Pliocene facts for kids
The Pliocene was a short period in Earth's history. It was a geological epoch, which is a big chunk of time. It started about 5.3 million years ago (mya). It ended around 2.6 million years ago. The Pliocene came after the Miocene epoch. It was followed by the Pleistocene epoch.
Contents
The Pliocene Epoch
Earth's Changing Climate
During the Pliocene, the Earth kept getting cooler. It also became much drier. This change had a big impact on plants. Tropical rainforests started to shrink. Deciduous forests, which lose their leaves, also got smaller.
Instead, large Grasslands began to grow. This was important for animals. Many plant-eating mammals changed their diets. They became grazers, meaning they ate mostly grass. Before, they were browsers, eating leaves and twigs.
Early Humans and Animals
The Pliocene was a key time for human evolution. Some apes started to live on the savannah instead of in the forests. These early human relatives are called Australopithecines. They began to walk upright on two legs. This was a big step in the story of Hominids.
Many different animals lived during the Pliocene. Large mammals were common. These included early elephants, giraffes, and camels. There were also many types of marine animals. These lived in the oceans and seas.
Images for kids
-
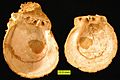
The thorny oyster Spondylus right and left valve interiors from the Pliocene of Cyprus
-
The limpet Diodora italica from the Pliocene of Cyprus
-
The scaphopod Dentalium from the Pliocene of Cyprus
-
Chesapecten, barnacles and sponge borings (Entobia) from the Pliocene of York River, Virginia
See also
 In Spanish: Plioceno para niños
In Spanish: Plioceno para niños