Ammonia solution facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Ammonia solution |
|
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | Ammonium hydroxide |
| Other names | Ammonia water |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| PubChem | |
| KEGG | C01358 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:18219 |
| RTECS number | BQ9625000 |
| SMILES | [OH2].[NH3] |
|
InChI
InChI=1/H3N.H2O/h1H3;1H2
|
|
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | |
| Molar mass | 0 g mol-1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Odor | "Fishy", highly pungent |
| Density | 0.91 g/cm3 (25 % w/w) 0.88 g/cm3 (35 % w/w) |
| Melting point | |
| Boiling point | |
| Miscible | |
| −31.5×10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH |
−80 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy S |
111 J/(mol·K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Moderately toxic |
| NFPA 704 |
|
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Ammonium chloride Ammonium cyanide |
| Other cations | Tetramethylammonium hydroxide |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
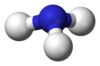
Ammonia solution, also known as ammonia water or ammonium hydroxide, is a mixture of ammonia gas and water. You might see it written as NH3(aq), where "aq" means it's dissolved in water. Even though it's called ammonium hydroxide, it's not really a separate chemical compound. It's more like ammonia gas mixed into water.
Contents
What Makes Ammonia Solution a Base?
When ammonia gas dissolves in water, a small part of it reacts with the water. This reaction creates two new particles: ammonium (NH4+) and hydroxide (OH−). The hydroxide particles are what make ammonia solution a "base" or an "alkali". Bases feel slippery and can neutralize acids. In a typical ammonia solution, only a tiny amount of the ammonia actually changes into these new particles. This means most of the ammonia is still in its original form, just dissolved in the water.
How Ammonia Dissolves in Water
Ammonia gas dissolves very well in water. But like many gases, it dissolves less as the water gets warmer. This means if you heat up an ammonia solution, some of the ammonia gas will escape into the air. This is why you can often smell ammonia when using cleaning products that contain it. Solutions with more ammonia dissolved in them are less dense, meaning they are lighter for their size.
Uses of Ammonia Solution
Ammonia solution has many different uses, especially in cleaning and some industrial processes.
Cleaning Around the House
Ammonia solution is a common ingredient in many cleaning agents. You'll find it in window cleaners and other household sprays. When you clean with it, the water evaporates, and the ammonia gas also evaporates. This helps leave surfaces like windows streak-free. You can buy ammonia solution by itself for cleaning. It might be plain, or have a lemon or pine scent. Sometimes, it's sold with soap added, which is often called "cloudy ammonia."
Making Other Chemicals
In factories, ammonia solution can be used to create other important chemicals. For example, it helps make Hexamethylenetetramine when mixed with formaldehyde. It also helps make Ethylenediamine from another chemical called 1,2-dichloroethane.
Cooling Systems
A long time ago, in the early 1900s, ammonia-water systems were popular in refrigerators. These were called "vapor absorption cycles." They worked by using the way ammonia dissolves and evaporates to create a cooling effect. Famous examples include the Electrolux and Einstein refrigerators. Today, other cooling methods are more common because they are more efficient.
Treating Water
Ammonia is used to make a chemical called chloramine. Chloramine is used to clean drinking water. It's often preferred over just using chlorine because it stays active in water pipes for longer. This helps keep the water safe from germs. Aquarists (people who keep fish) also use ammonia to prepare new fish tanks. This process, called fishless cycling, helps create a healthy environment for fish. It's important to use ammonia without any extra additives for this purpose.
Helping with Food Production
- Baking: A form of ammonia, called baking ammonia (which is ammonium carbonate and ammonium bicarbonate), was one of the first chemical ingredients used to make baked goods rise. It was originally made from deer antlers!
* Baking ammonia is special because it only works when heated. This means bakers don't have to wait a long time for yeast to work. * It's still used today for making crisp cookies and other baked goods. However, it's less popular now because of its strong smell and the development of modern baking powders. * In Europe, it's known as food additive E527.
- Acidity Control: Ammonia solution is also used in food to control how acidic it is. It helps lower acid levels in certain foods.
* In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) says it's generally safe to use in food if it's a special food-grade version. * Its ability to control pH also makes it good at stopping harmful microbes from growing in food.
Darkening Wood Furniture
In furniture making, a process called "ammonia fuming" was traditionally used to darken wood. This works best on wood that contains tannic acid, like oak. The wood is placed in a sealed container with ammonia solution. The ammonia fumes react with the tannic acid and natural iron in the wood. This reaction gives the wood a rich, dark, stained look. This method was very popular during the arts and crafts movement for staining oak furniture.
Treating Straw for Animals
Ammonia solution is used to treat straw, making it "ammoniated straw." This process makes the straw easier for cattle to digest and more nutritious for them to eat.
Using Ammonia in the Lab
In chemistry labs, ammonia solution is used in traditional tests to identify different substances. It can react with certain metals, like copper, to create a deep blue color. Ammonia solution can also dissolve some silver compounds, like those found in Tollens' reagent. You might also find it in solutions used to clean jewelry made of gold, silver, and platinum. However, it can harm soft or porous gemstones like opals and pearls.
See also
 In Spanish: Hidróxido de amonio para niños
In Spanish: Hidróxido de amonio para niños
- Ammonia
- Conjugate acid
 | Leon Lynch |
 | Milton P. Webster |
 | Ferdinand Smith |