Calvin cycle facts for kids
The Calvin cycle is a set of important chemical reactions that happen inside chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are like tiny factories inside plant cells. This cycle is a big part of photosynthesis, which is how plants make their own food.
You might hear the Calvin cycle called the Benson-Calvin cycle too. It's called "light-independent" because it doesn't need sunlight directly. Instead, it uses the energy that plants captured from sunlight in an earlier step of photosynthesis.
The cycle is named after Melvin Calvin. He won a Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1961 for discovering it. Melvin Calvin worked with his friends Andrew Benson and James Bassham at the University of California, Berkeley.
Contents
How the Calvin Cycle Was Discovered
Melvin Calvin and his team wanted to understand how plants turn carbon dioxide into food. They used a special type of carbon called carbon-14. This carbon-14 acted like a tiny tracker.
They fed this special carbon dioxide to tiny green plants called algae (Chlorella). Then, they followed where the carbon-14 went inside the plant. This helped them map out exactly how carbon travels through the plant during photosynthesis. They saw how it changed into carbohydrates (sugars) and other important plant parts.
Their work showed that sunlight doesn't directly act on carbon dioxide. Instead, sunlight first helps the plant's chlorophyll (the green stuff) capture energy. This energy then powers the Calvin cycle to make organic compounds.
Steps of the Calvin Cycle
The Calvin cycle has several steps that work like a loop. Here's how it generally works:
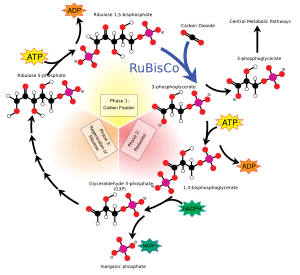
Step 1: Carbon Grab
- A five-carbon molecule called RuBP (Ribulose bisphosphate) acts like a catcher.
- It grabs one molecule of carbon dioxide from the air.
- When RuBP catches the carbon dioxide, they join together to form a new six-carbon molecule.
Step 2: Split and Energize
- The six-carbon molecule is not stable.
- An enzyme called RuBisCO quickly breaks it into two equal parts. Each part has three carbons.
- Energy from ATP and NADPH molecules is used here. These are like tiny energy packets made during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
Step 3: Sugar Leaves
- One of the three-carbon parts leaves the cycle.
- This three-carbon molecule is used to make sugar (like glucose). This sugar is the plant's food.
- The other three-carbon part continues to the next step of the cycle.
Step 4: Molecule Switch
- The remaining three-carbon molecule needs to be changed back into the five-carbon RuBP.
- More energy from ATP and NADPH is used for this change.
- This step gets the RuBP ready to grab another carbon dioxide molecule.
Step 5: Cycle Starts Again
- Once the five-carbon RuBP molecule is reformed, the cycle can start all over again.
- It's a continuous process that keeps making sugar for the plant.
What the Calvin Cycle Makes
The main product of the Calvin cycle is a three-carbon sugar phosphate molecule. This is often called G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate). These G3P molecules are the building blocks that plants use to make bigger sugars like glucose and other important organic compounds.
Every step in the Calvin cycle has its own special enzyme. These enzymes are like tiny helpers that speed up each chemical reaction.
See also
 In Spanish: Ciclo de Calvin para niños
In Spanish: Ciclo de Calvin para niños