Cryosphere facts for kids
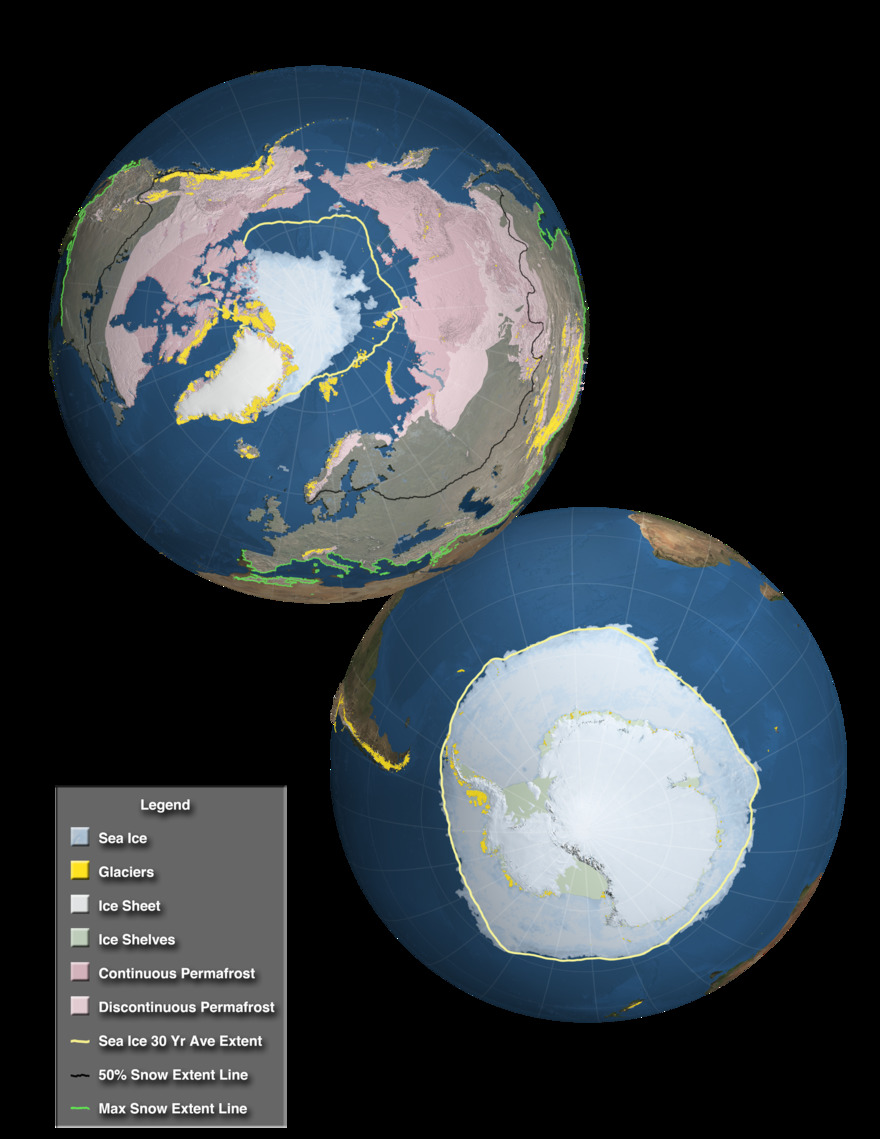
The cryosphere is a super cool part of our Earth where water is frozen solid! Think of it as Earth's icy zones. It includes things like sea ice (ice floating on the ocean), lake ice, river ice, snow cover, huge blocks of ice called glaciers, giant ice caps and ice sheets, and even frozen ground, which can include permafrost (ground that stays frozen for years).
This icy part of Earth often mixes with the hydrosphere, which is all the water on, under, and above Earth's surface. The cryosphere is a really important piece of Earth's global climate system. It affects how much energy the surface gets, how clouds form, where precipitation (like rain or snow) falls, how water moves around (this is called hydrology), and even how air and water travel in the atmosphere and oceans. Understanding the cryosphere helps us learn how Earth's climate works and how it changes. The word cryosphere comes from the Greek word cryo, which simply means "cold".
Contents
What Makes Up the Cryosphere?
The cryosphere is made of many different types of frozen water. Each part plays a special role in Earth's environment.
Sea Ice and Lake/River Ice
Sea ice forms when ocean water freezes. It floats on the surface of the ocean, mostly in the Arctic and Antarctic regions. Unlike icebergs, which break off from glaciers, sea ice forms directly from seawater. It can be thin and new, or thick and old, lasting for many years. Lake ice and river ice are similar, but they form on freshwater bodies like lakes and rivers during cold winters.
Snow Cover
Snow cover is simply the layer of snow that covers the ground. It's a very common part of the cryosphere, especially in areas that get cold winters. Snow reflects a lot of sunlight back into space, which helps keep Earth cool. It also stores water, releasing it slowly as it melts, which is important for rivers and water supplies.
Glaciers, Ice Caps, and Ice Sheets
These are massive bodies of ice that form on land from compacted snow over many years.
- Glaciers are like slow-moving rivers of ice. They flow down mountainsides or across land.
- Ice caps are dome-shaped masses of ice that cover less than 50,000 square kilometers of land.
- Ice sheets are much larger, covering more than 50,000 square kilometers. The two biggest ice sheets are in Greenland and Antarctica. These huge ice masses store a lot of Earth's freshwater.
Frozen Ground and Permafrost
Frozen ground is soil or rock that stays at or below 0°C (32°F) for at least two years. When it stays frozen for many years, it's called permafrost. Permafrost is found in very cold regions like the Arctic. It can be found on land and even under the ocean.
Why Is the Cryosphere Important?
The cryosphere is super important for our planet in many ways.
Controlling Earth's Temperature
The bright white surfaces of snow and ice reflect a lot of the sun's energy back into space. This is called the "albedo effect." It helps keep Earth cool. When ice and snow melt, darker surfaces like land or ocean are exposed. These darker surfaces absorb more sunlight, which can make Earth warmer. This is why the cryosphere plays a big role in Earth's temperature.
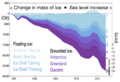
Affecting Sea Levels
Most of the ice in the cryosphere is on land, like glaciers and ice sheets. When this land ice melts, the water flows into the oceans, causing sea levels to rise. Rising sea levels can affect coastal communities around the world. Sea ice, on the other hand, is already floating in the ocean, so when it melts, it doesn't directly raise sea levels much, similar to how ice cubes melting in a glass don't make the water overflow.
Supporting Life and Ecosystems
Many animals, like polar bears, seals, and penguins, depend on the cryosphere for their homes and food. The frozen ground in permafrost areas also supports unique plants and ecosystems. Changes in the cryosphere can greatly affect these animals and plants.
Storing Freshwater
Glaciers and ice sheets hold a huge amount of the world's freshwater. This stored water is a vital resource for many communities, especially in regions where it melts and flows into rivers during warmer months.
How Is the Cryosphere Changing?
The cryosphere is very sensitive to changes in Earth's climate. Scientists are observing many changes:
- Melting Ice: Glaciers and ice sheets are melting at faster rates.
- Shrinking Sea Ice: The amount of sea ice, especially in the Arctic, has been decreasing.
- Thawing Permafrost: Permafrost is thawing in many areas, which can release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
These changes are important because they can affect global sea levels, weather patterns, and the habitats of many animals. Scientists use satellites, ground measurements, and computer models to study the cryosphere and understand how it is changing.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Criósfera para niños
In Spanish: Criósfera para niños
 | Stephanie Wilson |
 | Charles Bolden |
 | Ronald McNair |
 | Frederick D. Gregory |