Sydney Metro Northwest facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Sydney Metro Northwest |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
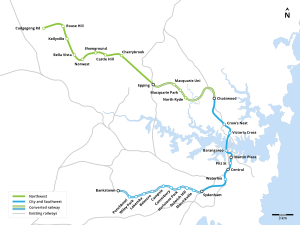
A map of the initial rail line plan, 2016
|
|
| Overview | |
| Status | Complete |
| Locale | Sydney, Australia |
| Stations | 13 (8 new stations, 5 stations converted) |
| Service | |
| Type | Rapid transit line |
| System | Sydney Metro |
| Rolling stock | Alstom Metropolis |
| History | |
| Opened | 26 May 2019 |
| Announced | 2011 |
| Start of major construction | 18 June 2014 |
| Completion | May 2019 |
| Technical | |
| Line length | 36 km (22 mi) |
| Number of tracks | 2 |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge |
| Electrification | 1,500 V DC from overhead catenary |
| Signalling | Alstom Urbalis 400 moving block CBTC ATC under ATO GoA 4 (UTO), with subsystems of ATP, Iconis ATS and Smartlock CBI |
The Sydney Metro Northwest was a big railway project in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. It built the first part of the Metro North West Line. This new line connects the north-western suburbs of Sydney, like Rouse Hill and Chatswood. It goes through areas such as Castle Hill and Epping.
The project also changed an older train line, the Epping to Chatswood rail link, to work with the new metro system. Transport for NSW managed this whole project. The completed Metro North West Line officially opened on May 26, 2019. Before June 2015, the project was known as the North West Rail Link (NWRL).
Contents
Building the Sydney Metro Northwest

Planning for this train line took a long time. It was announced, then cancelled, and then announced again many times since the 1990s. There were different ideas about how the new line would fit into Sydney's transport system.
Here are some of the ideas that were considered:
- A main train line connecting to the Main Northern line.
- A main train line connecting directly to the Epping to Chatswood line at Epping.
- A fast metro line from the north west to the city, called the North West Metro.
- A fast metro line connecting to a changed Epping to Chatswood line at Epping. This plan was chosen in the end. Trains would stop at Chatswood, with plans for a future extension to the city.
In June 2015, the project's name changed from "North West Rail Link" to "Sydney Metro Northwest." This new name covered the entire route from Rouse Hill to Chatswood.
How the Line Works
In 2011, the government thought about letting private companies help run the new train line. This would be a partnership between the government and private businesses.
In June 2012, it was decided that the line would use single-deck "Metro" style trains. These are different from the usual double-deck trains used in Sydney. In 2013, two groups of companies were chosen to build the trains and systems, and to operate the line. One of these groups, called Northwest Rapid Transit, was chosen in June 2014 to run the trains.
Construction of the Line
Work started with checking the ground in September 2011. Drilling machines dug holes up to 75 metres deep to understand the soil and rock underground. This helped engineers plan the tunnels and stations. The dirt from the tunnelling was also reused in other parts of Sydney.
Major Building Contracts
Three main contracts were given out to build the North West Rail Link.
- In June 2013, the contract for tunnels and station spaces was given to a group of companies including Thiess, John Holland, and Dragados.
- In December 2013, the contract for the above-ground parts, like bridges and viaducts, went to Italian companies Impregilo and Salini. This included building a 270-metre long bridge over Windsor Road at Rouse Hill.
- The final contract, for operating the trains and building the stations and rail systems, was given to the Northwest Rapid Transit group.
Changing the Epping to Chatswood Rail Link
The Epping to Chatswood rail link opened in 2009 as a regular heavy train line. It was later connected to the Northern Line. The government decided to close this line temporarily to change it into a metro line.
The Epping to Chatswood rail link closed on September 30, 2018, for about seven months. During this time, over 100 buses, called Station Link, replaced the trains. This allowed workers to upgrade the stations and tracks. The line reopened in May 2019 as part of the new Metro North West Line.
First Station Work in 2015
Project Completion
On January 14, 2019, the first driverless Metro train successfully traveled the entire route from Tallawong to Chatswood. The train line officially opened for passengers on May 26, 2019.
The Metro North West Line Route
The Sydney Metro Northwest project built eight new stations. It also converted five existing stations from the Epping to Chatswood rail link.
Here are the new stations built for the line:
- Tallawong (was called Cudgegong Road during planning)
- Rouse Hill
- Kellyville
- Bella Vista
- Norwest
- Hills Showground (was called Hills Centre, and Showground)
- Castle Hill
- Cherrybrook
These stations were already part of the Epping to Chatswood rail link and were changed for the Metro:
- Epping — where you can change to the T9 Northern Line and Central Coast & Newcastle Line
- Macquarie Park
- North Ryde
- Chatswood — where you can change to the T1 North Shore & Western Line and T9 Northern Line
Tallawong and Cherrybrook stations are built in open cuts, which means they are below ground but open to the sky. Castle Hill, Hills Showground, and Norwest stations are completely underground. Kellyville and Rouse Hill stations are above ground.
The two tunnels between Epping and Kellyville are 15.5 km long, making them the longest train tunnels in Sydney. They are also the deepest, going down 67 metres below ground at their deepest point. This is deeper than Sydney Harbour! Most of the tunnel was bored, but a section at Kellyville was built using a "cut-and-cover" method. Major tunnelling began in 2014.
Future Extension to Sydney CBD and Southwest
The Sydney Metro City & Southwest project will extend the Metro North West Line. It will go into the Sydney city centre and then to Bankstown. This extension will use a new tunnel from Chatswood, going under Sydney Harbour to Central and Sydenham. From Sydenham, it will connect to a newly changed line towards Bankstown. This extension started being built in 2017 and is expected to be finished in 2024.
Possible Western Extensions
There were also ideas to extend the line further west, possibly to connect with the existing Richmond railway line near Vineyard or Schofields. A study in 2018 suggested extending the Sydney Metro Northwest from Tallawong to Schofields. This would connect it to a proposed "North-South Link" that would serve the new Western Sydney Airport.
Train System and Infrastructure
A new train storage area was built at Tallawong Road in Rouse Hill, with space for 16 trains. There are also 3,000 new parking spaces at Cherrybrook, Hills Showground, and Kellyville stations for commuters.
The entire line uses electricity from overhead wires to power the trains. The above-ground sections use standard overhead wires. For the underground sections, a special rigid overhead system is used instead of wires.
There are special track sections called "crossovers" at some stations like Tallawong, Bella Vista, Castle Hill, and Chatswood. These allow trains to switch tracks or turn around.
The line also has modern technology to boost mobile phone signals, so passengers can have good 4G connections while traveling. The system is designed to run trains every 4 minutes during busy times, with plans to increase this to every 2.4 minutes in the future.
Train Automation
The Metro North West Line uses a very advanced signalling system called Alstom Urbalis 400. This system allows trains to drive themselves without a human driver (Grade of Automation 4, or UTO). There are no physical traffic lights on the tracks for this system. Instead, information about other trains and the track is sent directly to the train through a special communication system.
Platform Screen Doors
All stations on the Metro North West Line have Platform screen doors (PSDs). These are glass barriers between the platform and the tracks. They open only when a train is at the station, making it safer for passengers by preventing them from falling onto the tracks.
Earlier Ideas for the Line
Original 1998 Proposal
The North West Rail Link was first announced in 1998. It was part of a big plan to build eight new train projects by 2010. This first idea was for a $360 million train line from Epping to Castle Hill, with possible extensions later. However, this plan faced many delays and was eventually put on hold.
Metropolitan Rail Expansion Program
In 2005, the government announced a new $8 billion plan called the Metropolitan Rail Expansion Program (MREP). This plan included the North West Rail Link, with a new completion date of 2017. The proposed route would be 22 km long, with a 16 km tunnel section and a 4 km above-ground section. Six new stations were planned. However, this proposal was later replaced by a new idea called the North West Metro.
North West Metro
In 2008, the government changed the project again. It became a "metro" line called the North West Metro. This new plan extended the line all the way to the Sydney city centre. However, this project also faced funding problems and was eventually put on hold.
CBD Metro
Later in 2008, a shorter version called the CBD Metro was announced. This line would run from Rozelle to Central station. The North West Metro was put on hold indefinitely due to budget cuts.
Return to Original Idea
In 2010, the government cancelled the Sydney Metro project and went back to the original North West Rail Link idea. Construction was expected to start in 2017.
2011 Proposal
After a new government was elected in 2011, Premier Barry O'Farrell announced that building the North West Rail Link would be his first priority. Initial planning and ground investigations began by the end of 2011.
Proposed Route in 2011
The 2011 plan suggested a 23 km rail route with six new stations and the possibility of two more. The design was changed to a driverless rapid transit line with more frequent, smaller single-deck trains. All trains would stop at Chatswood, and passengers would need to change trains to go to the city.
Calling for Tenders
In 2011, the government started asking companies to bid for different parts of the project, like engineering, rail systems, and financial services. They wanted to see if private companies could help fund the project. The first major contract for design services was given to a group of companies including AECOM and Parsons Brinckerhoff.
Funding Challenges
The Australian Federal Government did not want to provide funding for the North West Rail Link. They preferred a different train line project. Even though a study showed the North West Rail Link would be very good for New South Wales, the Federal Government still did not give money. The State Government decided to build the line anyway, with or without federal funding.
Criticism and Challenges
- Some people, like the Mayor of The Hills Shire, thought the Metro Northwest should connect to the future Western Sydney Airport and other train lines.
- There were concerns that the line might need a lot of money from the government to operate, based on early predictions.
- Some people argued that double-deck trains would carry more passengers and be more comfortable for long trips. However, others said that single-deck metro trains with longitudinal seating (seats along the sides) are better for quick "hop-on, hop-off" journeys, especially for people with prams or trolleys.
- When the line opened, some bus services that connected the north-west to the city were changed. This meant some trips took longer. Also, many people found that the feeder bus services (buses that take people to the metro stations) were not frequent enough.
- Because of the bus issues, many commuters used the car parks at the metro stations, and these quickly filled up every morning. Experts suggested that more changes to feeder buses were needed, as building enough parking spaces would be very difficult.
- Some documents showed that the government had been warned that stopping the line at Chatswood would be inconvenient for northern suburbs commuters.
- The Greens NSW party also raised concerns about how many passengers the project could carry in the future.
Images for kids












