Roloway monkey facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Roloway monkey |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Roloway monkey at La Vallée de Singes | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Haplorhini |
| Infraorder: | Simiiformes |
| Family: | Cercopithecidae |
| Genus: | Cercopithecus |
| Species: |
C. roloway
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cercopithecus roloway (Schreber, 1774)
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Roloway monkey (Cercopithecus roloway) is a rare Old World monkey found only in tropical West Africa. It was once thought to be a type of Diana monkey. Now, scientists know it's its own special species. This monkey is listed as Critically Endangered. This means it's in great danger of disappearing forever. The main reasons are that its forest home is shrinking and people still hunt them for food.
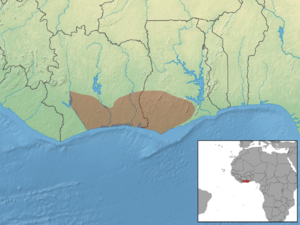
Roloway monkeys mostly live in trees. They can be found in forests in Ghana and some special areas in the Côte-D'Ivoire. One important place is the Tanoé forest in Côte-D'Ivoire. It's hard to study these monkeys in the wild. This is because there are so few of them, and they live in huge forests. But they are a unique and important animal that we need to protect.
Contents
About the Roloway Monkey
The Roloway monkey is a type of guenon monkey. They are actually the biggest of all 26 African guenon species. The Roloway monkey looks a lot like the Diana monkey. Both have dark fur over most of their bodies. They also have a dark reddish-brown patch on their lower back.
What Does a Roloway Monkey Look Like?
The Roloway monkey has a clear white beard under its black chin. Above its dark eyes, there's a white stripe of fur. Its face is dark black. This makes the bright white fur on its shoulders and chest stand out.
Roloway monkeys have a fairly flat skull. Unlike many other primates, their snout area is not very long. Their nostrils are close together and point downwards. Their chest and throat are bright white. They also have a white line of fur along the outside of each thigh. The fur on the inside of their thighs can be white, red, brown, or yellowish.
These monkeys have very long tails. Their tails are even longer than their bodies! Adult Roloway monkeys are about 40 to 55 centimeters (16 to 22 inches) long. Their tails can be 50 to 75 centimeters (20 to 30 inches) long.
Male monkeys weigh about 5 kilograms (11 pounds). Female Roloways are smaller, weighing about 2.5 kilograms (5.5 pounds). Roloway monkeys have special cheek pouches. They share this feature with all guenon monkeys. These pouches let them store food like fruits, nuts, and seeds. These foods make up most of their diet.
Like other guenon monkeys, Roloway monkeys have thumbs that can grasp things. They also have fingernails on all their fingers. Roloway monkeys can live a long time. They usually live for 20 to 30 years.
Where Roloway Monkeys Live
Roloway monkeys live in a small part of eastern Ivory Coast and the forests of Ghana. They are found between the Sassandra and Pra Rivers. They might also live in Burkina Faso and Togo.
Their Forest Home
Roloway monkeys live high up in the trees of old-growth forests. These are very old forests that humans have not changed much. They prefer moist, low-lying areas. They avoid places where humans have had a big impact. These primary forests are lush and have thick, moist plants. This helps the monkeys hide easily.
The places where Roloway monkeys live are very complex. The terrain is not simple. This means they have many places to hide and stay out of sight. They use small parts of these forests. Their groups tend to be small.
It's very hard to study them in the wild. This is because they are so few and they hide well. Even when scientists stayed in areas where the monkeys were usually found, they only saw a Roloway monkey once. Most Roloway monkeys that are found are taken to zoos. This is a way to help save them because their numbers are so low in the wild.
What Roloway Monkeys Eat
The Roloway monkey is an omnivore. This means they eat both plants and animals. They eat different fruits, flowers, and leaves. They also eat insects. Because they eat insects, they are also called insectivorous.
Their Diet Changes with Seasons
These monkeys look for large insects and eat them for food. They also eat insect larvae and eggs for extra nutrients. They can eat parts of about 130 different types of plants. These include trees, climbing plants, and epiphytes (plants that grow on other plants). Like many omnivores, they also eat ripe fruit pulp, small bugs, oily seeds, and young leaves.
Scientists believe the Roloway monkey changes its diet depending on the season. During the dry season, they eat more fruit and pulp. In the wet season, when more insects are available, they eat fewer fruits and seeds. Instead, they eat more insects. Changing their diet based on what's available helps them stay healthy. When they look for food, they try to find the easiest path. They might not swing or jump if there's a more direct way to get food.
How Roloway Monkeys Behave
Roloway monkeys are active during the day. They sleep high in the trees at night, like many other primates. They live in social groups of about 6 to 30 monkeys. Usually, there's one male, about 10 females, and their young. Males might move between groups. Females usually stay with the group they were born into. When there are fewer Roloway monkeys, staying in the same group can make it harder for them to recover.
Most of their day is spent looking for food. During rest times, they groom each other, play, and care for their young. This is when they form strong bonds. Rest time is also important for young monkeys to learn and grow. Roloway monkeys are social. They interact with other monkeys in their area. Younger Roloway monkeys are not as strong or outgoing as adults. They rely more on adults to learn about their surroundings. We still don't know much about their daily lives. This is because there are so few of them, and not much research has been done.
How Roloway Monkeys Communicate
Many primates have advanced ways of talking to each other. The Roloway monkey is no different. They make many different calls and sounds depending on the situation. They are known to croak, chuckle, and shriek. They also make loud yelling sounds when they sense danger. This warns other group members to flee.
Male monkeys often make a "gathering call." This tells the females and young to return to their home area, near the male. Roloway monkeys don't just use sounds to communicate. They also use body language. This includes facial expressions, posture, hand signals, and actions.
Their eyebrows can show how they feel. Raised eyebrows can mean they are showing a threat. Their eyes are also important. A Roloway monkey that stares is showing dominance and threats. They also use their mouth and teeth to show if they are dominant or submissive. A smile showing teeth usually means they are submissive. But if they are growling with their mouth wide open and jaw pushed out, they are being aggressive.
Within their groups, there are levels of rank. Clear communication, both physical and verbal, helps keep peace. It also reduces tension and fights. This is why grooming is so important. It helps them form stronger bonds and share information.
Roloway Monkey Reproduction
Most of what we know about Roloway monkey reproduction comes from studying the closely related Diana monkey. Their breeding habits are very similar. Roloway monkeys are polygynous. This means one male is the leader of the group.
Females have a 30-day estrous cycle. This cycle can happen at any time of the year. So, the male can mate with a female whenever she is ready. Female Roloways usually give birth to one baby. Twins are rare. The pregnancy lasts about six months. The mother is the main caregiver. However, other female monkeys, like sisters, might help care for the newborn. The mother feeds the baby milk for about six months. After that, the baby starts eating more adult foods like fruit, nuts, and seeds.
A Roloway monkey becomes an adult at about 3 to 4 years old. A young male usually leaves his birth group. He then looks for a new group to join or starts his own group to find mates. Roloway monkeys live for about 20 years in the wild. In zoos, they can live for more than 30 years. Monkeys in zoos sometimes have trouble breeding. But if their living conditions are like their natural homes, they can reproduce well.
Saving the Roloway Monkey
The Roloway monkey is a very threatened species. The IUCN first listed them as Endangered in 2008. As their numbers kept dropping, they were moved to Critically Endangered. This means they need conservation more than ever. The Roloway monkey is one of the top three most threatened monkeys in West Africa. Some even say it's the most threatened primate in all of Africa.
Dangers They Face
Roloway monkeys need old-growth forests to survive. The problem is that these forests are being cut down quickly for human use. This causes huge habitat loss for many animals, including the Roloway. Ghana, where most Roloway monkeys have been seen, has lost almost 90% of its forest land in the last 100 years.
This loss of habitat is a big problem. Roloway monkeys are not good at adapting to new areas. They need very specific things in their environment. As they lose their homes, their numbers have dropped a lot. The species is listed as one of "The World's 25 Most Endangered Primates".
It's thought that there are only about 2,000 Roloway monkeys left. Their numbers will keep falling. This is because hunters value their meat. Roloway monkeys are close to extinction not just because of hunting. Human expansion is also a cause. The large forests they once lived in are shrinking. Roads and transportation areas are growing. Also, much of the forest is being used for farming. This makes the land unlivable for the monkeys. Since the 1970s, fewer and fewer sightings happen each year. Recently, some areas where Roloways used to be found now report zero sightings.
Their natural predators, like the chimpanzee, leopard, and crowned eagle, are dangerous. But humans are the biggest threat. The Roloway monkey is a main target in Ghana's bushmeat trade. This trade is huge, selling thousands of pounds of meat in Ghana's markets. Roloway monkeys are popular for bushmeat because they are unique. Also, they tend to make loud noises when they communicate. This can make it easier for hunters to find them.
Recently, hunters have found so few Roloway monkeys that they don't even want to look for them anymore. It takes too long to find one, and they might not make enough money. So, hunting is a problem, but so is habitat loss. Humans are expanding quickly. To get more land for buildings, farms, and other needs, people are cutting down the forests where Roloways live. With less space to live, the monkeys are more threatened by hunting. They also can't grow their population as much. Humans are the main reason for their low numbers. This is due to hunting, more buildings, and breaking up their forest homes.
What's Being Done to Help
The Roloway monkey is now one of the top 25 most critically threatened primates in the world. We need to act fast to save this species. Many people know how threatened they are, but not enough is being done. CITES listed them as a Class A species under the African Convention of Nature and Natural Resources. But there are problems with making rules in the countries where Roloways live. Because of these problems, laws against poaching (illegal hunting) are not often enforced.
Some small groups have started in areas near the Tanoe forest and other places where monkeys have been found. But without government help, these groups might not succeed. Large conservation programs are trying to help this species recover. They use methods like breeding monkeys in zoos. Sadly, this breeding is not very successful right now. This is because there's nowhere safe to release the monkeys.
Right now, efforts are needed to find new places where the monkeys could live well. This would be after breeding programs create a larger group of monkeys that can be released. In 2020, the United Kingdom celebrated the first birth of a Roloway monkey in that country. There are breeding programs around the world. Many have not been very successful. But this birth was a small victory.
Breeding programs have faced challenges. The monkeys can have a hard time getting used to each other. They are not always willing to breed. Also, there are so few monkeys in zoos that breeding must be very careful. This is to avoid inbreeding, which could make their conservation status even worse.




