Afghan conflict facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Afghan conflict |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Cold War (1978–1991) and the War on Terror (2001–2021) | |||||
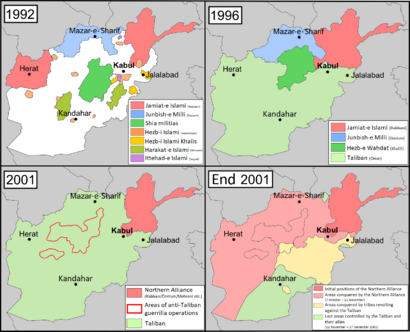 Development of the Afghan Civil War from the Peshawar Accord in April 1992 to the Battle of Tora Bora in December 2001 |
|||||
|
|||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||
| 1,405,111–2,584,468 | |||||
The Afghan conflict, also known as the Afghan crisis, describes a long period of wars and instability in Afghanistan. This conflict has kept the country in a state of fighting since the 1970s. Afghanistan became unstable after the government was overthrown in 1973. This event ended a peaceful time under King Mohammed Zahir Shah, who ruled for nearly 40 years.
The first major war began with the Saur Revolution in 1978. This revolution replaced the Republic of Afghanistan with the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan. A lot of fighting followed, leading the Soviet Union to send its military to help the new government. This started the Soviet–Afghan War in the 1980s.
After the Soviet Union left Afghanistan at the end of the Cold War, groups called mujahideen continued to fight the government. The government fell in 1992. The mujahideen groups could not agree on how to rule, so they started fighting each other. This led to a civil war with much violence. By 1996, a group called the Taliban, with support from Pakistan, took control of Kabul and most of the country. They created the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, which few countries recognized. However, a group called the Northern Alliance still controlled parts of northern Afghanistan, and fighting continued.
After the September 11 attacks in the United States, an American-led invasion removed the Taliban government in 2001. A new government was set up. For almost 20 years, the Taliban fought against this new government and a group of countries led by NATO. In 2021, after NATO forces left, the Taliban took control of most of Afghanistan again. Even though the main war has ended, some fighting continues. This includes clashes between the Taliban and a local branch of the Islamic State, as well as a group called the National Resistance Front.
Key Events in the Afghan Conflict
This section explains the most important events that shaped the long conflict in Afghanistan.
The Saur Revolution (1978)
- This event saw the Republic of Afghanistan and its leader, Mohammed Daoud Khan, overthrown.
- The People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) took over.
- They set up the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan, a socialist state that was close to the Soviet Union.
The Soviet–Afghan War (1979–1989)
- The Soviet Armed Forces sent troops to support the PDPA government against widespread rebellions.
- The main fight was between the Soviet-Afghan alliance and the Afghan mujahideen.
- The mujahideen received help from countries like the United States, the United Kingdom, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, China, and Iran.
- The war ended when the Soviet Union pulled out its troops in 1989.
Afghan Civil War (1989–1992)
- This was a continuation of the conflict between the Afghan government and the mujahideen.
- This time, Soviet forces were not directly involved.
- The Soviet Union still gave money to the Afghan government.
- The United States and Pakistan continued to support the mujahideen groups.
- The Democratic Republic of Afghanistan lasted until 1992, when the mujahideen took control of Kabul.
- They then formed the Islamic State of Afghanistan (ISA).
Afghan Civil War (1992–1996)
- This war started because different mujahideen groups began fighting against the new Islamic State of Afghanistan.
- Groups like Hezb-e Islami Gulbuddin, the Taliban, and al-Qaeda (supported by Pakistan) were involved.
- Other groups like Hezb-e Wahdat (supported by Iran) and Junbish-i Milli Islami (supported by Uzbekistan) also fought.
- Groups loyal to the Islamic State of Afghanistan received help from Saudi Arabia.
- The war ended in 1996 when the Taliban captured Kabul and most of the country.
- They then established the first Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan (IEA).
Afghan Civil War (1996–2001)
- This was a continuation of the war between groups loyal to the ISA and the Taliban-ruled IEA.
- The ISA loyalists formed the Northern Alliance. This group included Hezb-e Wahdat and Junbish-i Milli Islami, who had previously fought against the ISA.
- During this time, al-Qaeda increased its attacks against the United States.
- These attacks led to the September 11 attacks.
- After 9/11, the IEA lost almost all international support from Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates.
War in Afghanistan (2001–2021)
- This war began on October 7, 2001, with the United States' invasion of Afghanistan.
- The Taliban government was overthrown, and an internationally recognized Islamic Republic of Afghanistan was set up.
- The war turned into a long Taliban insurgency, where the Taliban fought against the Afghan government and NATO-led troops.
- Other groups like al-Qaeda and the Islamic State – Khorasan Province also fought.
- Talks between the Taliban and the United States led to an agreement for American and NATO troops to leave.
- As troops withdrew, the 2021 Taliban offensive took place.
- The Islamic Republic fell, and the Taliban established the second Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan.
Islamic State–Taliban Conflict (2015–present)
- This conflict started in 2015, during the post-9/11 war.
- Taliban members who disagreed with the main group formed a local branch of the Islamic State.
- This group attacked both the Taliban and NATO troops, but mostly targeted civilians.
- This fighting is still going on.
Republican Insurgency in Afghanistan (2021–present)
- This began in 2021 when forces loyal to the fallen Islamic Republic formed the National Resistance Front of Afghanistan.
- They gathered in the Panjshir Valley.
- Even though they are seen by some as the rightful government, they have not received foreign support.
- Taliban forces captured the Panjshir Valley in September 2021.
- Leaders of the National Resistance Front went to Tajikistan.
- Small groups of the National Resistance Front continue to fight the Taliban in Panjshir Province and Baghlan Province.
By 2014, it was estimated that between 1,405,111 and 2,084,468 people had been killed throughout the entire Afghan conflict.
See also
 In Spanish: Conflicto en Afganistán para niños
In Spanish: Conflicto en Afganistán para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |

