Battle of Grand Gulf facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Battle of Grand Gulf |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Vicksburg campaign | |||||||
 Battle of Grand Gulf |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| David D. Porter | John S. Bowen | ||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
| Mississippi Squadron | Bowen's Division | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 7 ironclad warships 10,000 men on transport vessels |
4,200 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 75 18 killed, 57 wounded |
22 3 killed, 19 wounded |
||||||
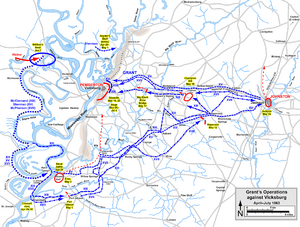
The Battle of Grand Gulf happened on April 29, 1863, during the American Civil War. It was part of Major General Ulysses S. Grant's plan to capture Vicksburg, Mississippi. Seven Union Navy ironclad warships, led by Admiral David Dixon Porter, attacked Confederate forts at Grand Gulf, Mississippi.
One of the forts, Fort Wade, was silenced by the Union ships. But the other, Fort Cobun, kept fighting strongly. Because of this strong defense, Grant and Porter decided not to land their soldiers at Grand Gulf. Instead, they landed at Bruinsburg, Mississippi. After the Confederates lost the Battle of Port Gibson on May 1, the forts at Grand Gulf became useless. The Confederates then left them. The soldiers who defended Grand Gulf later fought in the Battle of Champion Hill and the Battle of Big Black River Bridge. These battles led to the Siege of Vicksburg, which ended with a Confederate surrender on July 4. Today, you can visit the battlefield at Grand Gulf Military State Park. It became a historic site in 1972.
Contents
Why Was Grand Gulf Important?
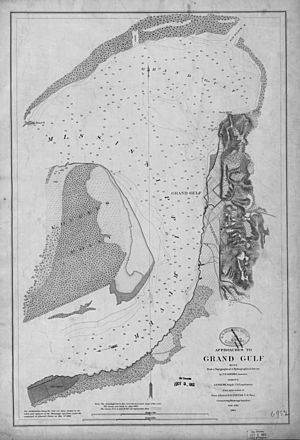
Grand Gulf was a town on the Mississippi River. In 1862, Confederate cannons there sometimes shot at Union Navy ships. Union troops tried to stop the Confederates from building defenses around the town. They even burned much of the town.
However, in March 1863, Confederate troops returned. Brigadier General John S. Bowen's soldiers began to make the defenses stronger. They brought in heavy cannons. These cannons were operated by skilled Confederate artillery units.
The Confederate Forts
The main defenses at Grand Gulf were two forts made of earth. They were called Fort Cobun and Fort Wade. Fort Cobun was very strong because it was built on a high point called Point of Rock. Its walls were about 40 feet thick.
Fort Wade was located about three-quarters of a mile downstream. It was only 20 feet above the river. There were also rifle pits (trenches for soldiers) connecting the two forts. Other cannons were placed nearby to protect the Big Black River.
Confederate soldiers from different units defended these positions. The 3rd and 6th Missouri Infantry Regiments defended the rifle pits. Other units protected nearby areas and watched for Union movements.
The Battle Begins
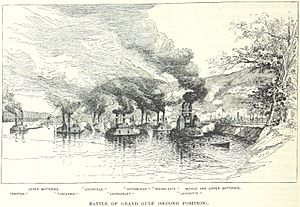
Admiral Porter decided to attack the forts at Grand Gulf. He used seven casemate ironclads, which were powerful armored ships. The attack started at 7:00 a.m. on April 29.
The ships moved in two groups. The first group included the USS Pittsburgh, USS Louisville, USS Carondelet, and USS Mound City. The second group had the USS Benton, USS Tuscumbia, and USS Lafayette.
The ironclads first aimed at Fort Cobun. Then, the first group of ships moved to focus on Fort Wade. The other three ships continued to attack Fort Cobun. As the ships passed Fort Cobun, they turned to face upstream. This allowed them to use their cannons more effectively.
Fighting the Forts
Even though the Union ships had many guns, they could only aim a few at the forts at one time. This limited their firepower. By 10:00 a.m., Fort Wade was badly damaged. One of its large cannons exploded. Colonel William F. Wade, who commanded the fort, was killed.
However, Fort Cobun kept fighting. A Confederate shot hit the USS Benton, destroying its steering wheel. Around 1:00 p.m., Fort Cobun started firing less often because it was running low on ammunition.
Despite this, Porter and Grant decided not to try landing soldiers. The Confederate defenses were still too strong. During the battle, Admiral Porter was hit by a shell fragment. It was a painful wound.
Battle Losses
The Union forces lost 18 men killed and 57 wounded, making a total of 75 casualties. The Confederates had 3 killed and 19 wounded, for a total of 22 casualties. One Union ship, the USS Tuscumbia, was badly damaged. It was not built very well, and its iron plating was not secure.
What Happened Next?
Later that afternoon, Porter sent his ships past Grand Gulf again. This time, the ships protected transport vessels carrying Union soldiers down the river. The ships successfully passed the forts. The Union lost one man during this movement, but the Confederates lost none.
After passing Grand Gulf, the Union soldiers were unloaded at Bruinsburg, Mississippi. Grant landed 17,000 soldiers there. This was the largest landing of soldiers by water in American history until D-Day in World War II.
March to Vicksburg
The soldiers immediately began marching towards Port Gibson, Mississippi. On May 1, they fought the Battle of Port Gibson against Bowen's Confederates. Bowen's forces were pushed back and had to retreat.
On May 3, the Confederates abandoned the forts at Grand Gulf. They made their cannons unusable and destroyed supplies they couldn't carry. Bowen's men then fought at the Battle of Champion Hill on May 16 and the Battle of Big Black River Bridge on May 17. Both battles were Confederate defeats.
These victories allowed Grant to begin the Siege of Vicksburg on May 18. The Confederate soldiers in Vicksburg surrendered on July 4. This was a major loss for the Confederacy in the Civil War.
Visiting the Battlefield Today
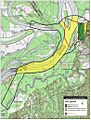
The place where the Battle of Grand Gulf happened is now Grand Gulf Military State Park. The park includes the land where Fort Wade and Fort Cobun once stood. You can also find an observation tower, a museum, and parts of the old town of Grand Gulf there. The park was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1972.
Images for kids
 | Bayard Rustin |
 | Jeannette Carter |
 | Jeremiah A. Brown |