Corvus (constellation) facts for kids
| Constellation | |
List of stars in Corvus
|
|
| Abbreviation | Crv |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Corvi |
| Pronunciation | genitive |
| Symbolism | the Crow/Raven |
| Right ascension | 12h |
| Declination | −20° |
| Area | 184 sq. deg. (70th) |
| Main stars | 4 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars |
10 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 3 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 1 |
| Brightest star | γ Crv (Gienah) (2.59m) |
| Messier objects | 0 |
| Meteor showers | Corvids Eta Corvids |
| Bordering constellations |
Virgo Crater Hydra |
| Visible at latitudes between +60° and −90°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of May. |
|
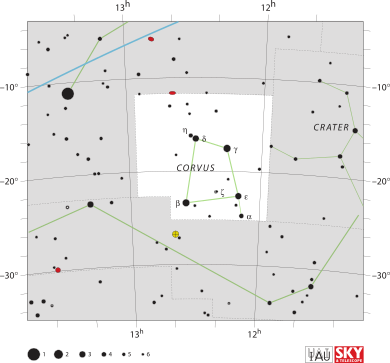
Corvus is a small constellation in the southern part of our night sky. Its name means "crow" in Latin. This constellation shows a raven, a smart bird often linked to stories about the god Apollo. It looks like the raven is sitting on the back of Hydra, the water snake constellation.
Corvus is one of the 48 constellations first listed by the ancient astronomer Ptolemy almost 2,000 years ago. The four brightest stars in Corvus—Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi—form a clear four-sided shape, or quadrilateral, in the sky. This shape makes Corvus easy to spot.
Gamma Corvi, also called Gienah, is the brightest star in Corvus. It shines with a brightness of 2.59. Gienah is a huge, aging blue star, much bigger and brighter than our Sun. Another interesting star, Eta Corvi, has two rings of dust and rocks orbiting it, like a mini solar system in the making. Scientists have also found planets orbiting three other stars in Corvus. There might even be a fourth star system with planets!
Contents
Corvus: The Crow Constellation
Stories from the Stars: Mythology of Corvus
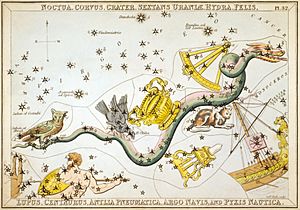
Long ago, people looked at the stars and created amazing stories. In ancient Babylonian star catalogues, dating back to at least 1100 BCE, Corvus was known as the Raven. Just like in later Greek stories, it was shown sitting on the tail of the Serpent, or Hydra.
The Babylonians believed this constellation was sacred to Adad, their god of rain and storms. It appeared in the sky just before the rainy season. Some historians think Corvus, along with the nearby constellations Crater (the Cup) and Hydra, were symbols of the underworld. They might have marked a gateway to the land of the dead.
The Myth of Apollo and the Crow
One famous Greek myth tells the story of Apollo, the god of music and light, and a crow. In this story, Apollo had a pure white crow. He asked the crow to fetch some water for him. On its way, the crow got distracted by some delicious figs and stopped to eat them.
Instead of telling Apollo the truth, the crow lied. It claimed that a snake, Hydra, had prevented it from getting the water. To try and prove its lie, the crow even brought back a snake in its talons. Apollo, being a god, knew the crow was lying. In his anger, he punished the crow by turning its beautiful white feathers black. He then threw the crow (Corvus), the cup (Crater), and the snake (Hydra) into the night sky. As a lasting punishment, the crow in the sky is forever thirsty, with the cup of water just out of its reach.

Corvus Around the World
Many different cultures have seen the constellation Corvus in their own unique ways. In Chinese astronomy, the stars of Corvus are part of the Vermilion Bird of the South. The four main stars of Corvus were seen as a chariot. One star, Zeta Corvi, was even called Changsha, meaning a coffin.
In Indian astronomy, the five main stars of Corvus were thought to represent a hand or a fist. This was part of their nakshatra system, which divides the sky into lunar mansions.
Polynesian sailors used Corvus as a guide for navigating the vast ocean. They had different names for it, like Mee in the Marquesas Islands and Te Manu in Pukapuka. The Torres Strait Islanders saw Corvus as the right hand of a giant fishing man, holding a fruit.
The Bororo people of Brazil imagined Corvus as a land tortoise. The Tucano people of the Amazon region saw it as an egret, a type of bird. The Tupi people of Brazil might have seen Corvus as a grill or barbecue for cooking fish.
Finding Corvus in the Sky
Corvus is the 70th largest constellation in the sky. It covers a small area, about 0.446% of the entire night sky. It is surrounded by other constellations: Virgo to the north and east, Hydra to the south, and Crater to the west.
The International Astronomical Union uses "Crv" as the official three-letter abbreviation for Corvus. Because Corvus is in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere, people living south of 65°N latitude can see the entire constellation.
Stars of Corvus
There are 29 stars in Corvus that are bright enough to be seen without a telescope, if the sky is dark enough. The four main stars—Delta, Gamma, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi—form a distinct shape called an asterism. This shape is sometimes called "the Sail" or "Spica's Spanker." Even though these stars are not super bright, they stand out because they are in a dim part of the sky.
The Brightest Stars
- Gamma Corvi (Gienah): This is the brightest star in Corvus. It is a blue-white giant star, much larger and brighter than our Sun. It is about 154 light-years away from Earth. Gienah is also a binary star, meaning it has a smaller companion star orbiting it.
- Delta Corvi (Algorab): This is a double star that you can see with a small telescope. The main star is blue-white and about 87 light-years away. It is surrounded by warm dust. Its companion is an orange dwarf star, also with dust around it.
- Beta Corvi (Kraz): This star marks the raven's chest. It is a yellow bright giant star, about 146 light-years from Earth. It used to be a blue-white star but has grown and cooled as it aged.
- Epsilon Corvi (Minkar): This star is the raven's nostril. It is a red giant star, much larger and brighter than the Sun, located about 318 light-years away.
Stars with Planets
Scientists have found planets orbiting several stars in Corvus:
- HD 103774: This star has a planet about the size of Neptune orbiting it every 5.9 days.
- HD 104067: An orange dwarf star with a planet that is 3.6 times the mass of Neptune. This planet orbits its star every 55.8 days.
- WASP-83: This star has a planet about the size of Saturn. It was discovered in 2015 when it passed in front of its star, a method called transit.
- HD 111031: This star, similar to our Sun, might also have a planet, but it needs more confirmation.
Other Interesting Stars
- Eta Corvi: This yellow-white star is about 59 light-years away. It is special because it has two debris disks, which are rings of dust and rocks, orbiting it. These disks could be where new planets are forming.
- Alpha Corvi (Alchiba): This white star is about 48.7 light-years away. Its brightness changes slightly over three days, suggesting it might be a binary star or a pulsating star.
- Zeta Corvi: This blue-white star has a disk of gas around it. It is about 420 light-years away and might be part of a multiple star system.
- 31 Crateris: This star was once mistakenly thought to be a moon of Mercury! It is actually a distant binary star system with a very hot blue-white star.
- TV Corvi: This is a fascinating system called a dwarf nova. It has a white dwarf star and a brown dwarf star orbiting each other very closely, every 90 minutes. It brightens dramatically from time to time. The famous astronomer Clyde Tombaugh discovered its changing brightness in 1931.
- Ross 695: This small red dwarf star is one of the closest stars to Earth in Corvus, only about 28.9 light-years away. It is too faint to see without a telescope.
Amazing Deep-Sky Objects
Corvus does not have any Messier objects, but it does have several interesting galaxies and a planetary nebula that amateur astronomers can observe.
Galaxies in Corvus
The NGC 4038 Group is a collection of galaxies found in Corvus and Crater. The most famous members are the Antennae Galaxies, also known as NGC 4038 and NGC 4039. These are two galaxies that are crashing into each other! From Earth, they look a bit like a heart shape. Their name comes from the long "tidal tails" of stars and gas that stretch out from them, like antennae.
This cosmic collision is causing lots of new stars to form. The Antennae Galaxies are about 45 million light-years away. Scientists have also found mysterious, very bright X-ray sources within them. These could be rare types of binary stars or even intermediate-mass black holes.
Another galaxy in this group is NGC 4027, sometimes called the Ringtail Galaxy. It is a barred spiral galaxy with a twisted shape. This distortion is probably from a past collision with another galaxy.
Other Cosmic Wonders
- NGC 4361: This is a planetary nebula in the center of Corvus. It looks a bit like a small elliptical galaxy, but the bright star at its center tells us it's actually a cloud of gas and dust shed by a dying star.
- NGC 4782 and NGC 4783: These are two elliptical galaxies that are merging together. They are located in the northeastern part of Corvus, about 200 million light-years away.
- Stargate (asterism): Corvus also contains a cool asterism called the Stargate. An asterism is a recognizable pattern of stars, but it's not an official constellation.
Meteor Showers from Corvus
Two meteor showers are known to come from Corvus:
- Corvids: German astronomer Cuno Hoffmeister first discovered and named the Corvids in 1937. They were observed between June 25 and July 2. However, this shower has not been seen since.
- Eta Corvids: In January 2013, the MO Video Meteor Network announced the discovery of the Eta Corvids. Around 300 meteors were seen between January 20 and 26, and their existence was confirmed later that year.
See also
 In Spanish: Corvus (constelación) para niños
In Spanish: Corvus (constelación) para niños
- Corvus (Chinese astronomy)
 | George Robert Carruthers |
 | Patricia Bath |
 | Jan Ernst Matzeliger |
 | Alexander Miles |



