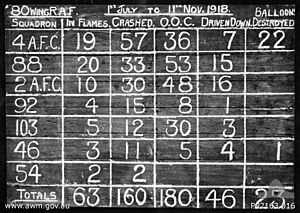
In May 1918, the squadron moved to France. There, it flew planes for scouting missions and dropped bombs during the day. These missions happened on the Western Front. In June, the squadron became part of No. 80 Wing RAF. This happened after the Royal Air Force was created. The squadron was closed down on October 1, 1919.
Reforming the Squadron
The squadron was started again on August 10, 1936. It was called No. 103 (Bomber) Squadron. This time, it was a light bomber squadron. It flew biplane Hawker Hind bombers. A biplane has two sets of wings, one above the other.
The squadron then moved to RAF Usworth. In July 1938, No. 103 Squadron got newer planes. These were the more advanced Fairey Battle monoplane bombers. A monoplane has only one set of wings.
No. 103 Squadron in World War II

When World War II began, the squadron was sent to France. It was part of the RAF Advanced Air Striking Force. On May 10, 1940, the German army invaded France, Belgium, and the Netherlands. The squadron was very busy during the Battle of France. It lost many planes and pilots. In mid-June 1940, the squadron left France. It went back to RAF Abingdon in England.
No. 103 Squadron then moved to RAF Newton. It became part of RAF Bomber Command. In October 1940, it got new Vickers Wellington bombers. These planes flew missions to targets in Europe. The squadron moved to a new airfield, RAF Elsham Wolds, in July 1941.
In July 1942, the Wellingtons were replaced. The squadron started flying Handley Page Halifax bombers. These were then replaced in late October 1942 by Avro Lancaster bombers. No. 103 Squadron flew Lancasters for the rest of the war. They flew many missions to Germany and other parts of Europe.
During World War II, 103 Squadron flew over 6,000 missions. This came at a high cost in both people and planes. On February 14, 1943, the squadron was sent to bomb Milan, Italy. The lead bomber was hit by bombs from another plane. It crashed on the edge of the city. Parts of this bomber were found in 1990. This happened when the Milan Metro (subway) was being expanded. At the end of World War II, on November 26, 1945, the squadron was closed. It was renamed to 57 Squadron.
Flying Jet Bombers in Germany
No. 103 Squadron was started again on November 30, 1954. This time, it was at RAF Gütersloh in West Germany. It was part of the RAF Second Tactical Air Force. During this short time, the unit flew English Electric Canberra jet bombers. However, the squadron was closed down again on August 1, 1956.
Helicopter Missions in Cyprus
No. 103 Squadron was reformed at RAF Nicosia, Cyprus, on August 1, 1959. It was created by renaming 284 Squadron. From then on, it became a support unit. It used Bristol Sycamore HR.14 helicopters. These helicopters helped with search and rescue missions. They also helped move injured people and keep peace. No. 103 Squadron was closed on July 31, 1963. Its work was split into two smaller units.
Serving in the Far East
No. 103 Squadron was reformed again in the Far East. This happened at RAF Seletar, Singapore, on August 1, 1963. It was created by renaming 110 Squadron. At that time, it used Westland Whirlwind HAR.10 helicopters.
In 1969, the squadron moved to RAF Changi. Then, in 1971, it moved to RAF Tengah. In November 1972, the Westland Whirlwind helicopters were replaced. The squadron got more modern Westland Wessex helicopters. But three years later, No. 103 Squadron was closed for the last time. This happened on August 1, 1975, at RAF Tengah.
Aircraft Used by No. 103 Squadron
| From | To | Aircraft | Version |
|---|---|---|---|
| December 1917 | March 1919 | Airco DH.9 | |
| August 1936 | Late 1938 | Hawker Hind | |
| Late 1938 | October 1940 | Fairey Battle | Mk.I |
| October 1940 | July 1942 | Vickers Wellington | Mk.Ic |
| July 1942 | October 1942 | Handley Page Halifax | Mk.II |
| October 1942 | November 1945 | Avro Lancaster | Mks.I & III |
| November 1954 | August 1956 | English Electric Canberra | B.2 |
| August 1959 | July 1963 | Bristol Sycamore | HR.14 |
| August 1963 | November 1972 | Westland Whirlwind | HAR.10 |
| November 1972 | August 1975 | Westland Wessex | HC.2 |
Squadron Bases

| From | To | Base | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 September 1917 | 8 September 1917 | RFCS Beaulieu, Hampshire | Formed here as RFC unit |
| 8 September 1917 | 12 May 1918 | RFCS Old Sarum, Wiltshire | |
| 12 May 1918 | 21 October 1918 | Serny, France | |
| 21 October 1918 | 26 October 1918 | Floringhem, France | |
| 26 October 1918 | 25 January 1919 | Rochin, France | |
| 25 January 1919 | 26 March 1919 | Maisoncelle, France | |
| 26 March 1919 | 1 October 1919 | RAF Shotwick, Flintshire | 1st Disbandment |
| 10 August 1936 | 26 February 1937 | RAF Andover, Hampshire | |
| 26 February 1937 | 2 September 1938 | RAF Usworth, County Durham | |
| 2 September 1938 | 1 April 1939 | RAF Abingdon, Oxfordshire | |
| 1 April 1939 | 2 September 1939 | RAF Benson, Oxfordshire | |
| 2 September 1939 | 28 November 1939 | Challerange, France | |
| 28 November 1939 | 15 February 1940 | Plivot, France | |
| 15 February 1940 | 16 May 1940 | Bétheniville, France | |
| 16 May 1940 | 4 June 1940 | Rhèges/Saint-Lucien Ferme | |
| 4 June 1940 | 14 June 1940 | Ouzouer-le-Doyen, France | |
| 14 June 1940 | 15 June 1940 | Sougé, France | |
| 15 June 1940 | 16 June 1940 | RAF Abingdon, Oxfordshire | Air echelon only |
| 16 June 1940 | 3 July 1940 | RAF Honington, Suffolk | |
| 3 July 1940 | 11 July 1941 | RAF Newton, Nottingham | |
| 11 July 1941 | 26 November 1945 | RAF Elsham Wolds, Lincolnshire | 2nd Disbandment |
| 30 November 1954 | 1 August 1956 | RAF Gütersloh, West Germany | 3rd Disbandment |
| 1 August 1959 | 31 July 1963 | RAF Nicosia, Cyprus | 4th Disbandment |
| 1 August 1963 | 28 March 1969 | RAF Seletar, Singapore | |
| 28 March 1969 | 15 September 1971 | RAF Changi, Singapore | |
| 15 September 1971 | 31 July 1975 | RAF Tengah, Singapore | 5th Disbandment |
 | Isaac Myers |
 | D. Hamilton Jackson |
 | A. Philip Randolph |