Economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic facts for kids
The COVID-19 pandemic caused major changes to the world's economy. It led to the COVID-19 recession, a time when business slowed down across the globe. Many businesses in the service industry, like restaurants and hotels, were affected by COVID-19 lockdowns, when people had to stay home.
The pandemic caused:
- The 2020 stock market crash, a time when the value of companies dropped quickly.
- Problems getting products from factories to stores, known as the 2021–2023 global supply chain crisis.
- A rise in prices for many goods, called the 2021–2023 inflation surge.
- Shortages of items like computer chips, which are needed for phones and game consoles.
- Panic buying, where people bought more than they needed, leaving shelves empty.
To help people and businesses, governments provided a large amount of money, called stimulus. The pandemic also played a part in a global energy crisis and food shortages in the years that followed.
During the first part of the pandemic, many businesses lost money and had to let workers go. Companies that relied on face-to-face contact, like travel and tourism, were hit the hardest. However, government help prevented many businesses from having to close down for good. The travel and tourism industry alone was one of the most affected sectors.
As the world began to recover, there was a lot of uncertainty about the future. Experts disagreed on how long the effects would last and what the recovery would look like. One major effect was a big increase in prices for everyday items, partly because energy costs went up as the world's economy started to get back on track.
Contents
A Global Economic Slowdown
In 2020, stock markets around the world had their worst crash since 1987. The world's largest economies shrank. The International Labour Organization estimated that the world lost the an amount of work equal to 400 million full-time jobs between April and June 2020.
In Europe, business investment dropped sharply, especially when lockdowns were in place. Many companies became worried about the future. A report from the European Investment Bank in 2020-21 showed that uncertainty was the biggest reason companies were not investing. Because of the pandemic, about half of European companies started using more digital technology, like working online.
Government debt in the European Union (EU) also grew. This is because governments spent more money to support people and businesses. The EU's economy saw the biggest drop ever recorded in a single quarter. The impact was different across countries. Southern Europe was hit harder than Central and Eastern Europe.
Some industries were affected more than others. Businesses that need people to be physically present, like travel, arts, and restaurants, suffered the most. Other industries, like farming and banking, were less affected.
Economic Recovery Programs
Countries and cities around the world created programs to help their economies recover. Some of these programs included Next Generation EU and the Pandemic Emergency Purchase Programme.
Pandemic Emergency Purchase Programme (PEPP)
The Pandemic Emergency Purchase Programme (PEPP) was started by the European Central Bank in March 2020. Its goal was to keep prices stable and make sure money was available for businesses and governments during the pandemic. The program allowed the bank to buy bonds from both private companies and governments. This helped to calm down financial markets and keep borrowing costs low. The program was very flexible, which helped it adapt to the changing situation. It ended in March 2022.
Next Generation EU (NGEU)
The Next Generation EU (NGEU) is a large economic recovery plan started by the European Union in July 2020. It aimed to help the EU recover from the pandemic by investing in green energy, digital technology, and public health. It was the first time that EU member states borrowed money together on a large scale to fund a recovery.
The plan included several parts, with the largest being the Recovery and Resilience Facility (RRF). This part provided money to EU countries for specific projects and reforms, especially those focused on making their economies greener and more digital. Countries like Italy and Spain received large amounts of funding. The NGEU is credited with helping the European economy grow after the pandemic.
Environment
A 2020 study found that the pandemic itself had a small direct effect on climate change. However, the study showed that a well-planned economic recovery could help reduce global warming. For a big impact, the world's economies would need to make major changes to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels.
The United Nations Environment Programme found that of all the money spent on recovery in 2020, only a small amount went toward fighting climate change. An analysis of the G20 countries found that about 6% of their recovery money was spent on areas that would cut greenhouse gas emissions, like electric cars and renewable energy.
Agriculture and Food
The pandemic created challenges for food security around the world. In 2022, these challenges contributed to a global food crisis.
Financial Markets
The pandemic caused major turmoil in financial markets, including stocks, bonds, and commodities like oil. In March 2020, there was a stock market crash and a collapse in oil prices. The United Nations Development Programme expected that developing countries would lose a huge amount of income and that the economic effects could last for years.
Manufacturing
The pandemic caused a global shortage of computer chips, which are used in everything from cars to video game consoles.
This led to a crisis in car production in 2021. In the United States, major car companies had to shut down their factories. In the United Kingdom, car production in July 2021 fell to its lowest level since 1956.
Arts, Entertainment, and Sports
The pandemic had a huge impact on the arts and culture. Museums, theaters, and other cultural institutions around the world closed. Events, concerts, and performances were canceled or postponed. Many people working in these fields lost their jobs.
Cinema
With cinemas closed, the global box office lost billions of dollars. At the same time, streaming services like Netflix became more popular. The release of almost all major movies was delayed, and film production was stopped.
Sports
Most major sporting events were canceled or postponed. This included the 2020 Summer Olympics in Tokyo, which were moved to 2021.
Television
The production of many TV shows was shut down or delayed. However, streaming of TV shows and movies increased by over 30% worldwide in March 2020.
Video Games
The pandemic caused some delays in the production of video game consoles due to supply chain problems. Major gaming events like E3 2020 were canceled. However, the video game industry was not hit as hard as other entertainment sectors. Much of the work could be done remotely, and games could be sold digitally.
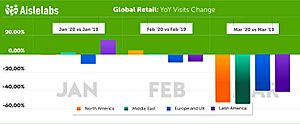
Retail

The retail industry was heavily impacted. Shopping centers around the world reduced their hours or closed. The number of people visiting stores dropped significantly. At the same time, there was huge demand for certain products, which led to empty shelves in many stores.
Some retailers started offering contactless home delivery or curbside pickup for items bought online. This "retail to go" model became very popular.
Many well-known department stores faced financial trouble. Some, like J.Crew and JCPenney, had to file for bankruptcy.
E-commerce
The pandemic led to a massive boom in e-commerce, or online shopping. With people staying home, fewer shopped in physical stores. Online sales grew by 34% in 2020 and continued to grow in 2021. The pandemic changed how people shop, and many of these changes have continued.
Restaurant Sector

The restaurant industry was hit hard. Many cities and states forced restaurants to close for sit-down dining. They could only offer takeout and delivery. This meant that many servers and bartenders were laid off. To support local restaurants, some people participated in events like the "Great American Takeout," encouraging people to order takeout.
Tourism
Tourism was one of the sectors most affected by the pandemic. This was because of:
- Travel restrictions and quarantines.
- Fear of being in crowded places like airports.
- Concerns about getting sick in another country.
- Many tourism businesses going bankrupt.
- Rising costs for flights.
Transportation
The pandemic caused major disruptions in transportation. There were not enough workers for trucking and at ports, which created bottlenecks.
Aviation

The aviation industry was severely affected by travel restrictions and a drop in demand. With far fewer passengers, many planes flew empty or flights were canceled altogether. Airlines parked thousands of planes that were not in use.
Cruise Lines
Cruise lines had to cancel sailings. News stories about sick passengers on quarantined ships hurt the industry's image, and bookings dropped.
Losing Jobs
The International Labour Organization predicted that the world would lose the equivalent of 195 million full-time jobs in the second quarter of 2020 alone.
In March 2020, more than 10 million Americans lost their jobs and applied for government help. The lockdown in India left tens of millions of migrant workers unemployed. In Spain, nearly 900,000 workers lost their jobs after the country went into lockdown. Many other countries faced similar situations.
Economic Impact Around the World
The pandemic affected every country, but the impact was different from place to place.
China
The pandemic began in China, and its economy was the first to be hit. Factories and stores closed, and travel was restricted. The sale of new cars dropped by 92% in the first two weeks of February 2020. However, China's economy began to recover later in 2020. It was the only major economy to grow that year, partly due to strong government measures to control the virus and support the economy.
United States
In the U.S., the stock market saw its biggest weekly loss since the 2008 financial crisis. Many businesses, schools, and public events were closed or canceled. In April 2020, more than 20 million Americans filed for unemployment, a record high. The government passed several large aid packages to help people and businesses, including the CARES Act.
Europe
The economy of the European Union shrank significantly in 2020. The Bank of France declared that the French economy was in a recession. In the Republic of Ireland, thousands of people lost their jobs in a very short time, and the government launched several programs to provide financial support. In Italy, a nationwide quarantine was put in place, and most businesses were closed.
South America
Countries in Latin America and the Caribbean were already facing slow economic growth before the pandemic. The crisis made the situation worse. The region's economy shrank by 8.1% in 2020, and millions of people fell into poverty.
See also
- Contactless payment
- Distance learning
- Financial market impact of the COVID-19 pandemic
- Remote work
- Shortages related to the COVID-19 pandemic