Acariformes facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Acariformes |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
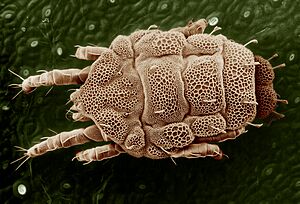
| Trombidium holosericeum (Trombidiformes: Trombidiidae) |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Chelicerata |
| Class: | Arachnida |
| Subclass: | Acari |
| Superorder: | Acariformes Zakhvatkin, 1952 |
| Clades and orders | |
|
|
Acariformes are a huge group of tiny creatures called mites. They are also known as Actinotrichida. Mites are small arachnids, related to spiders and ticks. Acariformes are the most diverse group of mites. Scientists have found over 32,000 different kinds, but they think there could be hundreds of thousands more! These tiny animals live in many places around the world.
Contents
What are Acariformes?
Acariformes are one of the two main types of mites. The other main group is called Parasitiformes. Acariformes are incredibly varied. They live in almost every habitat on Earth. You can find them in soil, water, plants, and even on other animals.
Main Groups of Acariformes
Scientists divide Acariformes into two big groups: Sarcoptiformes and Trombidiformes. There was also a smaller, older group called Endeostigmata. These Endeostigmata mites are very tiny. They have soft bodies and eat things like fungi, algae, and small invertebrates. These small invertebrates include nematodes and rotifers.
Ancient History: Acariformes Fossils
Acariformes have been around for a very long time. The oldest known fossils of these mites were found in Scotland. They came from a place called the Rhynie chert. These fossils are about 410 million years old! This means Acariformes lived during the early Devonian period. One of the largest fossil acariform mites ever recorded was Immensmaris chewbaccei. It lived during the Cretaceous period. This mite was over 8 millimeters long. Its body was quite big for a mite.
Different Lifestyles of Acariformes
Acariformes mites have many different ways of living. They can eat various foods. Some are helpful, while others can be pests.
Sarcoptiformes: Tiny Eaters and Parasites
The Sarcoptiformes group mostly eats solid food. Many are microherbivores, meaning they eat tiny plants. Others are fungivores, eating fungi. Some are detritivores, which means they eat decaying matter. This helps to clean up the environment.
Some Sarcoptiformes, like certain Astigmatina, live with vertebrates. Vertebrates are animals with backbones. They also live with insects that build nests. Famous examples include house dust mites. These mites live in our homes. Other Sarcoptiformes cause skin problems. These include scab mites and mange mites. Some also live on stored food products or on feathers and fur.
Trombidiformes: Plant Pests and Predators
The Trombidiformes group is well-known for causing problems for plants. Many species are plant parasites. They can damage crops and other plants. For example, spider mites are common plant pests. Eriophyidae mites also harm plants.
However, not all Trombidiformes are pests. Many species are predators. They hunt and eat other small creatures. Some also eat fungi. You might have seen some of the most noticeable Trombidiformes. These are the bright red velvet mites. They are relatively large and easy to spot. They belong to the family Trombidiidae.
Interestingly, some mites in the Oribatida group are important for certain animals. Small poison dart frogs, like the strawberry poison-dart frog, eat these mites. The mites contain special chemicals called alkaloids. These chemicals help the frogs create their strong poisons. Frogs that do not eat these mites do not develop the same poisons.
How Acariformes Reproduce
Most Acariformes mites reproduce sexually. This means they need a male and a female partner. However, some species have found other ways to reproduce. These species use a method called parthenogenesis. Parthenogenesis means they can reproduce without a partner. A female can produce offspring on her own.
Scientists once thought that species reproducing this way did not last long. But some groups of parthenogenetic Oribatida mites are very old. They likely appeared between 400 and 300 million years ago. This shows that reproduction without a partner can be very successful. In some cases, species that reproduce without a partner can even go back to sexual reproduction.
Examples of Acariformes
Here are some examples of Acariformes mites:
- Eriophyidae: These are plant parasites. An example is Acalitus essigi, known as the redberry mite.
- Sarcoptiformes
- Cheese mites: Found in cheese.
- Epidermoptidae: A family of mites.
- Gastronyssidae: Another family of mites.
- Sarcoptes scabiei: This mite causes scabies in humans.
- Trombidiformes
- Demodecidae: This family includes Demodex mites. These mites live in hair follicles.
- Erythraeidae: A family of mites.
- Labidostommatidae: Another family of mites.
- Polydiscia deuterosminthurus: A specific type of mite.
- Smarididae: A family of mites.
- Spider mites: Common plant pests. An example is Tetranychus urticae.
- Tarsonemidae: Many of these are plant pests. An example is Acarapis woodi.
- Tydeidae: A family of mites.