Peenemünde facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Peenemünde
|
||
|---|---|---|

Seaport
|
||
|
||
| Country | Germany | |
| State | Mecklenburg-Vorpommern | |
| District | Vorpommern-Greifswald | |
| Municipal assoc. | Usedom-Nord | |
| Elevation | 3.0 m (9.8 ft) | |
| Population
(2022-12-31)
|
||
| • Total | 351 | |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) | |
| Postal codes |
17449
|
|
| Dialling codes | 038371 | |
| Vehicle registration | VG | |
Peenemünde is a small town in north-eastern Germany. It is located on Usedom island, right by the Baltic Sea. The town is famous for its history during World War II. This is where the world's first working large liquid-propellant rocket, called the V-2, was created.
Contents
Exploring Peenemünde
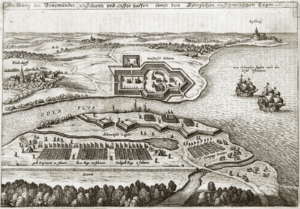
Peenemünde is a village with its own seaport. It sits at the very end of a sandy strip of land. This is where the Peene River flows into the Baltic Sea. The village is on the north-western part of Usedom Island.
You can reach Peenemünde by ferry boat across the Peene River. There are also boat trips along the Baltic coast to Rügen Island. The local train station is the last stop on the Usedomer Bäderbahn line. This line connects Peenemünde to Zinnowitz and other towns. There is also an airfield nearby for planes.
A Look Back in Time
Early Days of Peenemünde
Many years ago, around the 900s and 1000s, Peenemünde was part of a region called Circipania. This area was home to a Slavic tribe known as the Circipanes. Later, in the late 1100s, the region became part of the Duchy of Pomerania.
The town of Peenemünde was first mentioned in official records in 1282. In 1630, during a war, the country of Sweden took control of the settlement. This was confirmed in 1648 by a peace treaty. Later, in 1720, Peenemünde became part of Prussia. It was even attacked by Sweden again in 1757 during another war.
Peenemünde and World War II
During World War II, Peenemünde played a very important role. It was a secret place where Germany developed and built powerful rockets. These included the V-1 and the V-2 rocket. The town's docks were used to recover parts of V-2 rockets after test launches over the Baltic Sea.
Scientists like Wernher von Braun worked on these rockets in Peenemünde. They were sometimes called "Peenemünders." A group of people who opposed the war, led by a priest named Heinrich Maier, secretly shared plans of the V-1, V-2, and the research station with the Allies. This information helped the Allies plan air attacks.
On August 17-18, 1943, Allied bombers attacked the research facility. This attack caused a lot of damage. It delayed the launch of the V-2 prototype rocket by about two months. Sadly, 123 people died in the attack, including a scientist named Walter Thiel. Wernher von Braun survived by hiding in a bunker.
On May 5, 1945, the entire island was taken over by the Soviet Red Army. Today, you can still see the ruins of a gas plant that made liquid oxygen at the entrance to Peenemünde.
After the War
After World War II, Peenemünde's port became a naval base for the Soviet Union. In 1952, it was given to the armed forces of East Germany. The port was used by the East German sea police. Later, in 1956, the headquarters for the East German navy was set up in Peenemünde.
Today, Peenemünde is home to the Peenemünde Historical Technical Museum. This museum opened in 1992. It is located in the old power station of the former Army Testing Site. The museum shows exhibits about World War II, including a V-1 flying bomb and a V-2 rocket. It is part of the European Route of Industrial Heritage.
See also
 In Spanish: Peenemünde para niños
In Spanish: Peenemünde para niños