COVID-19 vaccine facts for kids
A COVID-19 vaccine is a special medicine that helps your body fight off the COVID-19 disease. COVID-19 is caused by a tiny germ called the SARS-CoV-2 virus. In 2020, many scientists around the world worked hard to create these vaccines.
Two main types of vaccines, called mRNA vaccines, were approved in late 2020. One was made by Pfizer and the other by Moderna. Both were very good at preventing COVID-19, working over 90% of the time. More vaccines became available in early 2021.
Countries had different ways of giving out the vaccines. The United Kingdom used its health service. Canada used its military. The United States sent vaccines to each state, and then each state decided how to give them out.
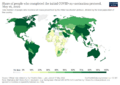
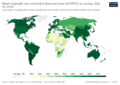
The United Kingdom was the first to approve the Pfizer vaccine. They started giving it to people on December 8, 2020. The United States began on December 14, starting with doctors and nurses in New York City. By April 2021, millions of people worldwide had received a COVID-19 vaccine.
Contents
How Vaccines Were Developed
In early 2020, experts thought a COVID-19 vaccine would take at least 18 months to make. However, many groups worked very fast. The World Health Organization (WHO) helped raise money to speed up vaccine development. The United States government also started "Operation Warp Speed" to create a vaccine quickly.
Scientists had to test vaccines carefully. They first tested them in animals. Then, they tested them in small groups of people. Finally, they tested them in many thousands of people to make sure they were safe and worked well.
Different Types of COVID-19 Vaccines
Scientists created different kinds of vaccines to fight the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Each type works a little differently to teach your body how to protect itself.
PittCoVacc: An Early Idea
Scientists at the University of Pittsburgh in the United States invented an early vaccine idea called PittCoVacc. This vaccine was designed to protect against SARS-CoV-2. It was one of the first vaccine ideas to be studied by other scientists.
Scientists had worked on similar viruses before. This helped them create PittCoVacc quickly. They knew that a part of the virus, called a "spike protein," was important for teaching the body to fight the virus.
They made tiny pieces of these spike proteins in the lab. They put these proteins into mice using a special patch with tiny needles. These needles were made of sugar and protein and melted into the skin. The skin is a good place for vaccines because it has many immune cells. The mice then made protective molecules called antibodies. These antibodies would help fight the virus.
Messenger RNA (mRNA) Vaccines
Other scientists developed vaccines that use something called messenger RNA. Think of mRNA as a set of instructions. These vaccines give your body instructions to make a small, harmless piece of the virus. Your body then learns to recognize this piece and fight it off.
mRNA vaccines can be made faster than other types. However, they need to be stored in very cold places, much colder than a normal refrigerator.
Moderna Vaccine
The company Moderna developed an mRNA vaccine. In late 2020, Moderna announced that its vaccine was about 94.5% effective. This means it was very good at preventing people from getting sick with COVID-19. This vaccine also needed to be kept very cold, but not as cold as some others. It started being given out in early 2021.
Pfizer-BioNTech Vaccine
The German company BioNTech and Pfizer worked together to create another mRNA vaccine. They called their project "Project Lightspeed" because they wanted to make the vaccine very fast.
To help people trust the vaccine, Pfizer shared all the details of how they were testing it. This is usually a secret for companies. In November 2020, Pfizer announced their vaccine was about 90% effective. They asked for permission to use it quickly in emergencies. This vaccine is also known by its special name, tozinameran.
Adenovirus Vaccines
The adenovirus is a common virus that causes colds. Scientists have used adenoviruses in vaccines for many years because they usually don't harm people much. For COVID-19 vaccines, scientists take a harmless adenovirus and attach pieces of the SARS-CoV-2 virus to it. When this vaccine is given, your body's immune system learns to recognize these pieces. Then, if you ever come across the real SARS-CoV-2 virus, your body knows how to fight it.
Oxford-AstraZeneca Vaccine
A team from the University of Oxford developed a COVID-19 vaccine using an adenovirus. They had a head start because they were already working on a vaccine for a similar virus. They took the spike protein from SARS-CoV-2 and put it on an adenovirus. This vaccine is called ChAdOx1 nCoV-19. It was tested in many people and became available in 2020.
Ad5-nCOV Vaccine
A Chinese company called CanSino Biologics also made a vaccine using an adenovirus. This vaccine also uses the spike protein from SARS-CoV-2. The Chinese government allowed this vaccine to be given to people in the Chinese military.
Johnson & Johnson Vaccine
The Johnson & Johnson company made a COVID-19 vaccine that also uses an adenovirus. A good thing about this vaccine is that it does not need to be stored in very cold temperatures, unlike some other vaccines.
Inactivated Virus Vaccines
Some vaccines use the actual SARS-CoV-2 virus, but they change it to make it harmless. This is called an inactivated virus vaccine. Your body learns to recognize this harmless virus. Then, it can fight off the real, harmful virus if you are exposed to it.
CoronaVac
The company Sinovac in China and a research center in Brazil worked together to make a vaccine called CoronaVac. This is an inactivated virus vaccine. It started being tested in many people in July 2020.
Sinopharm Vaccine
The company Sinopharm, which belongs to the government of China, also made an inactivated virus vaccine. This vaccine also started being tested in many people in mid-2020.
Other Vaccine Research
Scientists are always looking for new ways to make vaccines.
Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) Vaccine Study
Scientists at the University of Melbourne are studying an old vaccine called the Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine. This vaccine has been used for over 100 years to protect people from tuberculosis. Scientists have noticed that it also helps protect people from other diseases. They are studying if it can help protect people from COVID-19 too. Since it's an old vaccine, doctors already know it's safe.
Nasal Vaccines
Some scientists are working on "nasal vaccines." These are vaccines that doctors spray into your nose instead of injecting them with a needle. Scientists think these might work even better because the SARS-CoV-2 virus often enters the body through the nose and mouth.
Images for kids
-
Conceptual diagram showing three vaccine types for forming SARS‑CoV‑2 proteins to prompt an immune response: (1) RNA vaccine, (2) subunit vaccine, (3) viral vector vaccine
-
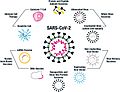
Vaccine platforms being employed for SARS-CoV-2. Whole virus vaccines include both attenuated and inactivated forms of the virus. Protein and peptide subunit vaccines are usually combined with an adjuvant in order to enhance immunogenicity. The main emphasis in SARS-CoV-2 vaccine development has been on using the whole spike protein in its trimeric form, or components of it, such as the RBD region. Multiple non-replicating viral vector vaccines have been developed, particularly focused on adenovirus, while there has been less emphasis on the replicating viral vector constructs.
-
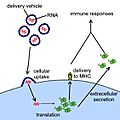
Diagram of the operation of an RNA vaccine. Messenger RNA contained in the vaccine enters cells and is translated into foreign proteins, which trigger an immune response.
-
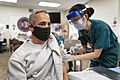
Covid vaccination for children aged 12–14 in Bhopal, India
-
Inside of a vaccination center in Brussels, Belgium, February 2021.
See also
 In Spanish: Vacuna contra la COVID-19 para niños
In Spanish: Vacuna contra la COVID-19 para niños