Heavy-footed moa facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Heavy-footed moaTemporal range: Late Pleistocene-Holocene
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
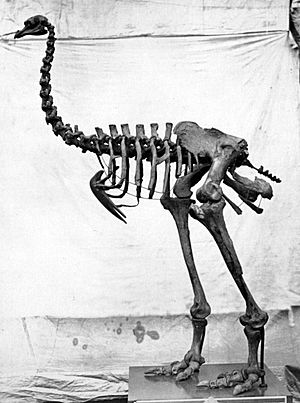
| P. elephantopus skeleton photographed by Roger Fenton | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | †Dinornithiformes |
| Family: | †Emeidae |
| Genus: | †Pachyornis |
| Species: |
†P. elephantopus
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Pachyornis elephantopus (Owen, 1856) Lydekker 1891 non Cracraft 1976
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
List
Dinornis elephantopus Owen, 1856
Euryapteryx elephantopus (Owen 1856) Hutton 1892 Dinornis queenslandiae De Vis, 1884 Pachyornis queenslandiae (De Vis 1884) Oliver 1949 Dromiceius queenslandiae (De Vis 1884) Miller 1963 Euryapteryx ponderosus Hutton, 1891 non Hamilton 1898 Pachyornis immanus Lydekker, 1891 Euryapteryx immanis (Lydekker 1891) Lambrecht 1933 Pachyornis inhabilis Hutton, 1893 Pachyornis major Hutton, 1875 Pachyornis rothschildi Lydekker, 1892 Pachyornis valgus Hutton, 1893 Euryapteryx crassa Benham 1910 non (Owen 1846) Hutton 1896 Pachyornis murihiku Oliver 1949 |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The heavy-footed moa (Pachyornis elephantopus) was a type of moa, a large bird that could not fly. It lived only on the South Island of New Zealand. This moa preferred flat areas like shrublands, sand dunes, grasslands, and forests.
Moa belong to a group of birds called ratites. These birds are special because they are flightless and have a flat sternum (breastbone) without a keel, which is the part where flight muscles usually attach. Scientists now think that the early ancestors of these birds could fly. They likely flew to the southern lands where their fossils are found today.
The heavy-footed moa was quite large. It stood about 1.8 m (5.9 ft) tall and could weigh up to 145 kg (320 lb). Only a few complete or partly complete moa eggs have been found. Three of these are believed to be from the heavy-footed moa, all found in Otago. These eggs were about 226mm long and 158mm wide. This makes them the second largest moa eggs ever found, after the single egg from the South Island giant moa.
Contents
Discovering the Heavy-Footed Moa
The heavy-footed moa was first discovered by W.B.D. Mantell. He found its bones at Awamoa, near Oamaru, and took them to England. Bones from several different birds were put together to create a full skeleton. This skeleton was then placed in the British Museum. The famous scientist Richard Owen gave this new species the name Dinornis elephantopus.
Where the Heavy-Footed Moa Lived
The heavy-footed moa was found only on the South Island of New Zealand. Its home covered most of the eastern side of the island. There were slightly different types of this species in the northern and southern parts of its range.
These moa mostly lived in low-lying areas. They liked dry, open places such as grasslands, shrublands, and dry forests. They did not live in high mountain areas or sub-alpine regions. In those colder, higher places, another type of moa, the crested moa (Pachyornis australis), lived instead.
During a time when the Earth was warming up, called the Pleistocene-Holocene warming event, glaciers melted. This created more of the dry, open habitats that the heavy-footed moa liked. As a result, they were able to spread out and live in more places across the island.
What the Heavy-Footed Moa Ate
Before people arrived, New Zealand had a very special group of plants and animals. There were no native land mammals. Moa birds, including the heavy-footed moa, filled the role of large plant-eaters, similar to how large mammals do in other parts of the world. This changed when Polynesian settlers arrived around the 13th century, bringing mammals with them.
Scientists used to wonder exactly what the heavy-footed moa ate. Its unique head and beak shape suggested it ate different things than other moa species. Its preferred dry, shrubby home hinted that it might eat tougher plants. Eating different foods would have helped it avoid competing with other moa species that lived in the same areas.
In 2007, a scientist named Jamie Wood studied the contents of a heavy-footed moa's gizzard for the first time. The gizzard is a muscular part of a bird's stomach that helps grind food. They found parts of 21 different plant types. These included Hebe leaves, various seeds, and mosses. They also found a lot of twigs and wood, some of which were quite large. This discovery showed that the heavy-footed moa was indeed able to eat tough plants. But it also showed that it had a varied diet and could eat many different plant parts, even wood.
The only natural predator of the heavy-footed moa (before humans and other mammals arrived) was the Haast's eagle. However, recent studies of ancient droppings, called coprolites, have shown that these moa also had several types of parasites living on or inside them. These included nematode worms, which are a type of roundworm.
Museum Specimens
A complete skeleton of a heavy-footed moa from Otago, New Zealand, is on display. You can see it in the Collectors' Cabinet gallery at Leeds City Museum in the UK.



