Artists of the Tudor court facts for kids
The artists of the Tudor court were the painters and illustrators who worked for the kings and queens of England's Tudor dynasty. This period lasted from 1485, when Henry VII became king, until 1603, when Elizabeth I died.
These artists often ran their own workshops with assistants and students. They created many different types of art. This included tiny portrait miniatures, large portraits painted on wood, and decorated books. They also designed family emblems and fancy decorations for parties, tournaments, and other special events.
Even though there were English artists, many came from other countries. A lot of them were from the Low Countries (like modern-day Belgium and the Netherlands), but also from Italy and Germany. Some artists only stayed for a short time. However, many lived in England for several years or even the rest of their lives.
Contents
What Made Tudor Art Special?
During the Tudor period, England was quite separate from the rest of Europe's art world. Before this, the Wars of the Roses had caused a lot of problems for artists. By 1485, art, except for building design, was not doing well.
The Tudor kings and queens often invited foreign artists to England. They welcomed them warmly, just like other European countries did. Painters from the Low Countries were very popular. French artists also influenced important English artists like Lucas Horenbout and Nicholas Hilliard. Horenbout started the English tradition of portrait miniatures, and Hilliard became its greatest master.
The Protestant Reformation meant that religious paintings almost disappeared. Also, people weren't very interested in ancient myths until the very end of the Tudor era. Because of this, portraits became the most important type of painting for court artists. Most of the art that survived from this time are portraits.
We know many portraits have been lost. For example, Hans Holbein the Younger made many detailed drawings for portraits. But only a few of the actual paintings from these drawings still exist today. Portraits ranged from small, private miniatures, painted quickly from life, to large, symbolic paintings of Elizabeth I. These big portraits, like the Rainbow Portrait, were full of hidden meanings in her clothes, jewelry, and the background.
A lot of effort also went into decorating buildings and objects. These decorations were often temporary. The "Serjeant Painters" were lower-ranking royal painters. They probably did most of this decorative work, often following designs from the more important "King's Painters." The Master of the Revels was in charge of festivals and tournaments. This office also asked artists for help with decorations.
Jewelry and metalwork were seen as very important. Much more money was spent on them than on paintings. Holbein designed many amazing metal ornaments for tables, which are now gone. Hilliard was also a skilled goldsmith. Henry VIII loved music, building palaces, and tapestries. He owned over 2,000 tapestries, which cost far more than he ever spent on painters.
Queen Elizabeth I spent much less money. She hardly built anything new herself. But she was very interested in painting. She kept her own collection of miniatures locked away. She even wrote the names of the people in the portraits on the paper they were wrapped in. It's said that she had paintings burned if they didn't show her the way she wanted to be seen.
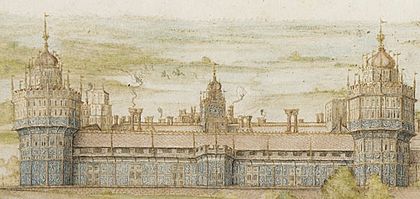
Nonsuch Palace, started by Henry VIII in 1538, was the most modern and impressive palace of the Tudor period. Its inside and outside were covered with huge amounts of sculpted stucco reliefs. These decorations covered over 2,000 square meters (21,000 sq ft). There was probably a lot of decorative painting too. Italian artists were brought in to create these unique designs. Visitors were amazed by the palace, and the few surviving pieces show their descriptions were true.
Who Were the Court Artists?
Many artists at the Tudor court were connected by family, marriage, and training. Lucas Horenbout (also called Hornebolt) started painting for Henry VIII in the mid-1520s. His sister, Susannah, also an illustrator, worked with him. It is believed that Lucas Horenbout taught Hans Holbein the Younger how to paint miniatures when Holbein worked for Henry VIII in the early 1530s.
Lucas and Susanna Horenbout's father, Gerard Horenbout, was a famous manuscript illustrator. He also worked for the Tudor court for a short time. In Bruges, Gerard worked with Sanders Bening and his son Simon. Simon Bening's oldest daughter, Levina Teerlinc, also trained as an illustrator. She started working for Henry VIII in late 1546. She continued as court painter for Henry's son Edward VI and for both his daughters, Mary I and Elizabeth.
Levina Teerlinc then taught Nicholas Hilliard the art of miniature painting. Hilliard was a goldsmith's apprentice. He married the daughter of Queen Elizabeth's jeweler and became the best miniaturist of his time. John Bettes the Elder had his son, John the Younger, train with Hilliard. Hilliard's most famous student, Isaac Oliver, later worked for Anne of Denmark and Henry, Prince of Wales. Oliver was married to the niece of Marcus Gheeraerts the Younger. Gheeraerts was also related by marriage to John de Critz the Elder, who continued the artistic family tradition into the next royal period. Many of these artists were Protestant refugees from other countries.
Artists Who Lived in England
- Meynnart Wewyck: Lived in England from about 1502 to 1525. He painted portraits for both Henry VII and Henry VIII.
- Lucas Horenbout: A pioneer of miniature painting. He was the King's Painter from 1531 until he died in 1544.
- Anthony Toto and Bartolommeo Penni: Italian artists.
- Hans Holbein the Younger: Spent many years in England on two visits. He painted some of the best portraits of the Tudor period.
- Levina Teerlinc: A miniaturist and lady-in-waiting to the queens.
- John Bettes the Elder: Worked on decorations at Whitehall Palace from 1531 to 1533. He also painted portraits and miniatures.
- Gerlach Flicke: A German portrait painter. He lived in London from about 1545 until he died in 1558.
- Hans Eworth: In England from about 1549. He was a portrait painter and designed for royal events.
- Steven van Herwijck: A portrait medal maker. He visited in 1562 and lived in England from 1565 until he died in 1567.
- Steven van der Meulen: Arrived by 1561 and became an English citizen in 1562. He was active until his death in 1563.
- Marcus Gheeraerts the Younger: A Flemish Protestant refugee who came to England as a child. He was a portrait painter.
- George Gower: An English portrait painter.
- Nicholas Hilliard: A miniaturist and goldsmith for Elizabeth I from about 1572.
- Hieronimo Custodis: A Flemish exile portrait painter. He worked from 1589 until his death in 1593.
- Sir William Segar: A portrait painter and expert in coats of arms.
- John de Critz the Elder: Arrived from Flanders as a child. He was a portrait painter.
- Robert Peake the Elder: An English portrait painter. He also worked for royal events and later became a serjeant painter.
- Isaac Oliver: Hilliard's student and later a rival artist.
- Rowland Lockey: Another student of Hilliard.
Artists Who Visited England
- Pietro Torrigiano: A sculptor from Florence. He made Henry VII's tomb and other monuments during a long stay. He was one of the few portrait sculptors at the Tudor court.
- Michael Sittow: Probably painted Henry VII and a portrait of Catherine of Aragon.
- Antonio Solario: A Venetian painter who may have painted an altarpiece for a London merchant in 1514.
- Girolamo da Treviso: Hired mainly as a military engineer, but also left an important painting.
- Nicolas Bellin: Brought from Fontainebleau to work on Nonsuch Palace.
- Lucas Cornelisz. de Cock: A Dutch portrait and history painter. He was probably in England from about 1527 to 1532.
- William or Guillim Scrots: Employed by Henry VIII from at least 1545 and stayed with Edward VI until the king died in 1553.
- Antonis Mor or Antonio Moro: A portrait painter for the Habsburg royal family. He visited with Philip II of Spain.
- Marcus Gheeraerts the Elder: A Flemish Protestant refugee. He stayed nine years, then returned in 1585 until his death.
- Quentin Metsys the Younger or Massys.
- Cornelius Ketel: Stayed eight years, painting historical scenes and portraits.
- Lucas de Heere: A Protestant refugee who returned to Flanders after ten years when it was safe.
- Joris Hoefnagel: In England from about 1569 to 1571, making drawings for a book of city maps. He painted A Fête at Bermondsey while in England.
- Federico Zuccari: Visited for six months, painting Elizabeth and Leicester.
Serjeant Painters

The "Serjeant Painter" was a royal job. These painters were often in charge of decorative work.
Here are the people who held this job:
- John Browne: He was a heraldic painter from 1502. He became "King's Painter" in 1511/12. In 1527, he was named the first Serjeant Painter. This happened when Lucas Horenbout, a foreign artist, became the "King's Painter," which was then a higher position. Browne died in 1532.
- Andrew Wright: Held the job from 1532 to 1544. Not much is known about him.
- "Antony Toto" (Antonio di Nunziato d'Antonio): A Florentine artist, he became Serjeant Painter in 1544 and died in 1554. He was the first Serjeant Painter known for being an artist, not just a craftsman. None of his paintings are known to exist today. He worked on Nonsuch Palace with his colleague Bartolommeo Penni.
- Nicolas Lizard (or Lisory): A French artist, he held the post from 1554 until his death in 1571.
- William Herne or Heron: From 1572 to 1580.
- George Gower: From 1581 until he died in 1596.
- Leonard Fryer: From 1596 to 1607. Very little is known about him.
- John de Critz the Elder: From 1603, joining after Elizabeth's death.
Payments to Artists
The royal records from this time still exist, but they can be hard to understand. Payments often included money for expensive materials. Artists also had to pay their assistants from these amounts. Some artists received regular payments, called annuities, which were usually topped up for specific works. Artists were also expected to give gifts to the monarch, often on New Year's Day or their birthday.
Here are some examples of royal annuities:
- Meynnart Wewyck: Received 100 shillings every six months in 1525.
- Lucas Hornebolte: Received either £33 6s or £62 10s from 1525 until he died.
- Hans Holbein: Received £30, but he also did work outside the court.
- Levina Teerlinc: Received £40.
- Nicholas Hilliard: Received a gift of £400 in 1591 and an annuity of £40 from 1599. He usually charged £3 for a miniature not for the royal family.
The money spent on metalwork, building palaces, and Henry VIII's tapestries was much, much larger than these amounts for painters.
Galleries
Miniatures
-
Lucas Horenbout, Manuscript portrait of Henry VIII, 1525–26
-
Holbein, Catherine Howard c. 1540; probably the only image of her from life.
-
Attributed to Levina Teerlinc, An Elizabethan Maundy, c. 1560
-
Nicholas Hilliard, Young Man Amongst Roses c. 1588
Preparatory Drawings
-
Sketch of Lady Elyot by Holbein in chalk, pen, and brush on paper, 1532–33, Royal Collection, Windsor
-
Companion sketch of Sir Thomas Elyot by Holbein, Royal Collection, Windsor. Neither portrait has survived.
-
Preliminary chalk sketch for a portrait of Elizabeth I by Federico Zuccari, 1570s, which has not survived.
Panel Paintings
-
Henry VII no longer thought to be by Michael Sittow, c. 1505.
-
Christina of Denmark in mourning, 1538. A possible bride for Henry VIII, whom Holbein was sent to paint.
-
Mary I by Anthonis Mor, c. 1541
-
Elizabeth I as a Princess, formerly attributed to William Scrots, c. 1546
-
Margaret Audley, Duchess of Norfolk, 1562, companion to portrait of the Duke, by Hans Eworth
-
Portrait of Lady Kitson by George Gower, 1573
-
The Earl of Essex in tilting armor by William Segar, 1590
Paintings on Canvas
-
Henry VIII after a Holbein of 1537. Later copy by unknown artist after Hans Holbein the Younger's destroyed mural at Whitehall Palace.
-
The Ditchley Portrait of Elizabeth by Marcus Gheeraerts the Younger, 1592
See Also
- English Renaissance
- Renaissance art
- Tudor England
- English monarchy
- English art
- Court painters
- 15th century in England
- 16th century in England
- 17th century in England
- Medieval English artists
- Lists of artists
- Lists of British artists
- Portraits of the English royal family
- Material culture of royal courts
- English royal court
 | Bessie Coleman |
 | Spann Watson |
 | Jill E. Brown |
 | Sherman W. White |

























