Open star cluster facts for kids
An open star cluster is a group of hundreds or thousands of stars. These stars are all about the same age because they formed together from a huge cloud of gas and dust. They are also known as galactic clusters.
Scientists have found over 1,100 open clusters in our Milky Way galaxy, and there are likely many more. Gravity holds these clusters together, but not very strongly. Because of this, they can break apart when they get too close to other star clusters or gas clouds. Most open clusters last for a few hundred million years, but the biggest ones can survive for billions of years.
More massive star groups, called globular clusters, have much stronger gravity. This allows them to stay together for a lot longer. Open clusters are only found in spiral and irregular galaxies. These are galaxies where new stars are actively forming.
How Open Clusters Form
Young open clusters might still be inside the giant gas cloud where they were born. Their bright light makes this cloud glow, creating what scientists call an H II region. Over time, the strong light and energy from the cluster push the gas cloud away. Usually, about 10% of the gas in a cloud turns into stars before the rest of the gas is pushed away.
Why Open Clusters Are Important
Studying open clusters helps us understand how stars change and grow over time. All the stars in a cluster are roughly the same age and have similar chemical makeup. This makes it easier to study their properties, like their distance, age, and what they are made of, compared to single stars.
Some open clusters are bright enough to see without a telescope! Famous examples include the Pleiades, the Hyades, and the Alpha Persei Cluster.
Images for kids
-
The Pleiades is one of the most famous open clusters.
-
Many open clusters discovered by the VISTA telescope. They were hidden by dust in the Milky Way. Credit ESO.
-
NGC 265, an open star cluster in the Small Magellanic Cloud.
-
Infrared light shows a dense open cluster forming in the heart of the Orion nebula.
-
The "Pillars of Creation" in the Eagle Nebula. Here, young, massive stars are evaporating the gas cloud.
-
NGC 2367 is a very young star group on the edge of the Milky Way.
-
NGC 346, an open cluster in the Small Magellanic Cloud.
-
A cluster of stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud lights up the Tarantula Nebula.
-
NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy is a very large open cluster surrounded by an H II region.
-
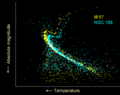
Hertzsprung-Russell diagrams for two open clusters. NGC 188 is older and shows a lower turn off from the main sequence than M67.
-
M11, also known as 'the Wild Duck Cluster', is a very rich cluster found towards the center of the Milky Way.
See also
 In Spanish: Cúmulo abierto para niños
In Spanish: Cúmulo abierto para niños
 | William L. Dawson |
 | W. E. B. Du Bois |
 | Harry Belafonte |