Zeno of Elea facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Zeno of Elea
|
|
|---|---|

Portrait of Zeno of Elea by Jan de Bisschop (1628–1671)
|
|
| Born | c. 495 BC Elea
|
| Died | c. 430 BC (aged around 65) Elea or Syracuse
|
| Era | Pre-Socratic philosophy |
| Region | Western philosophy |
| School | Eleatic |
|
Main interests
|
Metaphysics, ontology |
|
Notable ideas
|
Zeno's paradoxes |
|
Influences
|
|
|
Influenced
|
|
Zeno of Elea (born around 495 BC, died around 430 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher. He lived in Magna Graecia, which was a Greek area in Southern Italy. Zeno was part of the Eleatic School, a group of thinkers started by his teacher, Parmenides.
Zeno is famous for his clever and confusing puzzles, known as Zeno's paradoxes. These paradoxes often tried to show that ideas about motion and many things existing at once were actually impossible. Famous philosophers like Plato and Aristotle even called him the inventor of the "dialectic," which is a way of finding truth by discussing different ideas.
Contents
Zeno's Life: What We Know
We don't know many exact facts about Zeno's life. Most of what we know comes from ancient writings.
Early Life and Teachers
One important source is a book by the philosopher Plato called Parmenides. This book describes a made-up visit Zeno and Parmenides supposedly made to Ancient Athens around 450 BC. At that time, Parmenides was about 65, Zeno was nearly 40, and Socrates was a very young man. Plato described Zeno as "tall and fair to look upon." He also said that Zeno was thought to be very close to Parmenides when he was young.
Another ancient writer, Diogenes Laërtius, wrote about Zeno in his book Lives and Opinions of Eminent Philosophers. He said that Zeno was the son of Teleutagoras. However, he was adopted by Parmenides. Diogenes Laërtius also mentioned that Zeno was very good at arguing both sides of any question.
Zeno and Tyrants
Some stories say that Zeno was involved in trying to overthrow a cruel ruler, or "tyrant," in his hometown of Elea. These stories are old and vary a lot.
- One story says Zeno was arrested and tortured. He supposedly refused to name his friends who were part of the plan.
- Another version claims that Zeno bit off the tyrant's ear or nose.
- A different story says he bit off his own tongue and spat it at the tyrant.
- Some accounts even say he was crushed to death.
These stories show that Zeno was seen as a brave person who stood up for his beliefs. However, it's hard to know exactly what happened.
Zeno's Writings
Plato tells us that Zeno wrote a book of paradoxes when he was young. Sadly, this book has been lost over time. Plato said Zeno's book was brought to Athens during his visit. Zeno himself supposedly said he wrote the book to defend Parmenides' ideas. He also claimed it was published without his permission.
The main information we have about Zeno's arguments about motion comes from Aristotle's book Physics. Another important source is a commentary on Aristotle's work by Simplicius of Cilicia.
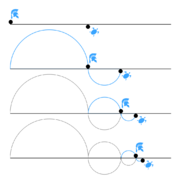
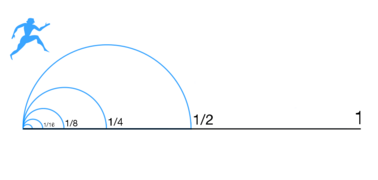
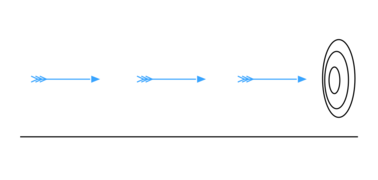
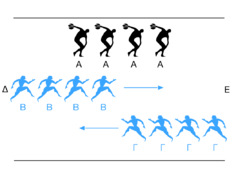
Zeno's Famous Puzzles: The Paradoxes
Zeno's paradoxes have confused and fascinated thinkers for over 2,000 years. They have challenged philosophers, mathematicians, and scientists. An ancient writer named Proclus said Zeno created "not less than forty arguments" that showed contradictions. Today, we only know about nine of them. The most famous ones are his arguments against motion. These were described by Aristotle.
Zeno's Lasting Impact
Zeno's arguments are thought to be some of the first examples of a special way of proving things. This method is called reductio ad absurdum. This Latin phrase means "to reduce to the absurd." It's a way of showing that an idea is false by proving that it leads to a ridiculous or impossible conclusion. Parmenides is believed to be the first to use this type of argument.
This method of argument became known as the epicheirema. Aristotle described it as a "dialectical syllogism." It's a way to break down an opponent's argument by showing its flaws. Zeno used this method so much that a few centuries later, the philosopher Seneca the Younger joked about it. He said, "If I agree with Parmenides, only the One is left; if I agree with Zeno, not even the One is left." This meant Zeno's arguments could make even simple ideas seem to disappear!

The famous mathematician Bertrand Russell called Zeno's paradoxes "immeasurably subtle and profound." This shows how important and deep Zeno's ideas were.
Zeno is also seen as one of the first philosophers to think about the idea of mathematical infinity. This is a very complex idea that is still studied today.
See also
 In Spanish: Zenón de Elea para niños
In Spanish: Zenón de Elea para niños
- Incommensurable magnitudes
- List of speakers in Plato's dialogues
 | Aurelia Browder |
 | Nannie Helen Burroughs |
 | Michelle Alexander |