Fallow Deer facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Fallow Deer |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Male (buck) | |
 |
|
| Female (doe) | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: |
Cervinae
|
| Genus: |
Dama
|
| Species: |
D. dama
|
| Binomial name | |
| Dama dama (Linnaeus, 1758)
|
|
 |
|
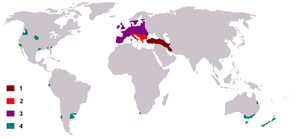
| Range 1: Native 2: Possibly native 3: Early human introductions 4: Modern human introductions |
|
The Fallow Deer (Dama dama) is a type of deer that belongs to the deer family, Cervidae. These animals first lived in Eurasia, which includes Europe and Asia. Over time, people have moved them to many other parts of the world, such as Australia.
Male fallow deer are called bucks, females are called does, and their babies are called fawns. They usually live for about 12 to 16 years. All fallow deer have white spots on their backs and black tips on their tails. Only the bucks grow antlers, which are wide and shaped like a shovel.
Fallow deer are grazing animals, meaning they eat grass and other plants. They prefer to live in areas that have both mixed woodlands and open grasslands. They like to stay together in large groups, sometimes with as many as 150 deer.
Contents
About Fallow Deer: Appearance and Behavior
A male fallow deer is called a buck, a female is a doe, and a young one is a fawn. Adult bucks are about 140 to 160 centimeters (55 to 63 inches) long. They stand about 85 to 95 centimeters (33 to 37 inches) tall at the shoulder. Bucks typically weigh between 60 and 100 kilograms (130 to 220 pounds).
Does are a bit smaller. They are usually 130 to 150 centimeters (51 to 59 inches) long and 75 to 85 centimeters (30 to 33 inches) tall at the shoulder. Does weigh about 30 to 50 kilograms (66 to 110 pounds). The largest bucks can be up to 190 centimeters (75 inches) long and weigh 150 kilograms (330 pounds).
Fawns are born in spring, measuring around 30 centimeters (12 inches) tall and weighing about 4.5 kilograms (10 pounds). Fallow deer generally live for 12 to 16 years.
Fallow Deer Coat Colors
Fallow deer can have many different coat colors. There are four main types: common, menil, melanistic, and leucistic. These are natural color variations, not albinism.
- Common: This is the most typical color. Their coat is chestnut brown with white spots, especially noticeable in summer. In winter, their coat becomes darker and the spots are less clear. The area around their tail is light with a black edge, and their tail has a black stripe.
- Menil: These deer have more distinct spots than the common type in summer. They do not have black around their rump or on their tail. In winter, their spots are still clear on a darker brown coat.
- Melanistic (black): These deer have a black coat all year round, sometimes shading to grayish-brown. They do not have a light-colored tail patch or any spots. They can sometimes be mistaken for sika deer.
- Leucistic (white): Fawns are cream-colored, and adults become pure white, especially in winter. They have dark eyes and noses, and no spots. This is a true color variety, not albinism.
Most herds have the common coat color, but menil deer are also quite common. The melanistic (black) variation is rarer, and the white (leucistic) type is even rarer. However, some wild herds in New Zealand have a high number of melanistic deer.
Antlers and Habitat
Only male fallow deer (bucks) grow antlers. From three years old, their antlers become broad and shovel-shaped, which is called "palmate." In their first two years, their antlers are just single spikes.
Fallow deer are grazing animals, meaning they eat grass and other plants. They prefer to live in areas that have a mix of woodlands and open grasslands. During the breeding season, called the rut, bucks spread out. Females move between them. At this time, fallow deer are less grouped than usual. For the rest of the year, they try to stay together in groups of up to 150.
Speed and Agility
Fallow deer are very agile and fast when they are in danger. They can run up to 48 kilometers per hour (30 miles per hour) over short distances. While they are not as fast as some other deer like roe deer, they are still quick. Fallow deer can also jump quite high, up to 1.75 meters (5.8 feet) high, and up to 5 meters (17 feet) in length.
Where Fallow Deer Live: Distribution and History
The fallow deer is a type of deer that originally lived in Eurasia. During the last ice age, they were found across most of Europe. Later, their natural home became limited to the Middle East and possibly parts of the Mediterranean region. Another type, the Persian fallow deer, lived further southeast in western Asia. This type is bigger and has larger antlers.
In the Levant (an area in the Middle East), fallow deer were an important food source for people during the Stone Age. However, their numbers went down later, possibly because the climate became drier and there were fewer wooded areas.
Fallow Deer in Argentina
Fallow deer were brought to Victoria Island in Argentina by a rich person named Aaron Anchorena. He wanted to create more hunting opportunities. He released many European and Asian animals, including fallow deer, onto the island. These new animals now live there and compete for land and food with native deer like the South Andean deer and Pudú deer.
Fallow Deer in Britain and Ireland
The Romans helped spread fallow deer across central Europe. For a long time, people thought the Normans brought them to Great Britain for hunting in royal forests. However, recent discoveries at Fishbourne Roman Palace show that fallow deer were in southern England as early as the first century AD. It's not clear if these deer escaped and formed wild groups, or if they died out and were later reintroduced by the Normans.
Fallow deer are now common across the UK mainland. They live in most of England and Wales, especially in lowland areas. Old populations exist in the New Forest and the Forest of Dean. Many other groups started from deer that escaped from parks. They are less common in northern England but are found in parts of Scotland, like the Tay Valley and around Loch Lomond.
According to a 2007 survey, their numbers have increased since 2000. In Ireland, a large, long-established herd of about 450 fallow deer lives in Phoenix Park in Dublin.
Many fallow deer in the Forest of Dean and Epping Forest are of the black color type. There is also a special group called "long-haired fallow deer" in Mortimer Forest on the border of England and Wales. A large part of this group has long hair, distinct ear tufts, and longer body hair.
Fallow Deer in Rhodes, Greece
The fallow deer population on the island of Rhodes in Greece is generally smaller than those in central and northern Europe. However, they have similar colors. In 2005, scientists found that the Rhodian fallow deer are genetically unique from all other populations. This means they are very important to protect. At the entrance to the harbor of Rhodes city, there are now statues of a fallow deer buck and doe. These statues stand where the famous Colossus of Rhodes once stood.
Fallow Deer in the United States
Fallow deer have been brought to parts of the United States more recently. A small group of wild fallow deer lives on a barrier island in Georgia. Fallow deer have also been introduced in Texas, along with many other types of deer. They are often hunted on large game ranches there. They also live in Rhode Island.
In Pennsylvania, fallow deer are considered farm animals because there are no wild groups breeding there. If wild fallow deer are seen in Pennsylvania, it's usually because they escaped from farms or special preserves.
A herd of white fallow deer lives near Argonne National Laboratories in northeastern Illinois.
A small herd of about 15 mostly white fallow deer lives at the Belle Isle Nature Zoo on Belle Isle in Detroit, Michigan. For a long time, this herd roamed freely on the island. Later, they were kept in an enclosed area.
A small herd in Land Between the Lakes National Recreation Area (LBL) in Kentucky and Tennessee is thought to be the oldest in the United States. The Hillman Land Company brought this herd to LBL in 1918. At one time, it was the largest fallow deer population in the country. Today, the herd has fewer than 150 deer, and hunting them is not allowed. Even though LBL focuses on native animals, the fallow deer herd is kept for people to see and because of its historical importance.
Fallow Deer in South Africa
Fallow deer have been introduced to the Cape Province in South Africa. They are also popular in rural areas of KwaZulu-Natal for hunting. In parts of the Gauteng province, they are used to make ranches look nicer. In the Eastern Cape, they were brought to game farms for hunting because they are considered exotic. Fallow deer have adapted very well to the South African environment, especially in cooler areas like the Highveld, where they have access to savanna grasslands.
Fallow Deer in New Zealand
Fallow deer were brought to New Zealand starting in 1860. There are now large herds in several low-altitude forests across the country.
Historical Herds
One famous historical herd of fallow deer is in the Ottenby Preserve in Öland, Sweden. In the mid-17th century, King Karl X Gustav built a stone wall about 4 kilometers (2.5 miles) long to keep a royal fallow deer herd. This herd still exists today. Another well-known herd is in Phoenix Park in Ireland. This herd of 400–450 fallow deer are descendants of the original deer introduced in the 1660s.
What's in a Name?
The name "fallow" comes from the deer's pale brown color. The scientific name, dāma or damma, is a Latin word that was used for deer, gazelles, and antelopes. This Latin word is also the root of the German word Damhirsch, the French daim, the Dutch damhert, and the Italian daino.
In Croatian and Serbian, the fallow deer is called jelen lopatar, which means "shovel deer." This name comes from the unique shovel-like shape of the male's antlers. The Hebrew name for the fallow deer is yachmur. This name comes from the Aramaic language, where chamra means "red" or "brown."
See also
 In Spanish: Dama (género) para niños
In Spanish: Dama (género) para niños










