Peaking power plant facts for kids

A peaking power plant (or peaker) is a special kind of power station. It only turns on when people need a lot of electricity. Think of it like a backup generator for a whole city! These plants are different from "base load" plants, which run all the time.
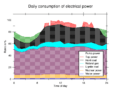
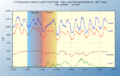
Peaker plants are super important during "peak hours." These are times when many people use electricity at once. For example, on a very hot afternoon, everyone might turn on their air conditioners. This causes a huge jump in how much power is needed. Peaker plants jump in to meet this sudden high demand.
Because these plants don't run all the time, the electricity they make can be more expensive. They are built to start up quickly and provide power fast.
Contents
Why Do We Need Peaker Plants?
Electricity is tricky because it's hard to store in large amounts. We need to make it exactly when people want to use it. Most power plants, like big coal or nuclear power plants, are designed to run constantly. They provide the steady, everyday power.
But sometimes, the demand for electricity goes way up. This can happen:
- On hot summer days when air conditioners are blasting.
- On cold winter evenings when heaters are on.
- When people come home from work and turn on lights, TVs, and appliances.
Peaker plants fill this gap. They make sure there's always enough power, even during these busy times. Without them, there could be blackouts or power shortages.
Types of Peaking Power Plants
Many different kinds of power plants can act as peakers. Here are some common examples:
Hydropower Plants
Hydropower plants use the force of moving water to make electricity. They are great peakers because they can start and stop very quickly. When more power is needed, operators can open the dam gates and let more water flow through the turbines.
Pumped-Storage Hydro Plants
This is a special type of hydropower. It has two reservoirs, one high up and one low down. When electricity demand is low (like at night), they use cheap power to pump water from the lower reservoir to the upper one. When demand is high, they release the water from the upper reservoir. This water flows downhill through turbines to make electricity. It's like a giant battery!
Gas-Fired Power Plants
Many peaker plants burn natural gas to create electricity. These plants can also start up quite fast. They are often used because natural gas is a cleaner-burning fossil fuel compared to coal.
What Isn't Used as a Peaker?
Some types of power plants are not good for peaking. For example:
- Nuclear power plants are designed to run continuously. It takes a long time to start them up or shut them down.
- Solar power and wind power depend on the weather. They can't be turned on just when we need them most, unless they are combined with large battery storage systems.
Peaker plants are a vital part of our electricity system. They help keep the lights on and our devices running, even when everyone is using a lot of power!
Images for kids
-
Kearny Generating Station, a former coal-fired base load power plant, now a gas-fired peaker, on the Hackensack River in New Jersey
 | Claudette Colvin |
 | Myrlie Evers-Williams |
 | Alberta Odell Jones |