Lahore facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Lahore
|
|||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Nickname(s): | |||||||||||||||||
|
Location in Punjab, Pakistan
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Country | |||||||||||||||||
| Province | |||||||||||||||||
| Division | Lahore | ||||||||||||||||
| District | Lahore | ||||||||||||||||
| Founded | Between 1st and 7th centuries CE | ||||||||||||||||
| City status | 1040 | ||||||||||||||||
| Capital status | 25 June 1206 27 May 1586 12 April 1801 |
||||||||||||||||
| Metropolitan status | 3 February 1890 | ||||||||||||||||
| Metropolitan seat | Lahore Town Hall | ||||||||||||||||
| Zones |
10
|
||||||||||||||||
| Government | |||||||||||||||||
| • Type | Metropolitan corporation | ||||||||||||||||
| • Body | Lahore Metropolitan Corporation | ||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||
| • Metro | 1,772 km2 (684 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||
| Area rank |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Highest elevation | 231 m (758 ft) | ||||||||||||||||
| Lowest elevation | 196 m (643 ft) | ||||||||||||||||
| Population
(2023)
|
|||||||||||||||||
| • Megacity | 13,004,135 | ||||||||||||||||
| • Rank |
|
||||||||||||||||
| • Metro density | 7,339/km2 (19,010/sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||
| • Language(s) | |||||||||||||||||
| • Dialect | Majhi (native & dominant) | ||||||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | General: Lahori English: Lahorite |
||||||||||||||||
| Religion (2017) | |||||||||||||||||
| Time zone | UTC+5 (PKT) | ||||||||||||||||
| Postal code |
53XXX – 55XXX
|
||||||||||||||||
| Dialing code | 042 | ||||||||||||||||
| Vehicle registration |
List
|
||||||||||||||||
| GDP (PPP) | $84 billion (2019) | ||||||||||||||||
| International airport | Allama Iqbal International Airport (LHE) | ||||||||||||||||
| Rapid Transit | Lahore Metrobus | ||||||||||||||||
| Abbreviation | LHR/ایل ایچ آر | ||||||||||||||||
| Patron saint | Ali al-Hujwiri | ||||||||||||||||
| HDI (2018) | 0.877 (very high) · 3rd | ||||||||||||||||
| Growth | |||||||||||||||||
| Literacy (2023) | 81% | ||||||||||||||||
| Constituencies in the National Assembly |
14 / 336
|
||||||||||||||||
| Sex ratio (2017) | 912 ♀/1000 ♂ | ||||||||||||||||
| Climate | BSh | ||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
Lahore is a very important city in Pakistan. It is the capital and largest city of the Punjab province. Lahore is the second-largest city in Pakistan, right after Karachi. It is also one of the 30 largest cities in the world, with over 14 million people.
Lahore is a big center for business, education, and culture in Pakistan. It has been the historic capital and cultural heart of the wider Punjab region. Many people think of Lahore as a modern and welcoming city. It is often called The Heart of Pakistan, the Paris of the East, and the City of Gardens. UNESCO has also named it a City of Literature.
The city of Lahore has a very long history, going back thousands of years. It became very important in the 10th century with the building of its Walled City. Lahore was the capital for many powerful empires, like the Mughal Empire. During the Mughal rule, from the late 1500s to the early 1700s, Lahore was one of the biggest cities in the world.
Later, Lahore was taken over by the British Raj in 1849. It became the capital of British Punjab. Lahore played a key role in the movements for independence from British rule. After Pakistan became a country in 1947, Lahore was made the capital of its Punjab province.
Lahore is located in central-eastern Punjab, along the Ravi River. It is the largest city in the world where people speak Punjabi. Lahore has a strong influence on Pakistan's culture and politics. It is a major center for publishing and literature. The city also has many top universities and is home to Pakistan's Punjabi film industry. It is also famous for Qawwali music.
Many tourists visit Lahore. Popular places include the Walled City of Lahore, the famous Badshahi Mosque and Wazir Khan Mosque, and several Sikh and Sufi religious sites. The Lahore Fort and Shalimar Gardens are also here, and both are UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The exact origin of Lahore's name is not fully known. Early historians wrote the city's name in different ways, like Luhawar or Lāhanūr.
One idea is that the name Lahore comes from Ravāwar. This name might be linked to the Ravi River. Another idea is that it comes from Lohar, which means "blacksmith".
There is also a legend that says Lahore's name comes from Lavpur, meaning "City of Lava". Lava was a son of Sita and Rama in an ancient story. The legend says he founded the city.
A Look at Lahore's Past
Lahore's early history is not very clear. Ancient records do not mention a city here when Alexander the Great visited in 326 BCE. This suggests Lahore might not have been a big city back then. However, a Chinese traveler named Xuanzang described a large, rich city in this area around 630 CE. This city might have been Lahore.
The first time Lahore is mentioned by name is in a book from 982 CE called Hudud al-'Alam. It describes Lahore as a town with "impressive temples, large markets and huge orchards".
Lahore became a truly important city in the 11th century. This was during the time of the Sufi saint Ali Hujwiri.
Medieval Times
Sultan Mahmud of the Ghaznavid Empire took control of Lahore between 1020 and 1027. He made Malik Ayaz its governor. Malik Ayaz helped rebuild the city after the invasion. He also built city walls and a strong fort. Lahore became a center for culture and learning, especially known for its poetry.
In 1152, Lahore officially became the eastern capital of the Ghaznavid Empire. When their main city, Ghazni, fell in 1163, Lahore became the only capital.
Delhi Sultanate and Mongol Invasions
In 1186, the Ghurid ruler Muhammad captured Lahore. After his death in 1206, Lahore became an important city for the Mamluk dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate. Many poets and scholars came to Lahore during this time.
However, Lahore faced many attacks from the Mongols. The city was badly damaged in 1241 by the Mongol army. Because of these invasions, Lahore became a frontier city. Its main administrative center moved south to Dipalpur.
Lahore had short periods of growth under different rulers, but it was often attacked. By 1398, when the Mongol conqueror Timur captured the city, it was no longer wealthy.
Mughal Empire's Golden Age
The Mughal Empire brought Lahore its most prosperous time. Many beautiful Mughal buildings in Lahore were built during this period.
Emperor Akbar's Contributions
In 1584, Emperor Akbar made Lahore the Mughal capital. He rebuilt the city's old fort, which is now the Lahore Fort. Akbar also rebuilt the city walls and expanded them. He set up the Akbari Mandi grain market, which is still used today. Many of Lahore's old mansions, called havelis, date from Akbar's time.
Jahangir and Shah Jahan's Legacy
Emperor Jahangir ruled in the early 1600s. Lahore's markets were busy and full of goods from all over. Jahangir chose to be buried in Lahore. His wife, Nur Jahan, built his tomb in 1637. Her own tomb is also nearby.
Jahangir's son, Shah Jahan, was born in Lahore in 1592. He added beautiful white marble to the Lahore Fort. He also built the famous Naulakha Pavilion in 1633. Shah Jahan gave Lahore some of its most famous buildings, like the Shahi Hammam (a royal bathhouse) in 1635. He also built the Shalimar Gardens and the stunning Wazir Khan Mosque in 1641. During his rule, Lahore's population was at its highest.
Aurangzeb's Additions
Aurangzeb, another great Mughal Emperor, also helped Lahore grow. He built the Alamgiri Bund embankment in 1662 to protect the city from the Ravi River. The largest Mughal building in Lahore, the Badshahi Mosque, was built by Aurangzeb in 1673. He also built the famous Alamgiri Gate of the Lahore Fort in 1674.
Decline of Mughal Rule
After Aurangzeb's death in 1707, the Mughal Empire became weaker. Lahore suffered during this time. Trade routes changed, and the city became less important. It was attacked several times by different groups.
Sikh Empire Period
In 1767, Sikh groups took control of Lahore. The city was divided among three rulers, which caused instability. Lahore's population dropped a lot, and many areas outside the city walls were abandoned.
Ranjit Singh's Rule
Ranjit Singh took control of Lahore in 1799. He became the ruler of the Sikh Empire. His rule brought back some of Lahore's past glory. He made Lahore the administrative capital of his empire. He also built a mint in the city in 1800.
Ranjit Singh improved the city's defenses by adding new walls and a moat. He also partly restored the Shalimar Gardens. He built the Hazuri Bagh Baradari in 1818 to celebrate getting the famous Koh-i-Noor diamond. He also built the Gurdwara Dera Sahib to mark the place where Guru Arjan Dev died.
However, during this time, some Mughal monuments were damaged. White marble was taken from several buildings to be used elsewhere. The Badshahi Mosque was even used as a storage place for ammunition and horses.
British Colonial Period
The British East India Company took control of Lahore in 1846. In 1849, Punjab became part of the British Indian Empire. At this time, Lahore had about 120,000 people.
The British built their new capital city south of the old Walled City. They called it "Civil Station." Many old Mughal buildings were reused by the British. For example, the Tomb of Anarkali became an Anglican church.
The British built the Lahore Junction railway station after the Indian Rebellion of 1857. It was designed like a medieval castle with thick walls to protect it from future uprisings. Important government buildings and businesses were built in Civil Station, especially along The Mall. This area became a fashionable commercial spot.
Many important buildings were built in the Indo-Saracenic style around 1887. These include the Lahore Museum and the Mayo School of Industrial Arts. Sir Ganga Ram, a civil engineer, designed many of Lahore's important buildings during this time. He is known as "the father of modern Lahore."
Lahore played a big part in the independence movements. In 1940, the All India Muslim League passed the Lahore Resolution. This resolution called for the creation of Pakistan as a separate homeland for Muslims in India.
After Partition
When British India was divided in 1947, Lahore experienced a lot of unrest. Many people moved in and out of the city. On August 17, 1947, Lahore was given to Pakistan. It became the capital of Pakistan's Punjab province.
After independence, Lahore slowly became important again as a center for business and culture. The Shah Alami Bazaar, which was destroyed in the 1947 riots, was rebuilt in 1949. The Tomb of Allama Iqbal was built in 1951 to honor the poet who inspired the Pakistan movement.
From 1955 to 1970, Lahore was the capital of all West Pakistan. The famous Minar-e-Pakistan was finished in 1968. It marks the place where the Pakistan Resolution was passed. With help from the United Nations, Lahore was rebuilt.
In 1974, the second Islamic Summit Conference was held in Lahore. The Walled City of Lahore began a restoration project in 2009.
Lahore's Location and Weather
Lahore is in the northeastern part of Pakistan. It is bordered by the Sheikhupura District to the north and west, Wagah to the east, and Kasur District to the south. The Ravi River flows on the northern side of Lahore. The city covers about 404 square kilometers.
Climate
Lahore has a hot, semi-dry climate. The hottest month is June, with temperatures often going above 45°C (113°F). The monsoon season starts in late June, bringing heavy rain in July, August, and September. January is the coolest month, with thick fog.
The highest temperature ever recorded in Lahore was 50.4°C (122.7°F) on June 5, 2003. The most rain in one day was 337 mm (13.3 inches) on August 1, 2024.
According to a report from 2024, Lahore is one of the most polluted cities in the world.
People of Lahore
Population Growth
Lahore's population was 11,126,285 in the 2017 Census. It has been growing by about 4.07% each year since 1998. In 2023, the population reached 13,004,135. More than 40% of the people in Lahore are under 15 years old.
Languages Spoken

Punjabi is the most common language spoken in Lahore. About 73.58% of people in Lahore speak Punjabi as their first language. This makes Lahore the largest Punjabi-speaking city in the world.
Urdu and English are also used as official languages. They are used in schools and government. Punjabi is also taught at universities and used in movies, plays, and newspapers in Lahore.
Religions in Lahore
Most people in Lahore are Muslims. According to the 2023 Census, 95.26% of Lahore's population is Muslim. Christians make up 4.64% of the population. There are also small numbers of Ahmadis, Hindus, Parsis, and Sikhs.
Lahore has some very holy sites for Sikhism. This makes it a major place for Sikhs to visit. There are two Hindu temples in the city: the Shri Krishna Mandir and the Valmiki Mandir.
City Layout and Buildings
Old City Charm
Lahore's modern look includes the historic Walled City of Lahore in the northern part. This area has several World Heritage Sites. The Walled City was not planned with straight lines. Instead, it grew with small streets and courtyards.
The Walled City is similar to other old cities in South Asia, like Peshawar and Delhi. They all started near a big river and had an old walled city and a royal fort.
Thirteen gates once surrounded the historic walled city. Some of the gates still standing are the Raushnai Gate and Lahori Gate. Southeast of the Walled City is the large British-era Lahore Cantonment.
Amazing Architecture
Lahore has many beautiful buildings from the Mughal Empire, Sikh Empire, and the British Indian Raj. The buildings in the Walled City of Lahore show Mughal and Sikh styles.
British Era Buildings
As the capital of British Punjab, Lahore's buildings were greatly influenced by the British. Many structures were built in the Indo-Gothic style. This style mixes Victorian and Islamic designs. The British also built the neoclassical Montgomery Hall, which is now the Quaid-e-Azam Library.
The British developed the green areas south of the Old City and the Cantonment. These areas have colonial-era buildings along tree-lined streets. Important buildings like the Lahore Museum and Aitchison College were built in the Indo-Saracenic style.
Parks and Gardens

Lahore is known as "the city of gardens" because it has so many. The Shahdara Bagh was one of the first Mughal gardens, built in the 15th century. It contains the Tomb of Jahangir. The Shalimar Gardens were built during Shah Jahan's rule. They were designed to look like the Islamic idea of paradise.
The Lawrence Garden was created in 1862. It was named after Sir John Lawrence, a British Viceroy. It has over 600 types of plants. The Circular Garden surrounds the Walled City on three sides.
Other parks include Hazuri Bagh, Iqbal Park, Gulshan-e-Iqbal Park, Model Town Park, and Jallo Park. The Bagh-e-Jinnah is a 141-acre botanical garden with fun and sports facilities, plus a library.
Economy and Business
Lahore is a major economic center. In 2008, the city's economy was estimated at $40 billion. It is growing quickly. Lahore contributes about 11.5% to Pakistan's national economy. It adds 19% to the economy of Punjab province. Lahore's economy is expected to reach $102 billion by 2025.
Lahore has about 9,000 industrial units. In recent years, it has moved from manufacturing to service industries. About 42% of its workers are in finance, banking, and social services. The city is Pakistan's biggest center for software and hardware. It also has a growing computer-assembly industry.
Lahore has always been a center for publishing. About 80% of Pakistan's books are published here. It is still the main center for literature, education, and culture in Pakistan.
The Lahore Expo Centre is a big project that opened in 2010. Defence Raya Golf Resort is a large golf course and luxury project. These projects help Lahore's economy grow.
Getting Around Lahore
Public Transport
Lahore has a good public transportation system. The main parts are the Lahore Metrobus and the Orange Line metro train. There is also a large network of buses that connect to the Metrobus.
Metrobus
The Lahore Metrobus is a fast bus service. It works with the local bus service to provide transport across Lahore and nearby areas.
Metro Train

The Orange Line Metro Train is an automatic train system. It is the first metro rail line in Pakistan. It is 27.1 kilometers long, mostly above ground. It can carry over 250,000 passengers every day. The trains can go up to 80 kilometers per hour. Commercial operations started on October 25, 2020.
There are also plans for two more metro lines: the Blue Line and the Purple Line.
Taxis and Rickshaws
Ride-sharing services like Uber and Careem are available. You can also find motorcycle rides.
Auto rickshaws are an important part of public transport. In 2019, there were about 82,000 auto rickshaws and 65,000 motorcycle rickshaws. Motorcycle rickshaws, called chingchi, are cheaper and can carry multiple passengers. Since 2002, auto rickshaws have used natural gas as fuel. Electric rickshaws were introduced in 2023.
Travel Between Cities
Railways
Lahore Junction Station is the main train station. It connects Lahore to many cities in Pakistan, including Peshawar, Islamabad–Rawalpindi, Karachi, and Quetta.
Buses
The Lahore Badami Bagh Bus Terminal is a main hub for buses traveling between cities. Many bus companies offer services to Punjab and other provinces.
Airports
Allama Iqbal International Airport is Pakistan's third busiest airport. It is on the eastern edge of the city. The new passenger terminal opened in 2003. The airport is named after the national poet, Muhammad Iqbal. It connects Lahore to many cities around the world.
City Government
Lahore is a metropolitan area managed by the Metropolitan Corporation Lahore. This group includes a mayor and nine deputy mayors, who are all elected. They are in charge of city planning, environmental rules, and providing city services.
The Mayor of Lahore is the elected leader of the Metropolitan Corporation. The mayor is responsible for managing government services and planning for the city's future.
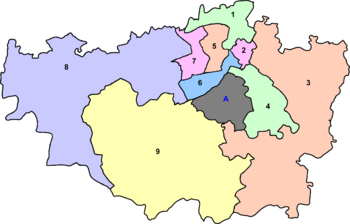
City Zones
Lahore is divided into 9 administrative zones. Each zone has several smaller areas called union councils. There are 274 union councils in total.
|
 |
Fun Festivals
People in Lahore celebrate many festivals throughout the year. These include Islamic, traditional Punjabi, Christian, and national holidays.
During public holidays, people decorate their houses and light up the streets. Many of Lahore's Sufi shrines hold yearly festivals called urs to honor their saints. The Data Darbar shrine's urs attracts up to one million visitors. The Mela Chiraghan festival is held at the shrine of Madho Lal Hussain.
Eid ul-Fitr and Eid ul-Adha are celebrated with decorated public buildings and shopping centers. People also remember the martyrdom of Imam Husayn during the first ten days of Muharram with large processions.
Basant is a traditional Punjabi festival that celebrates the start of spring. Lahore is the main place for Basant celebrations in Pakistan. People from all over come to the city for the festivities. Kite-flying competitions traditionally happen on rooftops. The Lahore Canal is decorated with floating lanterns. However, kite-flying has been banned by courts due to safety concerns.
Lahore's churches are beautifully decorated for Christmas and Easter. Shopping centers also have Christmas decorations.
Places to Visit


Lahore is a popular place for tourists in Pakistan. The Walled City of Lahore was renovated in 2014. It is famous for its UNESCO World Heritage Sites. Some popular sights are the Lahore Fort, which has the Sheesh Mahal and the Alamgiri Gate. The fort and the nearby Shalimar Gardens have been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1981.
The city has many historic Muslim religious sites. The most famous is the Badshahi Mosque, built in 1673. It was once the largest mosque in the world. Another popular place is the Wazir Khan Mosque, built in 1635. It is known for its beautiful tile work. Data Darbar is the largest Sufi shrine in South Asia.
Besides Islamic sites, there are two Hindu temples: the Krishna Temple and Valmiki Mandir. The Samadhi of Ranjit Singh is near the Walled City. It holds the ashes of the Sikh ruler Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
While the Walled City shows Lahore's old grandeur, areas like Defence Raya Golf Resort and Gulberg show its modern side.
Religious Sites
- Badshahi Mosque
- Dai Anga Mosque
- Data Darbar Complex
- Grand Jamia Mosque, Lahore
- Gurdwara Dera Sahib
- Gurdwara Janam Asthan Guru Ram Das
- Krishna Mandir, Lahore
- Lava Temple
- Masjid of Mariyam Zamani
- Moti Masjid (Lahore Fort)
- Neevin Mosque
- Sacred Heart Cathedral, Lahore
- Suneri Mosque
- Valmiki Temple
- Wazir Khan Mosque
Museums to Explore
- Army Museum Lahore
- Fakir Khana
- Islamic Summit Minar
- Lahore Museum
- National History Museum
- National Museum of Science and Technology
- Shakir Ali Museum
Historic Tombs
- Tomb of Allama Iqbal
- Tomb of Anarkali
- Tomb of Asif Khan
- Tomb of Dai Anga
- Tomb of Jahangir
- Tomb of Nur Jahan
- Buddhu's Tomb
- Cypress Tomb
Important Shrines
- Bibi Pak Daman
- Ali Hujwiri
- Mian Mir
- Madho Lal Hussain
- Baba Shah Jamal
Other Landmarks
- Shahi Hammam
- Alhamra Art Council
- Lahore Royal Fort
- Greater Iqbal Park
Historic Neighborhoods
- Anarkali
- Baghbanpura
- Heera Mandi
- Shahdara Bagh
- Walled City of Lahore
Learning in Lahore

Lahore is sometimes called Pakistan's educational capital. It has more colleges and universities than any other city in Pakistan. The literacy rate in Lahore is 81%. The city produces many professionals in science, technology, law, engineering, and medicine.
Most of the well-known universities are public. However, many private universities have also opened recently. Lahore University of Management Sciences (LUMS) is a top business school. Lahore is home to some of Pakistan's oldest and best educational institutes, including:
- Aitchison College, established in 1886
- Forman Christian College, established in 1864
- Government College University, Lahore, established in 1864
- King Edward Medical University, established in 1860
- Lahore College for Women University, established in 1922
- Lahore University of Management Sciences, established in 1986
- National College of Arts, established in 1875
- University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore, established in 1921
- University of the Punjab, established in 1882
- University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, established in 1882
Sports in Lahore
- Sports venues
-
Pakistan playing against Argentina in 2005
Lahore has hosted many international sports events. These include the finals of the 1990 Men's Hockey World Cup and the 1996 Cricket World Cup. The main offices for all major sports in Pakistan, like cricket, hockey, and football, are in Lahore. The head office of the Pakistan Olympic Association is also here.
Gaddafi Stadium is a famous cricket ground in Lahore. It was finished in 1959. The multi-purpose Punjab Stadium is mainly used for football matches.
Lahore has several golf courses, including the Lahore Gymkhana Golf Course. The Lahore Marathon is a yearly event where over 20,000 athletes from Pakistan and around the world participate.
- Professional Sports Teams from Lahore
| Club | League | Sport | Venue | Established |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lahore Qalandars | Pakistan Super League | Cricket | Gaddafi Stadium | 2015 |
| Wohaib | PFF League | Football | Punjab University Old Campus Ground | 1982 |
Sister Cities
Lahore has special connections with many cities around the world. These are called twin towns or sister cities.
 Istanbul, Turkey (1975)
Istanbul, Turkey (1975) Xi'an, Shaanxi, China (1992)
Xi'an, Shaanxi, China (1992) Kortrijk, Belgium (1993)
Kortrijk, Belgium (1993) Fez, Morocco (1994)
Fez, Morocco (1994) Bukhara, Uzbekistan (1995)
Bukhara, Uzbekistan (1995) Samarkand, Uzbekistan (1995)
Samarkand, Uzbekistan (1995) Isfahan, Iran (2004)
Isfahan, Iran (2004) Mashad, Iran (2006)
Mashad, Iran (2006) Glasgow, Scotland (2006)
Glasgow, Scotland (2006) Chicago, Illinois, United States (2007)
Chicago, Illinois, United States (2007) Belgrade, Serbia (2007)
Belgrade, Serbia (2007) Kraków, Poland (2007)
Kraków, Poland (2007) Coimbra, Portugal (2007)
Coimbra, Portugal (2007) Dushanbe, Tajikistan (2008)
Dushanbe, Tajikistan (2008) Córdoba, Spain (2008)
Córdoba, Spain (2008) Bogotá, Colombia (2009)
Bogotá, Colombia (2009) Amol, Iran (2010)
Amol, Iran (2010) Rio de Janeiro, Brazil (2015)
Rio de Janeiro, Brazil (2015)
Special Recognition
In 1966, the Government of Pakistan gave a special flag, the Hilal-i-istaqlal, to Lahore, Sargodha, and Sialkot. This was to honor their strong resistance during the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965. These cities were targets of attacks. Every year on Defence Day (September 6), this flag is raised in these cities to celebrate the courage of their people.
See also
 In Spanish: Lahore para niños
In Spanish: Lahore para niños
- Lahore Fashion Week
- Lahore Literary Festival
- Lahore Railway Station
- Lahori cuisine
- List of educational institutions in Lahore
- List of parks and gardens in Lahore
- List of people from Lahore
- Transport in Lahore
- Walled City of Lahore