V-2 facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Aggregat-4/Vergeltungswaffe-2 |
|
|---|---|

Peenemünde Museum replica of V-2
|
|
| Type | Single-stage ballistic missile |
| Place of origin | Nazi Germany |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1944–1952 |
| Used by | |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Peenemünde Army Research Center |
| Manufacturer | Mittelwerk GmbH |
| Unit cost | 100,000 RM January 1944, 50,000 RM March 1945 |
| Produced | 16 March 1942 – 1945 (Germany) Some assembled post-war |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 12,500 kg (27,600 lb) |
| Length | 14 m (45 ft 11 in) |
| Diameter | 1.65 m (5 ft 5 in) |
| Warhead | 1,000 kg (2,200 lb); Amatol (explosive weight: 910 kg) |
|
Detonation
mechanism |
Impact |
|
|
|
| Wingspan | 3.56 m (11 ft 8 in) |
| Propellant |
|
|
Operational
range |
320 km (200 mi) |
| Flight altitude |
|
| Maximum speed |
|
|
Guidance
system |
|
|
Launch
platform |
Mobile (Meillerwagen) |
The V-2 rocket (also known as Vergeltungswaffe 2) was the world's first ballistic missile. This means it was a rocket that followed a curved path to hit a target. It was also the first human-made object to fly into space!
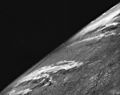
Many modern rockets are based on the V-2's design. The first successful launch happened on October 3, 1942, from Peenemünde, Germany. It reached an amazing height of 192 kilometers (about 119 miles).
The V-2 was created by Nazi Germany during World War II. It was used to bomb cities like London and Antwerp. The rocket traveled incredibly fast, about four times the speed of sound. This made it impossible to shoot down.
The first V-2 used as a weapon hit Paris on September 8, 1944. Another rocket hit London later that same day. Over 3,000 V-2 rockets were launched by the German military. These attacks sadly caused the deaths of many soldiers and civilians.
After the war, the winning countries took captured V-2 rockets. They used them to start their own space and missile programs. In the United States, German rocket scientists helped with this. They were led by Wernher von Braun, who had worked on the V-2 in Germany.
The first V-2 put together in the U.S. was launched in April 1946. This happened in White Sands, New Mexico. There were 66 V-2 rocket flights in the U.S., with the last one on October 29, 1951.
How the V-2 Rocket Was Developed
In the late 1920s, a young man named Wernher von Braun bought a book. It was called The Rocket into Interplanetary Spaces by Hermann Oberth. This book was about rockets and space travel.
Starting in 1930, von Braun studied at the Technical University of Berlin. There, he helped Oberth with tests on rockets that used liquid fuel. In 1933, he began working for the German Army. His job was to design and build rockets. The biggest and final rocket he worked on was called the A-4. Later, it became known as the V-2.
Building the Rockets
On December 22, 1942, Adolf Hitler ordered that the V-2 rockets be built in large numbers. Albert Speer, a high-ranking official, thought the final plans would be ready by July 1943. However, many problems still needed to be solved even by the autumn of 1943.
In May 1944, the Polish resistance group found a test rocket. They were able to transport it to the United Kingdom. This was part of a secret mission called Operation Most III.
Some people believed that Germany could have built 24,000 fighter planes instead of the V-2 rockets. The V-2s were not very accurate in hitting their targets.
Images for kids
-
A U.S. Army cut-away of the V-2
-
Rocket engine used by V-2, Deutsches Historisches Museum, Berlin (2014)
-
Operation Backfire V-2 rocket on Meillerwagen (SI Negative #76-2755).
See also
 In Spanish: Cohete V2 para niños
In Spanish: Cohete V2 para niños