United States Agency for International Development facts for kids

Seal of USAID
|
|

Flag of USAID
|
|
 Wordmark of USAID |
|
| Agency overview | |
|---|---|
| Formed | 1961 |
| Preceding agency |
|
| Dissolved | 2025 (de facto) |
| Headquarters | Ronald Reagan Building Washington, D.C., U.S. |
| Motto | "From the American people" |
| Employees | 600 |
| Annual budget | $34 billion (FY 2025 total budgetary resources) |
The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) was a U.S. government agency that gave help to other countries. This help, called foreign aid, included disaster relief and support for economic growth. President John F. Kennedy created USAID in 1961 during the Cold War. The goal was to use soft power, which means using culture and aid instead of military force, to help people around the world.
For many years, USAID was the world's largest foreign aid agency. It spent about $23 billion each year from 2001 to 2024. The agency had projects in over 100 countries. These projects focused on things like education, health, protecting the environment, and supporting democracy. It is estimated that USAID's work helped prevent over 91 million deaths between 2001 and 2021.
In early 2025, the administration of President Donald Trump ended most of USAID's projects. By July 2025, the agency's work was moved to the State Department. While USAID is no longer active, only the Congress has the power to officially close it down. Experts believe that stopping USAID's funding could lead to many preventable deaths.
Contents
How USAID Was Created and Changed

In 1961, the U.S. Congress passed the Foreign Assistance Act. This law reorganized how the U.S. gave aid to other countries. It led to the creation of USAID. President John F. Kennedy established the agency to bring several different aid programs together under one roof. The main goal was to help countries grow and improve their societies.
For many years, USAID worked under the guidance of the Secretary of State. In 1998, Congress made USAID a more independent agency. This meant it could operate on its own, separate from the State Department, while still following the president's foreign policy.
Big Changes in 2025

In January 2025, President Donald Trump ordered a freeze on almost all foreign aid. This caused a lot of confusion. Many USAID employees were told to stay home. The agency's official website was also shut down.
A few days later, Elon Musk announced that he and President Trump were shutting down USAID. He called it a "criminal organization." Because Musk's company Starlink was being investigated by USAID's Inspector General, some people said he had a conflict of interest.
In February 2025, Secretary of State Marco Rubio announced that USAID was being combined with the State Department. Most of USAID's employees were let go. The agency's leaders were ordered to stop almost all projects. This included programs that fought diseases like smallpox and HIV.
Effects of the Shutdown
The shutdown of USAID had a huge impact around the world. It stopped help for many important projects. These included:
- Wartime aid in Ukraine.
- Hospital support in Syria.
- Education programs in Mali.
- Efforts to protect the Amazon rainforest.
The shutdown also affected food aid. The Famine Early Warning Systems Network, which predicted food shortages, was taken offline. In July 2025, it was reported that about 500 metric tons of emergency food biscuits were going to be destroyed. This food could have fed 1.5 million children for a week.
A study in the medical journal The Lancet estimated that ending USAID's programs could cause at least 14 million preventable deaths by 2030. This includes 4.5 million children under five years old.
Lawsuits and Legal Challenges
Several groups sued the Trump administration over the shutdown. They argued that the president did not have the power to close USAID without Congress's approval. One lawsuit was filed by the American Federation of Government Employees. Another was filed by the AIDS Vaccine Advocacy Coalition.
In March 2025, the Supreme Court ruled that the government had to pay for work that was already completed. However, the courts allowed the administration to continue with its plan to close the agency.
What Did USAID Do?

USAID had several main goals. It managed programs in low-income countries for different purposes.
- Disaster Relief: When a natural disaster or war happened, USAID provided help. This included food, water, and shelter for people in need.
- Poverty Relief: USAID worked to help people escape poverty. It supported health and education programs for the poorest communities. It also helped manage food aid from the U.S.
- Global Issues: The agency worked on problems that affect the whole world. This included protecting the environment, fighting diseases, and improving trade.
- U.S. Interests: USAID's work also supported American goals. For example, it helped allies and promoted stability in important regions.
- Economic Growth: A major goal was to help countries build strong economies. USAID gave advice and training to help nations manage their own resources and grow.
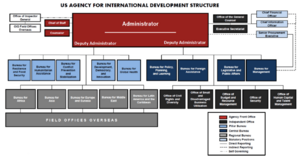
How USAID Was Organized
USAID had offices all over the world and a main headquarters in Washington, D.C.
Country Missions
USAID's work in each country was managed by a local office called a "mission." These missions worked with the country's government and other groups to plan projects. The staff included American Foreign Service officers and local professionals from that country.
As countries became more successful and needed less help, USAID would close its missions there. This happened in places like South Korea and Turkey. Sometimes, missions were closed if a country's government asked them to leave, as happened in Bolivia and Russia.
Washington Headquarters
The headquarters in Washington, D.C., was known as USAID/Washington. It helped set the overall policy for the agency. It was organized into different "Bureaus" that focused on specific regions or topics.
Some of the main bureaus included:
- Geographic Bureaus: These focused on regions like Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
- Global Health Bureau: This bureau worked on health issues around the world.
- Bureau for Humanitarian Assistance: This part of USAID responded to disasters and crises.
- Economic Growth, Education, and the Environment Bureau: This bureau focused on helping countries build their economies, improve schools, and protect nature.
Images for kids
-
The "Memorial Wall" at USAID headquarters honored employees who were killed in the line of duty.
-
Samantha Power was the USAID Administrator under President Biden.
-
A memorial for USAID officers killed in Sudan.