Broad-tailed hummingbird facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Broad-tailed hummingbird |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Adult male at a feeder | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Apodiformes |
| Family: | Trochilidae |
| Genus: | Selasphorus |
| Species: |
S. platycercus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Selasphorus platycercus |
|
 |
|
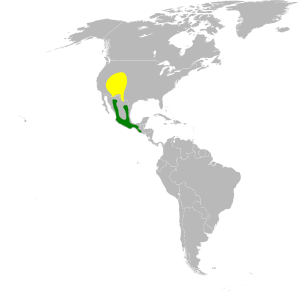
| Range of S. platycercus Breeding range Wintering range | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The broad-tailed hummingbird (Selasphorus platycercus) is a medium-sized hummingbird. You can find it in high mountain areas. These areas stretch from the western United States and Western Canada down to Mexico and Guatemala.
Contents
About This Hummingbird
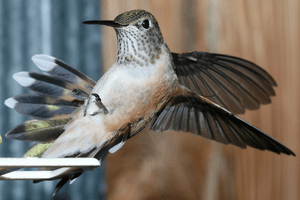
This hummingbird is about 4 inches (10 cm) long. Its wingspan is around 5.25 inches (13 cm). It weighs about 3.6 grams (0.13 oz). Female hummingbirds are usually a bit bigger than males.
Both male and female broad-tailed hummingbirds have a shiny, green back. This green color can seem to change in the light. They also have a white ring around their eyes. Their black tail is rounded and sticks out past their wing tips. This is how they got their name!
Males and females of this species look different. This is called sexual dimorphism. The male has a bright rose-red throat patch, called a gorget. This patch is very noticeable. Females are paler in color. They have cinnamon-colored sides and spotted cheeks. Males do not have these spots.
Hummingbird Family Tree
The broad-tailed hummingbird, Selasphorus platycercus, belongs to the order Apodiformes. It is part of the Trochilidae family. Hummingbirds are divided into different groups. The broad-tailed hummingbird is in the "Bee group." It is also part of the Selasphorus genus.
The Selasphorus genus has six members. These hummingbirds often have reddish-brown colors in their feathers. Males in this group have throat patches that range from orange to purple.
Other hummingbirds in this group include:
- Selasphorus sasin: Allen's hummingbird
- Selasphorus rufus: Rufous hummingbird
- Selasphorus scintilla: Scintillant hummingbird
- Selasphorus ardens: Glow-throated hummingbird
- Selasphorus flammula: Volcano hummingbird
The Selasphorus genus is found in two main areas. One group lives in North America. The other group lives in Costa Rica and Panama.
Where They Live
Their Home
You can often spot this hummingbird under pine and oak trees. They like to find food in open areas with flowers. They also live in grasslands among trees and bushes. For breeding, they prefer high mountain meadows and valleys. They also like areas with aspen or spruce trees.
Where They Are Found
Broad-tailed hummingbirds live from Guatemala to Mexico. In summer, they are found in the western United States and Western Canada. During winter, they mostly move to southern Mexico and Guatemala.
Traveling South for Winter
These hummingbirds sometimes migrate. This means they travel to warmer places for winter. Some populations in the northern parts of their range migrate. They spend winter in southern Mexico or Guatemala. Then they fly back to their breeding areas in spring.
Male hummingbirds usually arrive first at the breeding grounds. The females follow them. Some broad-tailed hummingbirds in southern Mexico and Guatemala do not migrate. They stay in the same place all year. This is called being "sedentary."
How They Behave
Sounds They Make
Broad-tailed hummingbirds make different sounds. Their call sounds like a sharp “cheet.” They often repeat this sound: “cheet cheet cheet cheet...”
Their wings also make sounds that help them communicate. They make two types of sounds with their wings. The first is a “wing hum.” This sound happens when the hummingbird simply flies. It's a low sound. Both males and females make this sound.
The second sound is a “wing trill.” Only male hummingbirds make this sound. They use it during their courtship displays to attract females. The wing trill is a buzzing sound. Other males can hear it from 50 meters away. Females can hear it from 75 meters away. This sound is made when air quickly passes through special feathers on their wings. Studies show that males who can't make this trill might lose their territory more easily.
What They Eat
Broad-tailed hummingbirds mainly eat insects and nectar from flowers. They prefer "hummingbird-flowered" plants. These flowers produce a lot of nectar. They often have red, tube-shaped petals. An example is the Aquilegia elegantula flower.
Raising a Family
Broad-tailed hummingbirds breed from central Montana in the north down to Guatemala. They do not form a pair bond. This means the male and female do not stay together. They breed when flowers produce the most nectar.
Courtship
Males perform a special aerial display to attract females. They fly high into the air and then dive down. As they dive, their wings make a trilling sound.
Building a Nest
Females often return to the same nest site each year. The female builds the nest all by herself. It usually takes about 4 to 5 days. The nest is shaped like a cup. It is attached to a tree branch with spider webs. The female adds lichen, moss, and other tree material to the outside. This helps to camouflage the nest. Sometimes, other females might steal nest material!
Caring for Chicks
The female lays two white eggs. Each egg is about 1.2 to 1.5 cm (0.5 to 0.6 in) long. She sits on the eggs to keep them warm for about 16 to 19 days. The chicks are born helpless and without feathers. Their feathers grow in about 10 to 12 days. The female stays with her young even after they can fly. She cares for them for several weeks.
How They Are Doing
This hummingbird species is listed as “Least Concern.” This means it is not an endangered species. It has a wide range and a good population size. However, one study showed that its population went down by 52% between 1966 and 2015. Still, these birds seem to adapt well to areas changed by humans.
See also
 In Spanish: Colibrí coliancho para niños
In Spanish: Colibrí coliancho para niños