Rose-ringed parakeet facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Rose-ringed parakeet |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Male | |
 |
|
| Female | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Psittacula
|
| Species: |
krameri
|
 |
|
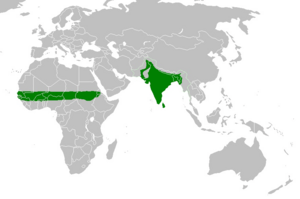
| Original (wild) range | |
The rose-ringed parakeet (Psittacula krameri) is also known as the ring-necked parakeet. It is a medium-sized parrot that belongs to the parrot family. These birds are originally from parts of Africa and South Asia. However, they now live in many other places around the world. This is because some pet birds have escaped and started new wild groups.
Rose-ringed parakeets look a bit different depending on if they are male or female. This is called sexual dimorphism. Adult males have a red and black ring around their neck. Females and young birds do not have this bright ring. They might have a faint grey ring instead. In the wild, these parakeets are mostly green. But birds raised as pets can come in many colors like blue, purple, or yellow.
These parakeets are about 40 cm (16 in) long, including their long tail feathers. Their wings are about 15 to 17.5 cm (5.9 to 6.9 in) long. In the wild, they are very noisy birds with a loud squawking call. Pet parakeets can even be taught to speak human words! They eat plants and do not migrate, meaning they stay in one place all year.
The rose-ringed parakeet is one of the few parrot species that can live well in places changed by humans. They have adapted to cities and areas where forests have been cut down. Because they are popular pets, many escaped birds have started living in cities around the world, especially in Europe. These parakeets can even survive cold winters in places like Northern Europe. The IUCN says these birds are of "least concern". This means their numbers seem to be growing. However, their popularity as pets and the damage they cause to farms have reduced their numbers in some of their native homes.
Contents
Where Rose-Ringed Parakeets Live
Since the 1800s, rose-ringed parakeets have spread to many new countries. They can breed further north than any other parrot species. They have done very well in places like London, England. They have also started living in the Netherlands. They have been less successful in the southern parts of the USA.
What Rose-Ringed Parakeets Eat
In the wild, rose-ringed parakeets mostly eat buds, fruits, vegetables, nuts, berries, and seeds. Wild groups of these birds often fly many miles to find food on farms and in orchards. This can cause a lot of damage to crops.
In India, they eat cereal grains. In winter, they also eat pigeon peas. In Egypt, during spring, they eat mulberry fruits. In summer, they eat dates. They often build their nests inside palm trees and eat from sunflower and corn fields.
Pet rose-ringed parakeets can eat many different foods. They can have fruits, vegetables, special bird pellets, and seeds. They can even have small amounts of cooked meat for protein. But it's important to avoid giving them oils, salts, chocolate, alcohol, or foods with preservatives.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
In northwest India, Indian rose-ringed parakeets form pairs between September and December. They do not stay with the same partner for life. They often find a new partner for the next breeding season. During the colder months, they choose and protect their nest spots. This helps them avoid fighting with other birds for good nesting places. Eating winter pea crops helps the female get the nutrients she needs to make eggs. From April to June, they take care of their young. The young birds, called fledglings, are ready to leave the nest before the rainy season starts.
Rose-Ringed Parakeets as Pets

Rose-ringed parakeets have been popular pets for a very long time. The ancient Greeks kept the Indian type of these parakeets. The ancient Romans kept the African type.
In recent years, many new colors of the Indian rose-ringed parakeet have become available. For example, there is a blue color morph. These birds have light blue feathers instead of green. They also do not have the neck rings that the normal green birds have.
How They Mimic Speech
Both male and female rose-ringed parakeets can copy human speech. First, the bird listens carefully to the sounds around it. Then, it tries to copy the voice of the human speaker. Some people raise rose-ringed parakeet chicks by hand. This helps the parrots become very friendly and good at learning to speak.
Images for kids
-
P. k. manillensis, Sri Lanka
See also
 In Spanish: Cotorra de Kramer para niños
In Spanish: Cotorra de Kramer para niños











