Carpenter facts for kids
A carpenter is a skilled person who works with wood. They can build many things, like houses, cabinets, and furniture. Carpenters are important in building projects because they handle so much of the work from start to finish. They are always learning new ways to work with wood and using new tools and materials.
Many carpenters choose to focus on a special type of work. Some are rough carpenters. They build simple, strong structures like house frames or crates for shipping. Others are finish carpenters. They focus on detailed and artistic work. This includes making fine furniture, cabinets, or even toys. Sometimes, wood carvers are also seen as a type of carpenter.
Contents
History of Carpentry
Wood has been one of the most important building materials for humans for a very long time, along with stone. As technology improved through the Stone Age, Bronze Age, and Iron Age, people got better at shaping wood. They used it to make tools, build shelters, and create weapons.
Some of the oldest signs of carpentry are ancient wooden well casings. One was found in the Czech Republic, made of oak and hazel wood from over 7,000 years ago. Another was found in Germany, built with special joints called mortise and tenon.
For a long time, carpentry skills were passed down by watching and doing, not by writing. Very few old texts talk about carpentry. One of the oldest is a book by Vitruvius called De architectura. After the printing press was invented in the 1400s, more guides and books about building started to appear.
Some of the oldest wooden buildings still standing today are temples in China, like the Nanchan Temple from 782 AD. Also, Greensted Church in England has parts from the 11th century. And the stave churches in Norway were built in the 12th and 13th centuries.
Carpentry in Modern Times
By the 1500s, sawmills became common in Europe. Later, in the 1700s, the Industrial Revolution brought new inventions like the steam engine and cut nails. These, along with the circular saw, led to a new way of building called balloon framing. This method used lighter wood pieces and was faster than older ways.
In the 1800s, electricity led to hand-held power tools and machines that made screws and wire nails. In the 1900s, concrete became common for foundations. This meant carpenters didn't need heavy wooden bases for buildings anymore. Also, drywall (plasterboard) started to replace plaster walls. New materials like plywood and engineered wood also became popular.
Becoming a Carpenter
Carpentry needs special training. This includes learning facts and getting lots of hands-on practice. In formal training, a carpenter starts as an apprentice. Then they become a journeyman. With enough experience, they can become a master carpenter.
You can get training before an apprenticeship in high school shop classes or community colleges. Some people also learn by working with carpenters for years, watching and helping.
Carpenters can work for a company or be self-employed. In some places, carpenters who run their own business need a license. This often means passing a test and having insurance.
Training Programs
There are many ways to learn carpentry. You can find seminars, certificate programs, and high school classes. There are also programs for new construction, restoring old buildings, and preserving historic ones. These are sometimes called pre-apprenticeship training.
In the United Kingdom, young carpenters often learn through apprenticeships. They can earn money and get real-world experience while working towards a national qualification.
Training often splits into two main areas: construction carpentry and cabinetmaking. In pre-apprenticeship, students spend time in classrooms and workshops. They learn math, special terms, and how to use tools. Construction carpentry students also do exercises to get ready for the physical work.
After this first training, students who pass are often assigned to a local union and work crews. They start as First Year Apprentices. Over the next four years, they become Second, Third, and Fourth Year Apprentices. They also go back to the training center for more detailed lessons.
Apprentices and Journeymen
In countries like Germany and Australia, you must complete a formal apprenticeship (usually 3-4 years) to be a professional carpenter. After finishing, you are called a journeyman carpenter.
Long ago, journeymen would travel to different areas. They learned new building styles and techniques before returning home. Today, journeymen don't have to travel. The term now means someone with a high level of skill. In the United States, union carpenters must pass a test to become an official journeyman. However, other skilled carpenters might also be called journeymen based on their experience.
In Canada, each province sets its own apprenticeship rules. Most are four years long. They include on-the-job training and classes. After finishing, a carpenter can get a Certificate of Proficiency or Qualification. There's also an extra Red Seal option. This allows carpenters to work anywhere in Canada after passing another exam.
Master Carpenter
After being a journeyman for a while, a carpenter might aim to become a master carpenter. In some countries, like Germany or Japan, this is a very hard process. It needs a lot of knowledge and skill. These countries often require master status for carpenters who want to hire and teach apprentices. In other places, like the United States, "master carpenter" can just mean a very skilled carpenter.
Skilled carpenters often move into related jobs. These include building shop displays, putting up scaffolding, making things in a workshop, or doing building maintenance.
Materials Carpenters Use
Carpenters used to work mainly with natural wood. This wood was prepared by splitting or sawing it into lumber (in America) or timber (in Britain). Today, carpenters use natural wood, engineered wood, and many other building materials. These materials are usually prepared by others and brought to the job site.
Modern carpenters do many different tasks. They install floors, windows, doors, and inside trim. They also put in cabinetry, roofing, and siding. They work with insulation, ceilings, and metal frames. They can also build custom furniture and displays.
Safety for Carpenters
Carpentry can be a dangerous job. Some risks include working with machines, flying materials, and loud noise. There are also dangers from electricity, dust, and chemicals.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) helps prevent injuries and accidents. They say that workplace deaths and injuries have gone down a lot since 1970. The most common causes of serious accidents are falls, being hit by objects, electric shocks, and getting caught in something.
To stay safe, employers must make sure work areas are free of known dangers. Floors should be clean and dry. Workers must be given safety gear, like personal protective equipment. They also need training about job dangers in a language they understand. For example, to prevent falls, railings should be put around openings and on high platforms. Safety harnesses and nets can also be used.
Safety is not just for the workers. Carpenters must build things that meet safety rules, like those for stairs and building codes. This helps keep the building safe for everyone who uses it for a long time.
Types of Carpenters
- Cabinetmaker is a carpenter who makes fine and detailed items. They specialize in making cabinets, wardrobes, dressers, and other storage furniture.
- Carpenter and joiner has many skills. They can do fine joinery, finish carpentry, framing, and make forms for concrete.
- Conservation carpenter works to protect old buildings. They maintain structures as they were first built or restore them to that condition.
- Cooper is a carpenter who makes barrels.
- Finish carpenter (also called trim carpenter) specializes in putting in decorative wood pieces. This includes door and window frames, mantels, crown mouldings, and baseboards. They work after the main framing is done, also hanging doors and installing cabinets.
- Formwork carpenter builds the temporary molds (called shuttering) that hold wet concrete until it dries.
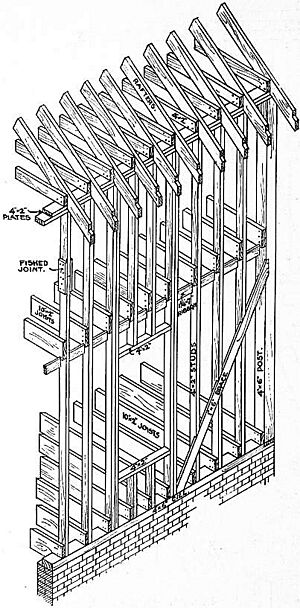
- Framer is a carpenter who builds the main wooden skeleton of buildings. They often use the platform framing method. A framer who uses large timbers and old-style joints is called a timber framer.
- Log builder builds structures by stacking horizontal logs with special joints.
- Joiner (an older name, less common now in North America) is someone who does fine woodworking. This includes cabinetry, furniture making, and making exact joints for things like musical instruments or parquetry floors.
- Luthier is a special carpenter who makes or fixes stringed musical instruments. The word comes from "lute."
- Restoration carpenter (see conservation carpenter).
- Set carpenter builds and takes apart temporary scenery and sets for movies, TV, and plays.
- Ship's carpenter specializes in fixing and maintaining wooden parts of ships that are in the water. They check the ship for leaks.
- Shipwright builds wooden ships on land.
- Trim carpenter (see finish carpenter).
Other Types of Carpentry
- Japanese carpentry has special names. A daiku is a general carpenter. A Miya-daiku builds temples and shrines. A sukiya-daiku works on teahouses and special homes. Sashimono-shi make furniture, and tateguya do inside finishing work.
- Green carpentry focuses on using materials that are good for the environment. These materials are energy-efficient and come from sustainable sources. Green carpenters also use building methods that use less material but still make strong structures.
- Recycled carpentry uses old wood and parts from broken furniture. They turn these discarded pieces into new wood products.
Images for kids
-
Carpentry includes such specialties as barrelmaker, cabinetmaker, framer, luthier, and ship's carpenter
-
Carpenter handling a plank used in scaffolding
See also
 In Spanish: Carpintería para niños
In Spanish: Carpintería para niños
 | Tommie Smith |
 | Simone Manuel |
 | Shani Davis |
 | Simone Biles |
 | Alice Coachman |