History of Afghanistan facts for kids
Afghanistan is a country with a very long and interesting history. Many powerful empires and kingdoms have risen and fallen here. Some of these include the Kushans, Ghaznavids, Mughals, and later the Hotak and Durrani dynasties. These last two helped create the modern country we know today.
Over thousands of years, many cities in Afghanistan were once the capitals of these great empires. Places like Balkh, Kabul, Herat, Ghazni, and Kandahar have all been important centers of power.
People have lived in Afghanistan for a very long time. The ancient Iranian peoples helped make Indo-Iranian languages common in the area. Because Afghanistan has successfully fought off foreign control in the past, especially in the 1800s and 1900s, it's sometimes called the "graveyard of empires."
Contents
Early History of Afghanistan
Prehistoric Times and Ancient Civilizations
Archaeological digs show that people lived in what is now Afghanistan at least 50,000 years ago. Farming communities here were among the first in the world. Many believe Afghanistan's ancient sites are as historically important as those in Egypt.
In the 20th century, discoveries showed that Afghanistan has always been connected to its neighbors through culture and trade. Tools and items from the Stone Age, Bronze Age, and Iron Age have been found. It's thought that cities began to appear around 3000 BCE. The ancient city of Mundigak, near Kandahar, was a key part of the Helmand culture.
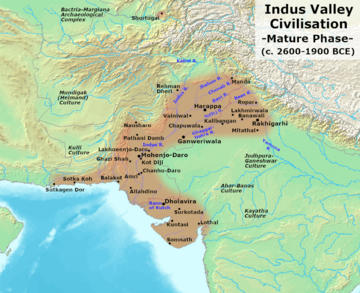
More recently, it was found that the Indus Valley Civilization reached into modern-day Afghanistan. An Indus Valley site was discovered on the Oxus River at Shortugai in northern Afghanistan. This shows Afghanistan was part of this ancient civilization.
After 2000 BCE, groups of semi-nomadic people from Central Asia moved south into Afghanistan. Many of these were Indo-European-speaking Indo-Iranians. These tribes later traveled further into South Asia, Western Asia, and Europe. At that time, the region was called Ariana.
By the mid-6th century BCE, the Achaemenid Empire took control of areas like Arachosia, Aria, and Bactria. An old writing on the tomb of Darius I of Persia lists the Kabul Valley as one of the 29 countries he conquered. The region of Arachosia, around Kandahar, was mostly Zoroastrian and helped spread this religion to Persia. Some people think it was the "second home" of Zoroastrianism.
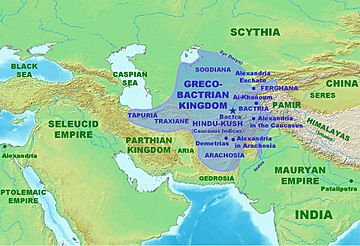
Alexander the Great and his forces arrived in Afghanistan in 330 BCE. After Alexander's short rule, the Seleucid Empire controlled the region. But in 305 BCE, they gave much of it to the Maurya Empire as part of a peace deal. The Mauryans ruled the area south of the Hindu Kush mountains until about 185 BCE. After their power weakened, the Greco-Bactrians took control again. Much of this area then became part of the Indo-Greek Kingdom. They were later defeated by the Indo-Scythians in the late 2nd century BCE.
The Silk Road became important in the first century BCE. Afghanistan became a busy trading hub, with routes connecting to China, India, and Persia. Goods like Chinese silk, Persian silver, and Roman gold were traded. Afghanistan also mined and traded lapis lazuli stones, mostly from the Badakhshan region.
During the first century BCE, the Parthian Empire took over the region. Later, in the first century CE, the large Kushan Empire, based in Afghanistan, became a big supporter of Buddhism. This made Buddhism popular throughout the area. The Kushans were later defeated by the Sassanids in the 3rd century CE. Over the next few centuries, other groups like the Kidarites, Hephthalites, and Turk Shahi ruled the region. Much of northeastern and southern Afghanistan remained strongly Buddhist.
Medieval History of Afghanistan
The Spread of Islam
Arab Muslims brought Islam to Herat and Zaranj in 642 CE. They began spreading eastward. Some local people accepted Islam, while others fought against it. Before Islam, the region had many different beliefs, including Zoroastrianism, Buddhism, Hinduism, Christianity, and Judaism. People often blended these beliefs. For example, some people supported Buddhism but also worshipped local Iranian gods.
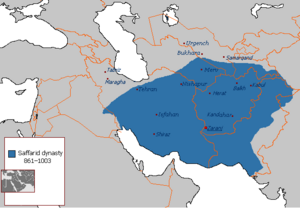
The Zunbils and Kabul Shahi were first conquered in 870 CE by the Saffarid Muslims. Later, the Samanids spread Islamic influence south of the Hindu Kush. It is said that Muslims and non-Muslims lived together in Kabul before the Ghaznavids came to power in the 10th century.
By the 11th century, Mahmud of Ghazni defeated the remaining Hindu rulers. He helped spread Islam across the wider region, except for Kafiristan. Mahmud made Ghazni an important city and supported thinkers like the historian Al-Biruni and the poet Ferdowsi. The Ghaznavid dynasty was later overthrown by the Ghurids in 1186. The Ghurids ruled Afghanistan for less than a century before being conquered by the Khwarazmian dynasty in 1215.
Mongol Rule and Later Empires
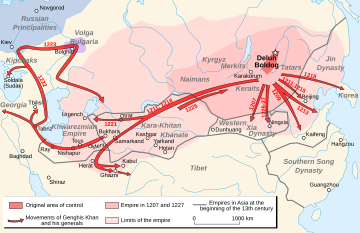
In 1219 CE, Genghis Khan and his Mongol army invaded the region. His troops are said to have destroyed cities like Herat, Balkh, and Bamyan. The damage caused by the Mongols forced many people to return to a farming way of life. Mongol rule continued with the Ilkhanate in the northwest.
Later, Timur (also known as Tamerlane) established the Timurid Empire in 1370. Under the rule of Shah Rukh, the city of Herat became a center of a cultural rebirth, similar to the Italian Renaissance in Florence.
In the early 16th century, Babur arrived from Ferghana and captured Kabul. Babur went on to conquer the Afghan Lodi dynasty in India. Between the 16th and 18th centuries, parts of Afghanistan were ruled by the Uzbek Khanate of Bukhara, the Iranian Safavids, and the Indian Mughals. During this time, the northwestern part of Afghanistan was known as Khorasan. Even up to the 19th century, many locals called their country "Khorasan."
Modern History of Afghanistan
The Hotak Dynasty
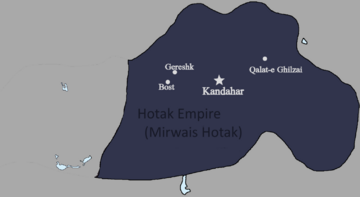
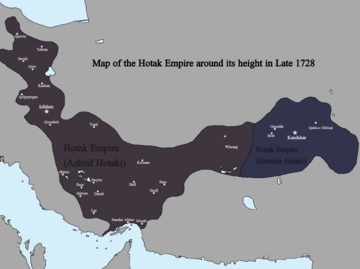
In 1709, Mirwais Hotak, a local leader, successfully rebelled against the Safavids. He defeated the Safavid governor of Kandahar and created his own kingdom. Mirwais died in 1715. His son, Mahmud, later led campaigns into Iran. In 1722, Mahmud led the Afghan army to the Persian capital of Isfahan, captured the city, and declared himself King of Persia. However, the Afghan dynasty was removed from Persia by Nader Shah in 1729.
End of the Hotak Dynasty
In 1738, Nader Shah and his forces captured Kandahar, the last Hotak stronghold. Soon after, Persian and Afghan forces invaded India. Nader Shah, along with his young commander Ahmad Shah Durrani, plundered Delhi. Nader Shah was killed in 1747.
Rise of the Durrani Empire
After Nader Shah's death in 1747, Ahmad Shah Durrani returned to Kandahar. He was chosen as the new leader by the Pashtun tribes. Starting in 1747, Ahmad Shah led many campaigns against the Mughal Empire and the Maratha Empire. He captured Kabul and Peshawar. He also conquered Herat in 1750 and Kashmir in 1752.
Ahmad Shah invaded India eight times during his rule. He saw Afghanistan as needing to expand and gain wealth from its neighbors. His first invasion in 1748 led to his army sacking Lahore. He was defeated in the Battle of Manupur (1748) and had to retreat. But he returned in 1749 and captured the area around Lahore and Punjab. From 1749 to 1767, Ahmad Shah led six more invasions. The most important was the Third Battle of Panipat, which stopped the expansion of the Maratha Empire in northern India.
After Ahmad Shah Durrani
Ahmad Shah Durrani died in October 1772. A civil war followed as his sons fought for power. His chosen successor, Timur Shah Durrani, became king after defeating his brother.
Timur Shah Durrani became king in November 1772. He worked to strengthen his own power and moved the capital from Kandahar to Kabul. Kabul was a better central location for the empire. Timur Shah fought many rebellions to keep the empire together. He also led successful campaigns against the Sikhs in Punjab. Timur Shah died in May 1793. He had many sons, which led to more civil wars over who would rule next.
His son, Zaman Shah Durrani, became king. His brothers, Mahmud Shah Durrani and Humayun Mirza, rebelled against him. Zaman Shah defeated Humayun and forced Mahmud Shah to be loyal. Zaman Shah led three campaigns into Punjab, capturing Lahore twice. But he had to retreat each time due to threats from Iran. Zaman Shah's rule ended when Mahmud Shah Durrani overthrew him. Mahmud Shah was then overthrown by his brother Shah Shuja Durrani in 1803. Shah Shuja tried to unite the empire but was defeated by Mahmud Shah in 1809, who became king again.
The Barakzai Dynasty and British Wars
By the early 1800s, the Afghan empire was threatened by the Persians in the west and the Sikhs in the east. Fateh Khan Barakzai, a tribal leader, put his brothers in powerful positions across the empire. In 1818, Fateh Khan was murdered by Mahmud Shah Durrani. This led to a civil war between the Sadozai and Barakzai families.
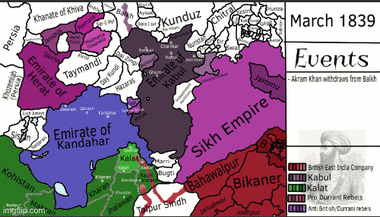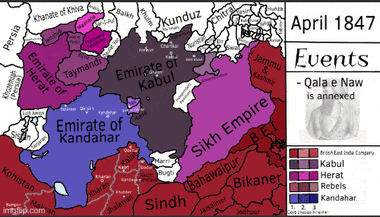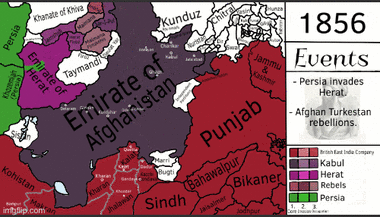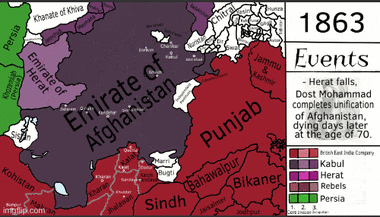
During this time, Afghanistan broke into many smaller states. The most important was the Emirate of Kabul, ruled by Dost Mohammad Khan starting in 1826. He was later given the title of "Amir al-Mu'minin" for fighting against the Sikh Empire. With the fall of the Durrani Empire, areas like Punjab and Kashmir were lost to Ranjit Singh, the ruler of the Sikh Empire.
In 1837, Dost Mohammad Khan tried to retake Peshawar. His son, Wazir Akbar Khan, led a large force but failed to capture the Jamrud Fort. However, they did kill the Sikh Commander. Around this time, the British were expanding from the east. This led to the First Anglo-Afghan War, a major conflict during "The Great Game" (a rivalry between Britain and Russia).
In 1839, a British force invaded Afghanistan. They captured Kandahar and Kabul. They replaced Dost Mohammad with the former Durrani ruler Shah Shuja Durrani, who was a puppet ruler. After an uprising where Shah Shuja was killed, the British forces suffered a terrible defeat in 1842, losing many soldiers. The British then gave up trying to control Afghanistan.
This allowed Dost Mohammad Khan to return as ruler. He spent most of his reign uniting the parts of Afghanistan that were lost during the civil war (1793–1863). He had friendly relations with the British. Dost Mohammad died in 1863. His successors fought for the throne in another civil war. Sher Ali Khan won this war.
In 1878, the British returned in the Second Anglo-Afghan War because they were worried about Russian influence. Britain gained control of Afghanistan's foreign relations in 1879, making it a British Protected State. In 1893, Amir Abdur Rahman Khan signed an agreement that divided the Pashtun and Baloch territories with the Durand Line. This line is still the border between Pakistan and Afghanistan today. Abdur Rahman Khan was known as the "Iron Amir" because he was very strict. He prevented railways and telegraph lines from being built, seeing them as threats. He died in 1901, and his son, Habibullah Khan, became king.
During World War I, Afghanistan remained neutral. Habibullah Khan was killed in 1919. His son, Amanullah Khan, took power. Amanullah Khan started the Third Anglo-Afghan War by invading British India.

After the war ended in 1919, Emir Amanullah Khan declared Afghanistan a fully independent state. He worked to end his country's isolation by forming relationships with other countries, especially the Soviet Union and Germany. He declared himself King of Afghanistan in 1926. After traveling in Europe, he introduced reforms to modernize Afghanistan. His wife, Queen Soraya, was important in fighting for women's education. Slavery was also ended in 1923.
Some of these reforms, like ending the traditional burqa for women and opening co-educational schools, upset many tribal and religious leaders. This led to the Afghan Civil War (1928–1929). King Amanullah gave up his throne in 1929, and Kabul fell to rebel forces. Mohammed Nadir Shah, Amanullah's cousin, defeated the rebels and became King. He slowed down the modernization reforms. He was killed in 1933 by a 15-year-old student.
Mohammed Zahir Shah, Nadir Shah's 19-year-old son, became king in 1933 and ruled until 1973. During his reign, Afghanistan joined the League of Nations in 1934. The 1930s saw improvements in roads, banks, and education. Afghanistan also built close ties with countries like Germany, Italy, and Japan.
Recent History of Afghanistan

Until 1946, King Zahir ruled with the help of his uncle, who was the prime minister. Another uncle, Shah Mahmud Khan, became prime minister in 1946 and allowed more political freedom. But he stopped this when it went too far. In 1953, Mohammed Daoud Khan, the King's cousin, became prime minister. He pushed for social reforms and closer ties with the Soviet Union.
Afghanistan remained neutral during World War II and the Cold War. However, it benefited from the Cold War rivalry. Both the Soviet Union and the United States gave aid to Afghanistan, building highways, airports, and other important structures. In 1973, while the King was in Italy, Daoud Khan led a peaceful coup and became the first president of Afghanistan, ending the monarchy.
Communist Rule and Soviet War

In April 1978, the communist People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) took power in a bloody coup. This event, called the Saur Revolution, started a series of events that changed Afghanistan from a peaceful country into a place of conflict. The PDPA introduced reforms that caused strong opposition and brutally punished those who disagreed. This led to a civil war by 1979.
Guerrilla fighters called mujahideen fought against the government. This quickly became a proxy war. Pakistan secretly trained these rebels, and the United States supported them through Pakistan. The Soviet Union sent military advisors to help the PDPA government.
In September 1979, the PDPA leader was killed by another party member, Hafizullah Amin, who became the new leader. The situation worsened under Amin. The Soviet Army invaded in December 1979, killing Amin. A new Soviet-backed government was put in place. Soviet troops were sent in large numbers, starting the Soviet–Afghan War.
The United States, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, and China continued to support the rebels, sending billions of dollars in money and weapons. The war lasted nine years and caused the deaths of between 562,000 and 2 million Afghans. About 6 million people fled Afghanistan, mostly to Pakistan and Iran. Many villages were destroyed, and millions of landmines were planted. After the Soviet withdrawal, the civil war continued until the communist government fell in 1992.
The war changed Afghan society. It led to a heavily armed society where powerful warlords became more important than traditional leaders.
Conflict After the Cold War
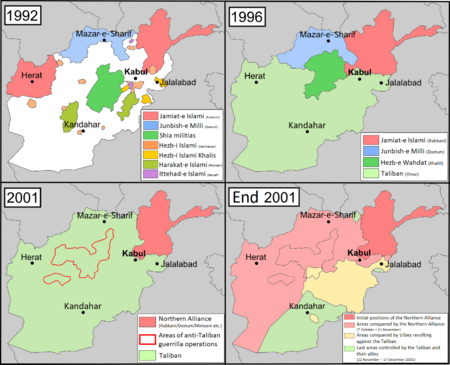
Another civil war began after a weak coalition government was formed by different mujahideen groups. There was a lot of chaos and fighting, and Kabul was heavily damaged. The Taliban appeared in September 1994. They were a group of students from Islamic schools in Pakistan, and they soon got military support from Pakistan.
The Taliban took control of Kandahar that year. They conquered more areas until they drove the government out of Kabul in 1996. They then set up an emirate. The Taliban were criticized internationally for their strict rules based on their interpretation of Islamic law, which led to harsh treatment of many Afghans, especially women. They also committed massacres and destroyed fertile land.
After the Taliban took Kabul, Ahmad Shah Massoud and Abdul Rashid Dostum formed the Northern Alliance to fight them. By 2000, the Northern Alliance only controlled 10% of the country. On September 9, 2001, Massoud was killed. Around 400,000 Afghans died in these internal conflicts between 1990 and 2001.
US Invasion and Islamic Republic
In October 2001, the United States invaded Afghanistan. They wanted to remove the Taliban from power because the Taliban refused to hand over Osama bin Laden, who was responsible for the September 11 attacks. Most Afghans supported the American invasion. US and UK forces bombed al-Qaeda training camps and worked with the Northern Alliance to end the Taliban rule.
In December 2001, after the Taliban were overthrown, an interim government was formed under Hamid Karzai. The International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) was created by the UN Security Council to help the new government and provide security. At this time, after two decades of war and a severe famine, Afghanistan had very high rates of infant deaths, low life expectancy, and damaged infrastructure. Many foreign countries began to provide aid to rebuild the country.
Meanwhile, Taliban forces started to regroup in Pakistan and launched an insurgency to regain control. Over the next decade, ISAF and Afghan troops fought many battles against the Taliban but could not fully defeat them. Afghanistan remained one of the poorest countries due to a lack of foreign investment, government corruption, and the ongoing Taliban insurgency.
Karzai tried to unite the country, and the Afghan government built some democratic structures, adopting a constitution in 2004. They tried to improve the economy, healthcare, education, and transport. ISAF forces also trained the Afghan National Security Forces. After 2002, almost five million Afghans who had fled the country returned home. The number of NATO troops in Afghanistan reached its highest point in 2011.
In September 2014, Ashraf Ghani became president after an election. This was the first time in Afghanistan's history that power was transferred democratically. On December 28, 2014, NATO officially ended its combat operations and gave full security responsibility to the Afghan government. Thousands of NATO troops stayed to train and advise Afghan forces and continue fighting the Taliban.
On February 19, 2020, a deal was made between the US and the Taliban in Qatar. This deal was a key reason for the collapse of the Afghan National Security Forces. After the deal, the US greatly reduced its air attacks, which took away a major advantage from the Afghan forces. This led to the Taliban taking over Kabul.
Second Taliban Era
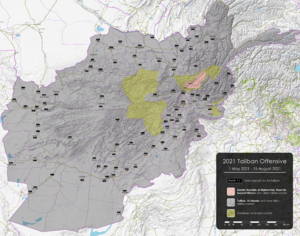
On April 14, 2021, NATO announced that its troops would start leaving Afghanistan by May 1. Soon after NATO troops began to withdraw, the Taliban launched an offensive against the Afghan government. They quickly advanced as Afghan government forces collapsed. The Taliban captured the capital city of Kabul on August 15, 2021, after taking control of most of Afghanistan. Many foreign diplomats and Afghan government officials, including President Ashraf Ghani, were evacuated. Many Afghan civilians also tried to flee.
An unofficial "coordination council" was formed to transfer state institutions to the Taliban. On August 17, the first vice president, Amrullah Saleh, declared himself caretaker president and announced an anti-Taliban front in the Panjshir Valley. However, by September 6, the Taliban had taken control of most of Panjshir Province. Saleh and Massoud later fled to Tajikistan.
Between 2001 and 2021, over 176,000 people were killed in the conflict, including many civilians. After the 2001 invasion, more than 5.7 million refugees returned to Afghanistan. However, in 2021, 2.6 million Afghans were still refugees, mainly in Iran and Pakistan, and another 4 million were displaced within the country.
The Taliban government is led by Hibatullah Akhundzada and acting prime minister Hasan Akhund, who took office on September 7, 2021. Akhund is one of the Taliban's founders. A new, all-male cabinet was formed. The United Nations did not recognize the previous Taliban government and worked with the government in exile instead.
Western nations stopped most of their aid to Afghanistan after the Taliban took over in August 2021. The World Bank and International Monetary Fund also stopped payments. More than half of Afghanistan's 39 million people faced severe food shortages in October 2021. Human Rights Watch reported in November 2021 that Afghanistan was facing widespread famine due to an economic crisis.
Although the main war ended in 2021, armed conflict continues in some areas. There is fighting between the Taliban and a local branch of the Islamic State, as well as an anti-Taliban insurgency. A year after the Taliban took power, former president Hamid Karzai said that while there was more stability and security, Afghanistan still needed a government that all its people felt represented by. He also said the country's economy was a "disaster."
See also
 In Spanish: Historia de Afganistán para niños
In Spanish: Historia de Afganistán para niños
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |