Hydrosphere facts for kids
The hydrosphere is all the water found on, under, and above the Earth's surface. This includes water in oceans, lakes, rivers, and even the air. It also includes water frozen in glaciers and ice caps. The word "hydrosphere" comes from Greek words meaning "water" and "sphere."
Earth's hydrosphere has existed for about 4 billion years. It is always slowly changing its shape. This happens because of things like seafloor spreading and continental drift. These processes constantly rearrange the land and oceans.
Our planet has a huge amount of water, about 1.386 billion cubic kilometers. Most of this water, about 97.5%, is saltwater found in the oceans. Only 2.5% is fresh water. A large part of this fresh water (68.9%) is frozen in ice and glaciers. About 30.8% is groundwater deep underground. Only a tiny amount, 0.3%, is easily available in lakes, rivers, and reservoirs.
The total weight of Earth's hydrosphere is enormous. It is about 1.4 million billion tonnes. This is about 0.023% of Earth's total weight. At any time, about 20 trillion tonnes of water are in the air as water vapor. Oceans cover about 71% of Earth's surface. The average ocean water has about 35 grams of salt per kilogram of water.
Contents
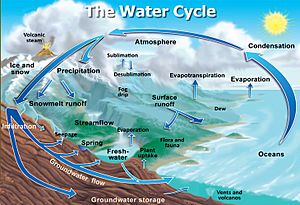
How Water Moves: The Water Cycle
The water cycle describes how water moves around our planet. Water changes its form and location constantly. It can be in the air as clouds, fall as rain or snow, or flow in rivers and oceans. It can also be stored underground as groundwater or frozen in polar ice caps.
The sun's energy, as heat and light, powers the water cycle. Gravity also helps water move from one place to another. Most water evaporation happens from the oceans. This water then returns to Earth as rain or snow. When snow and ice turn directly into vapor, it's called sublimation. When plants release water vapor through their leaves, it's called transpiration. Scientists often use the term Evapotranspiration to include all three processes: evaporation, sublimation, and transpiration.
The hydrosphere is like a closed system. This means the total amount of water on Earth stays pretty much the same. Water can get polluted or misused, but it is not created or destroyed. It just moves around. Scientists believe that water vapor does not escape into space.
Every year, a huge amount of water moves through the water cycle. About 577,000 cubic kilometers of water evaporate from oceans and land. The same amount falls back as rain or snow. The difference between the rain on land and the water that evaporates from land becomes the water in rivers and groundwater that flows into the ocean. This fresh water is vital for all life and human activities.
Water is essential for life. Since two-thirds of Earth is covered by water, our planet is often called the "blue planet." The hydrosphere also played a big role in forming Earth's atmosphere. When Earth first formed, it had a very thin atmosphere. As Earth cooled, gases and water vapor were released. This water vapor condensed and fell as rain, filling depressions and forming the oceans about 4 billion years ago.
The first life forms appeared in the oceans. These early organisms did not need oxygen. Later, tiny organisms called cyanobacteria evolved. They started turning carbon dioxide into food and oxygen. This process gradually filled Earth's atmosphere with oxygen. This unique atmosphere allowed for the amazing diversity of life we see on Earth today.
How Humans Affect the Water Cycle
Human activities have a big impact on the water cycle. Things like building dams directly change how water flows. Pollution from human activities can harm water systems. Climate change also affects weather patterns, leading to more extreme events like floods or droughts. Humans are also using more and more water for farming, cities, and industries.
How Long Water Stays in Different Places
Water stays in different parts of the hydrosphere for different lengths of time. For example, it takes about 2,500 years for all the water in the oceans to be completely refreshed. Water in permafrost and ice can stay there for 10,000 years. Deep groundwater and mountain glaciers hold water for about 1,500 years. Water in lakes stays for about 17 years, and water in rivers moves much faster, staying for only about 16 days.
Fresh Water for People
"Specific water availability" means how much fresh water is left for each person after all uses. Fresh water is not spread evenly across the world. Some areas can have floods at one time and water shortages just months later. In 1998, 76% of the world's population had less than 5,000 cubic meters of fresh water per person per year. By 1998, 35% of people faced "very low or catastrophically low water supplies." Experts predicted that by 2025, most of the world's population would live with low water supplies. Remember, only 2.5% of Earth's water is fresh, and only a tiny fraction (0.25%) is easily available for us to use.
Human Impact on Water Resources
Modern human activities greatly affect the hydrosphere. For example, diverting water, building cities, and pollution all change natural water processes. Humans are taking water from underground aquifers and changing rivers at a very fast rate.
The Ogallala Aquifer in the United States is a huge underground water source. It is used a lot for farming. If this aquifer runs dry, it could cause a loss of over $20 billion worth of food and fiber. This aquifer is being used much faster than it can refill naturally. This means it will eventually run dry.
Also, only one-third of the world's rivers flow freely. This is because of many dams, levees, and hydropower projects. These projects change habitats and water flow. Too much water use also makes streams that flow only sometimes become even drier. This is dangerous because these streams are very important for cleaning water and providing homes for animals.
Other ways humans impact the hydrosphere include eutrophication (too many nutrients in water), acid rain, and ocean acidification. Humans also depend on a healthy hydrosphere for many things. We use it for drinking water, transportation, fishing, farming, energy, and fun activities.
See also
 In Spanish: Hidrósfera para niños
In Spanish: Hidrósfera para niños
- Aquatic ecosystem
- Biosphere
- Climate system
- Cryosphere
- Lithosphere
- World ocean
- Pedosphere
- Water cycle
- Extraterrestrial liquid water
- List of largest lakes and seas in the Solar System
- Ocean world
 | Charles R. Drew |
 | Benjamin Banneker |
 | Jane C. Wright |
 | Roger Arliner Young |