Trigonometry facts for kids
Trigonometry comes from two Greek words: trigonon, meaning "three angles," and metron, meaning "measure." It's a branch of mathematics that studies the relationships between the sides and angles of triangles. It especially focuses on three important functions: sine (sin), cosine (cos), and tangent (tan). Trigonometry is closely connected to geometry.
Contents
Understanding Triangles and Their Parts
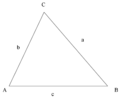
To understand trigonometry, it's important to know some special words for parts of a triangle.
What is a Right-Angled Triangle?
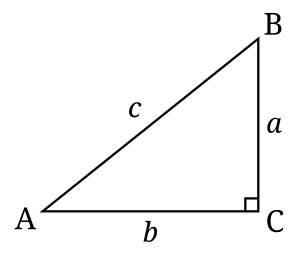
A right-angled triangle is a triangle that has one angle exactly equal to 90 degrees. This 90-degree angle is also called a "right angle." Trigonometry's main rules work best with these types of triangles. A triangle can only have one right angle.
Sides of a Right-Angled Triangle
- Hypotenuse: This is the longest side of a right-angled triangle. It's always the side directly across from the 90-degree angle. In the picture, side c is the hypotenuse.
- Opposite side: For any angle you pick (that isn't the right angle), the opposite side is the one that doesn't touch that angle's corner. For example, side a is opposite angle A.
- Adjacent side: For any angle you pick, the adjacent side is the one next to it that is NOT the hypotenuse. For example, side b is adjacent to angle A.
Key Trigonometric Ratios
There are three main ratios in trigonometry that help us link the angles and sides of right triangles.
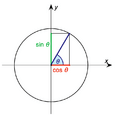
Sine (sin)
The sine of an angle is found by dividing the length of the opposite side by the length of the hypotenuse. 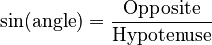
Cosine (cos)
The cosine of an angle is found by dividing the length of the adjacent side by the length of the hypotenuse. 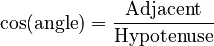
Tangent (tan)
The tangent of an angle is found by dividing the length of the opposite side by the length of the adjacent side. 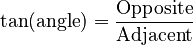
Remembering the Ratios: SOH-CAH-TOA
Many students use a special trick to remember these ratios called SOH-CAH-TOA:
- Sine = Opposite ÷ Hypotenuse
- Cosine = Adjacent ÷ Hypotenuse
- Tangent = Opposite ÷ Adjacent
How We Use Trigonometry
Trigonometry helps us "solve" triangles. This means if we know some parts of a triangle (like two sides and an angle, or two angles and a side), we can figure out all the missing sides and angles. This is useful in many areas of geometry.
Real-World Uses of Trigonometry
Trigonometry is very important in many jobs and studies:
- Surveying: Surveyors use it to measure distances and heights of land features.
- Mapmaking: It helps create accurate maps.
- Astronomy: Astronomers use it to calculate distances to stars and planets.
- Navigation: Sailors and pilots use it to find their way.
- Engineering: Engineers use it to design buildings and bridges.
There's also something called spherical trigonometry. This deals with triangles on the surface of a sphere, like the Earth. It's used in geodesy (measuring the Earth) and navigation.
Important Trigonometry Laws
These laws help us solve any triangle, not just right-angled ones.
Law of Sines
The Law of Sines helps us find missing sides or angles when we know certain pairs of angles and their opposite sides. 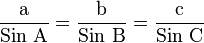
Law of Cosines
The Law of Cosines is like a super-powered Pythagorean theorem for any triangle. It helps find a missing side if you know two sides and the angle between them, or a missing angle if you know all three sides. 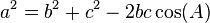
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Hipparchus is often called "the father of trigonometry."
See also
 In Spanish: Trigonometría para niños
In Spanish: Trigonometría para niños