False Indian plantain facts for kids
Hasteola suaveolens, often called the false Indian plantain or sweet scented Indian plantain, is a type of plant that lives for many years. It grows naturally in the northeastern and central parts of the United States. You can find it from Massachusetts down to Virginia and North Carolina, and as far west as Minnesota and Missouri.
Quick facts for kids False Indian plantain |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: |
Hasteola
|
| Species: |
H. suaveolens
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hasteola suaveolens |
|
| Synonyms | |
Contents
What Does It Look Like?
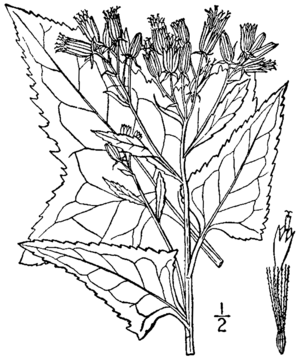
The false Indian plantain is a perennial herb. This means it's a plant without a woody stem that comes back year after year. It can grow quite tall, sometimes up to 240 centimeters (about 8 feet).
Its stems are smooth and do not have branches below the flowers. The leaves are shaped like spearheads, which is called "hastate." They are about 10 to 25 centimeters (4 to 10 inches) long. The leaves are also 5 to 15 centimeters (2 to 6 inches) wide. Their edges are "serrated," meaning they have small, saw-like teeth.
Flowers and Fruit
This plant blooms in late summer or early fall. Its flowers grow in flat-topped groups called "inflorescences." Each group has many small flower heads. These heads are made up of 18 to 55 tiny white or very pale yellow "disc florets." Unlike some other daisy-like flowers, it does not have "ray florets," which are the petal-like parts.
After the flowers, the plant produces a small fruit called a cypsela. This fruit has a fluffy top, known as a pappus, made of white bristles. This pappus helps the seeds float away in the wind.
Where Does It Grow?
Hasteola suaveolens naturally grows in 22 states east of the Mississippi River. It also grows in two states west of the river, all within the eastern and central USA.
Protecting the Plant
This plant is becoming rare in some areas. It is listed as an endangered species in Connecticut, Maryland, Minnesota, and New York. This means it is at risk of disappearing completely from these states. It is also listed as "threatened" in Iowa and Tennessee. In Rhode Island, it is considered "historical," which means it is thought to be gone from that area.
The false Indian plantain is now less common in the northern parts of its range. There might be only one group of these plants left in all of New England.
Its Favorite Places
In Virginia, this plant likes to grow in places like floodplain forests and along riverbanks. You can find it near the Potomac, Shenandoah, and New rivers.
The plant needs the right kind of habitat to survive. It can disappear from an area if land is developed or used differently. It also struggles when invasive species (plants that are not native) take over its space. In Minnesota, it used to grow in wet meadows near streams and marshes. But because many of these wet areas are gone, it might now only be found in wet ditches.