Dorado facts for kids
| Constellation | |
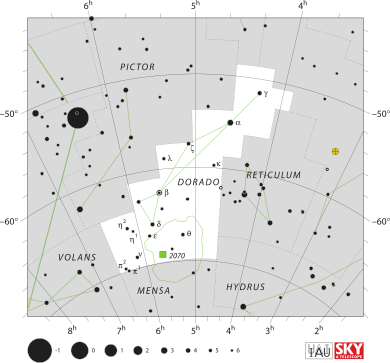
List of stars in Dorado
|
|
| Abbreviation | Dor |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Doradus |
| Pronunciation | /dəˈreɪdoʊ/, genitive /dəˈreɪdəs/ |
| Symbolism | the dolphinfish |
| Right ascension | 5h |
| Declination | −65° |
| Quadrant | SQ1 |
| Area | 179 sq. deg. (72nd) |
| Main stars | 3 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars |
14 |
| Stars with planets | 5 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 0 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 0 |
| Brightest star | α Dor (3.27m) |
| Messier objects | 0 |
| Meteor showers | None |
| Bordering constellations |
Caelum Horologium Reticulum Hydrus Mensa Volans Pictor |
| Visible at latitudes between +20° and −90°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of January. |
|
Dorado is a cool constellation you can find in the Southern Sky. Imagine a giant picture in the stars! This constellation got its name in the late 1500s. Today, it's one of the 88 official constellations recognized by astronomers.
The name "Dorado" comes from the Spanish word for "golden." It refers to the mahi-mahi fish, which is also called a "dolphinfish." Sometimes, it's even shown as a swordfish!
A super interesting fact about Dorado is that it holds most of the Large Magellanic Cloud. This is a whole other galaxy close to our own! The South Ecliptic pole, which is a special point in the sky, is also located in this constellation.
Even though "Dorado" is a Spanish word, astronomers use the Latin form Doradus when they name its stars. This is a common practice for constellations.
Contents
History of Dorado
Dorado was one of twelve new constellations named by a Dutch mapmaker named Petrus Plancius. He used observations from two explorers, Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman.
You could first see Dorado:
- On a celestial globe (a map of the stars) made in 1597 or 1598 in Amsterdam.
- In the first star atlas, called Uranometria, published in 1603 by Johann Bayer.
- In 1627, it was also called "Xiphias," which means swordfish. But the name Dorado eventually became the most popular.
In early 2020, something amazing was found in Dorado: TOI 700 d. This was the first Earth-sized planet discovered outside our solar system that might be in a "habitable zone" – meaning it could have liquid water! Astronomers found it using the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite.
Cool Features in Dorado
Stars in Dorado
Alpha Doradus is the brightest star in Dorado. It's a blue-white star, about 176 light-years away from Earth.
Beta Doradus is a special type of star called a Cepheid variable star. This means its brightness changes over time, getting brighter and dimmer in a regular pattern. It's a yellow supergiant star, about 1,040 light-years away. Its brightness changes over a period of about 9 days and 20 hours.
R Doradus is another interesting variable star in Dorado. It looks like the biggest star in the sky (besides our Sun) because of its huge apparent size.
S Dor is a super bright star called a hypergiant in the Large Magellanic Cloud. It's so important that a whole group of variable stars is named after it!
In 1987, a huge star explosion called Supernova 1987A happened in Dorado. It was the closest supernova seen since telescopes were invented! Its leftover cloud is called SNR 0509-67.5.
HE 0437-5439 is a hypervelocity star. This means it's moving so fast that it's actually escaping from our Milky Way galaxy and the Magellanic Cloud system!
The South Ecliptic pole, a special point in the sky, is located near the "head" of the fish in Dorado.
Deep-Sky Objects in Dorado
Dorado is packed with amazing deep-sky objects because it contains a big part of the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC).
The Large Magellanic Cloud is a satellite galaxy of our own Milky Way galaxy. Think of it as a smaller galaxy orbiting our bigger one! It's about 179,000 light-years away and is about 25,000 light-years wide. It has over 10,000 million stars! Its shape has been changed a bit by the gravity of our Milky Way.
Here are some cool objects in Dorado:
- NGC 1566 is a spiral galaxy that we see face-on, like looking straight down at a spinning pinwheel. It's the brightest galaxy in its own group of galaxies.
- NGC 1763 is a bright cloud of gas and dust, called a nebula. It's lit up by three very hot, bright stars.
- NGC 2080, also known as the "Ghost Head Nebula," is a huge cloud of gas about 50 light-years wide. It gets its name from two bright white patches that look like eyes. These patches are places where new stars are being born! Different parts of the nebula glow in different colors: green from oxygen, red from hydrogen, and yellow where both are present.
- The Tarantula Nebula is another famous object in the Large Magellanic Cloud. It's named for its spider-like shape and is so bright you can even see it without a telescope! It's much bigger and brighter than any nebula in our own Milky Way. Its light comes from a cluster of super bright stars at its center.
- N44 is a giant "superbubble" in the Large Magellanic Cloud, about 1,000 light-years wide. It's like a huge, empty bubble in space, carved out by the strong winds from 40 hot stars at its center. Inside N44, there's a smaller bubble called N44F, which is about 35 light-years across. It has an incredibly hot star at its center, blowing winds at 7 million kilometers per hour!
Dorado in Other Cultures
In Chinese astronomy, the stars of Dorado are part of two special groups called the "White Patches Attached" and the "Goldfish."
Namesakes
Two submarines of the United States Navy, the Dorado (SS-248) and Dorado (SS-526), were named after the same sea creature as the constellation.
Gallery
See also
 In Spanish: Dorado (constelación) para niños
In Spanish: Dorado (constelación) para niños
- Dorado in Chinese astronomy
- List of official constellations




