Birrbay facts for kids
The Birrbay people, also known as Birpai or Biripi, are an Aboriginal Australian group from New South Wales. They share a similar way of speaking, called a dialect continuum, with the Worimi people.
Contents
Birrbay Language
The Gathang language (also called Gadjang or Worimi) is the traditional language of the Birrbay people. It was spoken around the Port Macquarie area. In southern areas like Taree, the name Birpai is often spelled Biripi. Gathang was a common language used by the six tribes of the Worimi when they met. In 1932, a researcher named W. J. Enright found four older people who still spoke Gathang near Wauchope.
Birrbay Country
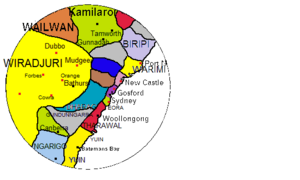
The Birrbay people are the traditional owners of about 7,250 square kilometers (2,800 square miles) of land. This land is located on the Mid North Coast of New South Wales. It stretches from Gloucester east to the coast, where the Manning River flows into the Pacific Ocean near Taree. The Birrbay mainly lived north of the Manning River. Their lands also included areas along the Forbes, [[Hastings River|Hastings (which they called Dhungang)], and Wilson rivers.
Birrbay Social Life
The Birrbay people had a special way of organising their groups. They divided their families into four main male groups:
- Wombo
- Kurraboo
- Wirraw
- Murrong
These male groups would marry into four female groups:
- Gooran
- Karragan
- Wangan
- Wirragan
Some traditions say that the Birrbay people moved between the coast and inland areas depending on the season. This helped them find the best food sources throughout the year. Modern Birrbay families often still follow these traditions when they can.
The Birrbay also had personal totems, which they called mari. These totems were often animals that were important to their clan. Some of the main totems included the shark, dolphin, and stingray.
Murrawin Ceremony
The Birrbay people practiced a special ceremony called Murrawin. This ceremony was also performed by the Dunghutti and Gumbaynggirr peoples. It was described by R. H. Mathews in 1900.
Unlike some other ceremonies, the Murrawin ceremony did not require everyone from the community to be there. Instead, two or three nearby tribes would meet. They would choose initiated men from each tribe and send them into the bush. These men would find a spot several miles away, clear it, and create a circular area about 6 meters (20 feet) across with raised earth.
At this spot, they would make bullroarers. These are special wooden instruments that make a roaring sound when whirled. The men would then return to the main camp. Over the next few nights, some elders would set up another site a few hundred meters away. They would whirl the bullroarers, sing special chants, and tap coolamons (traditional carrying dishes) with a nulla nulla (a type of club).
Gradually, the initiated men would gather at this special site. Once everyone was there, they would sometimes have a friendly shouting match, with each tribe playfully teasing the others. The next morning, the whole group would move camp. Women and young people would separate from the men. The men would then walk to the ceremonial ring they had prepared earlier, clicking their boomerangs as they went, and perform dances.
History of Contact
Birrbay oral histories tell a sad story about a massacre that happened around 1826 at Blackmans Point. It is believed that about 300 people were killed. While there isn't one single written account, a diary from Henry Lewis Wilson, who supervised convicts in the area, mentions a tragic event. He wrote that after two convicts were killed by Indigenous men, a group of soldiers "got round the blacks and shot a great many of them." The soldiers were sent to Sydney for trial but were not punished.
Historian Lyndall Ryan found other written records that support this story. She believes the Blackmans Point event mentioned by Wilson involved around 20 people. However, other massacres in the area may have caused the deaths of up to 300 people. Some of these massacres will be added to an official list of colonial massacres being put together by the University of Newcastle.
The area around Taree was first settled by William Wynter, a naval man, in 1831. He seemed to have a good relationship with the Birrbay people. His son, William, grew up among the Birrbay, learned their language, and was allowed to hunt with them. This suggests that the Indigenous people were peaceful. Three years later, people who cut cedar trees began setting up camps along the Manning River.
At the start of the 20th century, the wild highland areas and the Falls country near the Manning and Hastings rivers were a hiding place for an Aboriginal outlaw named Jimmy Governor.
Other Names for Birrbay
The Birrbay people have been known by several different names over time, including:
- Biripi
- Birippi
- Birrapee
- Birripai
- Birripi
- Bripi
- Brippai
- Waw-wyper
- Biribai
- Biribi
- Birpai
- Birpay
- Kattang
- Worimi
Notable Birrbay People
Many talented people come from the Birrbay community, including:
- Josh Addo-Carr, a rugby league player
- Latrell Mitchell, a rugby league player
- Jade North, an Australian soccer player who proudly shared his Biripi identity by getting a tattoo on his arm
- Nikita Ridgeway, a tattoo artist and graphic designer
- Ella Simon, an important historical figure and leader, who wrote an autobiography called Through My Eyes
- Kyah Simon, an international soccer player
Some Birrbay Words
Here are a few words from the Birrbay language:
- belbora/baalbora – a place of evil, often used for a massacre site
- bellbouri – a type of tea-tree
- bucker – knee
- groki – toad fish
- kimbriki – water reeds
- koribar – white cedar
- kundibakh – wild apples
- kureeki – ferns
- tareebin – native fig fruit, which is where the name Taree comes from, as these trees were common there
- tigerah – ironbark (a type of tree)