Spanish schooner Virgen de Covadonga facts for kids
class="infobox " style="float: right; clear: right; width: 315px; border-spacing: 2px; text-align: left; font-size: 90%;"
| colspan="2" style="text-align: center; font-size: 90%; line-height: 1.5em;" | 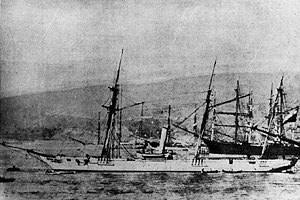
|}
The Virgen de Covadonga was a famous ship that sailed under both the Spanish and Chilean flags. She was a type of sailing ship called a schooner, also powered by a steam engine. This ship took part in two important conflicts: the Chincha Islands War and the War of the Pacific. She was built in 1859. Sadly, in 1880, the Covadonga hit a hidden floating mine near Chancay and sank.
Contents
- Building the Covadonga
- Covadonga in the Chincha Islands War
- Covadonga in the War of the Pacific
- The End of the Covadonga
- See also
Building the Covadonga
The construction of the Covadonga began with a special order on June 10, 1857. Her keel (the main bottom part of a ship) was laid down on February 13, 1858. This happened at the Arsenal de la Carraca shipyard in Cádiz, Spain.
She was a wooden schooner, which means she had sails but also a steam engine to help her move. The ship was officially launched on November 28, 1859. Building her cost a lot of money: 5 million Reales de Vellón.
The ship was named after the Battle of Covadonga. This battle was a very important event in Spanish history. It is seen as the start of the Reconquista, a long period when Christian kingdoms took back land from Muslim rule in Spain.
The Covadonga was officially put into service on October 8, 1858. Her first commander was Lieutenant Evaristo Casariego y García. She was first meant to be a mail boat, carrying letters and packages between Manila and Hong Kong. Her home base was the Naval Base of Manila in the Philippine Islands.
Covadonga in the Chincha Islands War
During the Chincha Islands War, the Covadonga helped the Spanish fleet. On November 26, 1865, the Chilean corvette Esmeralda captured the Covadonga. This happened during the Naval Battle of Papudo. The Esmeralda was led by Captain Juan Williams Rebolledo.
After being captured, the Covadonga joined the Chilean Navy on December 4, 1865. She kept her original name. During this war, she also fought in the Naval Battle of Abtao.
Covadonga in the War of the Pacific
In the War of the Pacific, the Covadonga and Esmeralda were the oldest and slowest ships in the Chilean navy. They were left to block the port of Iquique. There, they took part in one of the most important naval battles of the war.
On May 21, 1879, the Esmeralda fought the Peruvian ironclad Huáscar at the Naval Battle of Iquique. At the same time, the Covadonga was attacked by the Peruvian ironclad Independencia. The Independencia tried to ram the Covadonga but hit a hidden rock and sank. This happened during the Naval Battle of Punta Gruesa.
Later, on June 8, 1880, the Covadonga was hit by artillery fire from the shore at Arica, Peru. She had to be pulled onto the beach.
The End of the Covadonga
On September 13, 1880, the Covadonga was blocking the port of Chancay, Peru. Her sailors saw an empty boat floating by, filled with fresh fruit. When they tried to pull the boat closer, it exploded. The Peruvians had turned it into a floating mine. The Covadonga sank in less than 10 minutes.
Out of 109 crew members, 33 died in the disaster. This included the commander, Captain Pablo Ferrari. The gunboat Pilcomayo rescued 29 sailors. The Peruvians captured 48 others. Among those who died was Constantino Micalvi, a petty officer who had survived the Naval Battle of Iquique.
See also
 In Spanish: Goleta Covadonga para niños
In Spanish: Goleta Covadonga para niños
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | Virgen de Covadonga |
| Ordered | June 10, 1857 |
| Builder | Arsenal de la Carrara shipyard (Cádiz, Spain) |
| Cost | 5,000,000 Reales de Vellón |
| Laid down | 13 February 1858 |
| Launched | 28 November 1859 |
| Commissioned | 8 October 1859 |
| Captured | Battle of Papudo, 26 November 1865 |
| Fate | Captured by Chilean Navy during the Chincha Islands War |
| Name | Covadonga |
| Acquired | 26 November 1865 |
| Commissioned | 4 December 1865 |
| Fate | Sunk by a mine in Chancay, Peru during the War of the Pacific, 13 September 1880 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type | Screw-propelled schooner |
| Tons burthen | 630 tons |
| Length | 107 ft (33 m) |
| Propulsion |
|
| Sail plan | Brigantine sail rigging |
| Speed | 7 knots (13 km/h; 8.1 mph) on steam |
| Complement | 110 crewman |
| Armament |
|
| Notes | (*) Installed after 21 May 1879 |
 | Shirley Ann Jackson |
 | Garett Morgan |
 | J. Ernest Wilkins Jr. |
 | Elijah McCoy |

