Purple apple-berry facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Purple apple-berry |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Apiales |
| Family: | Pittosporaceae |
| Genus: | Billardiera |
| Species: |
B. longiflora
|
| Binomial name | |
| Billardiera longiflora Labill.
|
|
 |
|
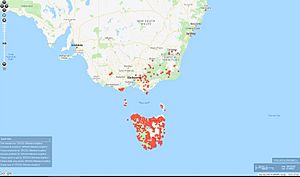
| Distribution Map of B. longiflora from The Atlas of Living Australia | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
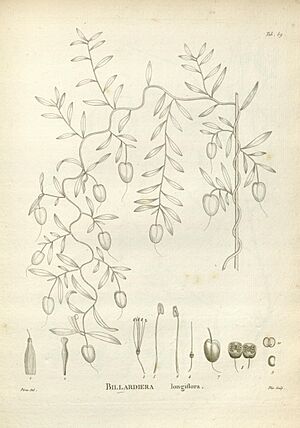
The purple apple-berry, also known as Billardiera longiflora, is a small Australian vine. You can find it in cool, wet forests from southern New South Wales all the way to Tasmania. A French botanist named Jacques Labillardière first described it in 1805. This vine has thin leaves, greenish-yellow flowers, and bright purple fruit. Good news: the fruit is safe to eat!
It belongs to the plant family Pittosporaceae and is part of the Billardiera group of plants.
Contents
How to Spot a Purple Apple-Berry
This vine is an evergreen climber. It likes to twine around smaller trees and bushes in forests. It can grow up to ten meters tall on taller trees!
You can recognize it by its narrow, oval-shaped and dark green leaves. These leaves are usually between 2 and 5 centimeters long. The stems are woody, brown, and look like wire.
The fruit is also easy to spot! It's shiny, bright purple or blue, and shaped like a small apple. These berries hang down among the dark green leaves. On Mount Wellington in Tasmania, some purple apple-berry fruits have even been found to be white!
Flowers of the Purple Apple-Berry
The flowers are shaped like tubes and can be pale yellow, purplish, or green. They are about 2.5 centimeters long. Each flower grows by itself. It has five petals that are connected by tiny hairs, five sepals, and several stamens.
These flowers smell nice! You can usually see them blooming from October to January.
Where the Purple Apple-Berry Lives
Billardiera longiflora is most often found in wet sclerophyll forests. These forests are usually less than 900 meters above sea level. Many of these forests are in southern Tasmania.
This plant loves to grow in the shady parts under the main trees. It needs moist soil to thrive. It can grow in most places in Tasmania, except for the very driest areas.
You might also find it in dry Eucalyptus forests, woodlands, and areas near rivers.
Collecting Purple Apple-Berry Seeds
The seeds are found inside the purple or blue fruit. Each fruit usually has about twelve seeds. When the seeds are ready, they are dark brown or maroon. To get the seeds out, you first need to dry the fruit. After drying, the fruit will split open.
The best time to collect seeds is usually in December and January.
Where Does it Come From?
The Billardiera longiflora is native to South-Eastern Australia. It grows naturally in the understory of wet forests. This includes New South Wales, Victoria, and Tasmania. It is very common across Tasmania. You can see a map of where it grows on The Atlas of Living Australia website.
In Tasmania, you can find it in many different areas. These include Break O'Day, Brighton, Burnie, Central Coast, Central Highlands, Circular Head, Derwent Valley, Devonport, Dorset, Flinders Island, Florentine Valley, Georgetown, Glamorgan-Spring Bay, Glenorchy, Hobart, Huon Valley, Kentish, King Island, Kingborough, Latrobe, Launceston, Meander Valley, Northern Midlands, Sorell, Southern Midlands, Waratah-Wynyard, West Coast, and West Tamar.
How Tough is the Purple Apple-Berry?
This plant is quite strong! It can handle moist, rocky, and shady places. It prefers soil that is loamy and drains water well. It is also known to be resistant to frost and drought.
The vines are very hardy. They can survive temperatures as low as negative seven degrees Celsius once they are well-grown.
Growing New Purple Apple-Berries
You can grow new purple apple-berries from seeds or from cuttings. If you use seeds, they should be ripe. Plant them just under the soil in autumn or early spring.
It's important to know that the seeds might not sprout right away. They can stay dormant until the conditions are just right, similar to their natural habitat.
Plant them in a spot that is protected and has some shade. In winter, you can add mulch around them. This gives them extra protection from cold temperatures.
Edible Uses of the Fruit
The fruit of the B. longiflora are the purple, apple-shaped berries. These berries are safe to eat! It's a good idea to remove the seeds before you eat them.
These berries don't have much pulp. They are often hollow and dry inside. Some people suggest using them to make jam, chutney, or jelly.
Related Plants
Billardiera is a genus of small vines and shrubs. All plants in this group are native to Australia. Here are a couple of other examples:
- Billardiera cymosa, also called the sweet apple-berry.
- Billardiera scandens, known as the common apple-berry.