White-crowned manakin facts for kids
Quick facts for kids White-crowned manakin |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Male | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Pseudopipra
|
| Species: |
pipra
|
 |
|
| Synonyms | |
Linnaeus, 1758
|
|
The white-crowned manakin (Pseudopipra pipra) is a small passerine bird. It belongs to the manakin family, called Pipridae. This bird is very common and can be found in many places.
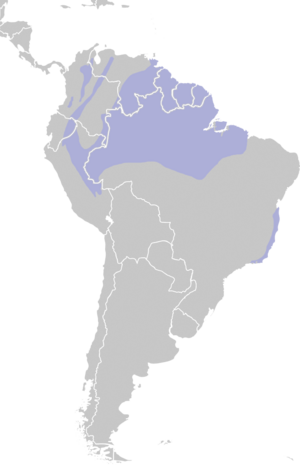
It is easy to spot, even the females. This bird lives in the tropical New World. Its home stretches from Costa Rica to northeastern Peru and eastern Brazil.
The white-crowned manakin used to be in the Pipra group. Now, it has its own special group called Pseudopipra. It is a small, round bird, about 10 cm long.
Male birds are black with a bright white crown on their head. They can even raise this white crown like a small crest! No other manakin has both an all-black body and a shiny white crown.
Female and young birds are olive-green. They have a grey head and throat. Their belly area is greyish-green or olive. When it's time to breed, males perform special dances to attract females. This bird is quite common. Experts say it is a "least concern" species, meaning it is not in danger.
Contents
What is a White-crowned Manakin?
The white-crowned manakin is a small, active bird. It lives in warm, tropical forests. These birds are known for their bright colors and unique behaviors.
They are part of a bird family called manakins. Manakins are famous for their amazing courtship displays.
How Scientists Name Birds
The white-crowned manakin was first described in 1758. A Swedish scientist named Carl Linnaeus gave it its first scientific name. He called it Parus pipra.
Scientists often change how birds are grouped. This happens as they learn more about them. The white-crowned manakin was once in the Pipra group.
Later, studies showed it was different from other Pipra birds. So, it was moved to its own group. This new group is called Pseudopipra. There are 13 different types, or subspecies, of this bird.
Where Does it Live?
The white-crowned manakin lives in many places. You can find it in southern Central America. It also lives in northern South America. Some populations are in the Amazon rainforest.
There is even a small group in eastern Brazil. This bird likes mountain foothills. It often breeds between 800 and 1600 meters high. In some areas, like northeastern Venezuela, it can be found closer to the sea.
Its Forest Home
This bird prefers the lower parts of wet forests. It also lives in tall, regrowing forests. You can find it in dense, humid forests.
Sometimes, it lives in younger forests. It can even be found in small forest patches within grasslands. In Ecuador, it prefers hilly forests. In the Colombian Andes, it usually lives between 600 and 1,200 meters high.
What Does it Look Like?
The white-crowned manakin is about 9 to 10 cm long. That's about the size of a small sparrow. Male birds weigh about 11 grams. Females are a bit heavier, around 12.8 grams.
It is a compact bird with a short tail. It has a strong, curved beak. Its legs are dark, and its eyes are red. The male's feathers are very striking.
Male and Female Birds
Adult males are mostly black. They have a bright white crown on their head. This white patch can be raised like a small crest.
When a male calls, it makes a buzzing sound, "jeeeee". When it's trying to attract a female, it adds a popping sound, "p-p-p chee".
Female birds and young males are olive-green. Their head and throat are grey. Their belly area is grey-green or olive. Females from the eastern Andes look brighter green. But their grey head and red eyes help tell them apart easily.
How Do They Behave?
Like other manakins, this bird has a special breeding display. Males gather in an area called a lek. Here, they perform to attract females.
However, the leks of this species are spread out. There are usually 3-4 males, far enough apart that they can just hear each other. They can be up to 100 meters apart.
Males fly between horizontal branches. These branches are usually 3–12 meters high. They can be up to 50 meters apart. Males fly with a swooping motion. If a female is watching, they fly slowly, like a butterfly.
What Do They Eat?
The white-crowned manakin eats low in the trees. Its main food is fruit. It also eats some insects. It catches both fruits and insects while flying.
Reproduction and Nests
White-crowned manakin nests are often in open forest areas. They like places with dense plants around them. Nests are often found in gaps where trees have fallen.
The nest is shaped like an open cup. It is made of brownish-yellow plant fibers. They also use parts of fungi and palm leaves. The outside of the nest is covered with dead leaves. Spider webs help hold it all together.
Nests are built in the fork of a small tree or shrub. They can be from 1 to 9.8 meters above the ground. Females lay two dirty white eggs. The eggs have many brownish markings. Each egg is about 20.5 × 13.5 mm in size.
Scientists do not yet know how long the eggs take to hatch. They also don't know how long it takes for the young birds to leave the nest. Only the female bird takes care of the eggs and young.
Conservation Status
This bird lives in a very large area. It is quite common. Scientists believe there are many white-crowned manakins in total.
The number of these birds might be slowly going down. But still, the International Union for Conservation of Nature says it is a "least concern" species. This means it is not currently in danger of disappearing.
However, future climate change could affect its habitat. This might impact where the white-crowned manakin can live.
Images for kids




