Ice Hockey World Championships facts for kids

IIHF World Championship Cup
|
|
| Sport | Ice hockey |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1920 (1920 Summer Olympics) 1930 (First individual event) |
| No. of teams | 16 (Top division) 12 (Division I) 12 (Division II) 12 (Division III) 6 (Division IV) |
| Country | IIHF member countries |
| Continent | Worldwide |
| Most recent champion(s) |
|
| Most titles | |
| Official website | IIHF.com |
The Ice Hockey World Championships are a huge international ice hockey tournament for men's teams. It happens every year and is organized by the International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF). The very first official championship was held way back at the 1920 Summer Olympics.
The IIHF, which is like the main boss for ice hockey around the world, started in 1908. Before the World Championships, there were the European Championships, which began in 1910. The hockey tournament at the 1920 Summer Olympics is seen as the first World Championship. From 1920 to 1968, the Olympic hockey winner was also named the World Champion for that year.
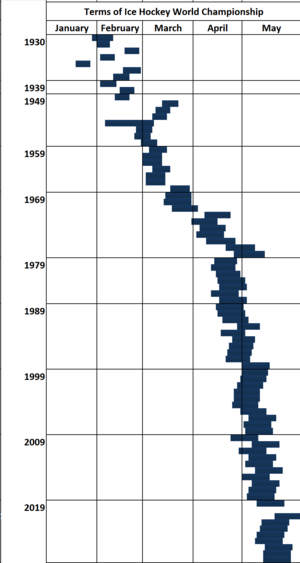
The first time the World Championship was held as its own event was in 1930. Twelve countries played in it. Over the years, the tournament grew, and more teams joined. This led to different groups, now called divisions, to include all the teams.
Today, the main World Championship group has 16 teams. There are also other divisions for more teams. The top eight teams in the main group play in a playoff round. The team that wins this playoff is crowned the World Champion! Many rules have changed over time, like allowing body-checking everywhere on the ice. Also, players started wearing helmets and goaltender masks in the 1970s.
For a long time, only "amateur" players could compete. This meant players from the National Hockey League (NHL) were not allowed. But starting in 1977, professional players could join. This made the tournament even more exciting! Players must be citizens of the country they play for.
Canada was super strong at the start, winning 12 titles between 1930 and 1952. Other teams like the United States, Czechoslovakia, and Sweden were also very good. Then, the Soviet Union joined in 1954 and became a huge rival to Canada. The Soviet Union dominated from 1963 to 1991, winning 20 championships!
After the Soviet Union broke up, new teams like Russia and the Czech Republic started playing. In recent years, the "Big Six" teams – Canada, Czechia, Finland, Russia, Sweden, and the United States – have become very evenly matched.
The World Championship happens at the same time as the NHL's Stanley Cup playoffs. This means some top NHL players might not be able to play for their national teams. They can only join if their NHL team is out of the playoffs.
The 2024 World Championship in Czechia was the most popular ever! Almost 800,000 people watched the games. The average crowd for each game was over 12,000 fans.
Contents
How Ice Hockey Championships Started

The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF) is the main group that runs ice hockey around the world. It was formed on May 15, 1908. Back then, organized ice hockey was quite new. The very first indoor game was played in Montreal, Canada, in 1875.
In 1887, some clubs in Montreal created the Amateur Hockey Association of Canada (AHAC). They made a proper schedule for games. Later, Lord Stanley donated the famous Stanley Cup. This cup was given to the best team.
The Ice Hockey European Championships were the first official tournament for national teams. They were held in Switzerland in January 1910. Great Britain, Germany, Belgium, and Switzerland were the first countries to play. In North America, professional hockey grew, and the National Hockey League (NHL) was formed in 1917. The European Championships stopped for a few years because of World War I.
Championship History
Early Olympic Tournaments (1920–1928)

The IIHF sees the ice hockey tournament at the 1920 Summer Olympics as the very first Ice Hockey World Championship. Seven teams played in it. These included Canada, the United States, and Sweden. Canada, with a team called the Winnipeg Falcons, won the gold medal. They scored 27 goals and only let in 1! The United States won silver, and Czechoslovakia took bronze.
After this, the first Winter Olympics were held in 1924. Every Olympic hockey tournament until 1968 was also counted as the World Championship. Canada won gold at the 1924 and 1928 Winter Olympics. In 1928, Sweden and Switzerland won their first medals.
Canada's Strong Start (1930–1953)
The first World Championship held as its own event was in 1930. Canada won the gold medal, beating Germany. Switzerland won the bronze. Canada continued to win many championships in the early 1930s.
In 1933, the United States won the gold medal. This was the first time a team other than Canada won the competition. At the 1936 Winter Olympics, Great Britain became the first non-Canadian team to win Olympic gold. Canada won most of the World Championships in the 1930s. Finland played in the tournament for the first time in 1939. World War II caused the championships to be cancelled from 1941 to 1946.
After World War II, Czechoslovakia's team got much better. They won the 1947 World Championships. In 1949, they won another championship, even with Canada playing.
At the 1952 Winter Olympics, Canada's Edmonton Mercurys won their second straight Olympic gold. This was Canada's 15th World Championship title. It was also the last time a Canadian team won Olympic hockey gold for 50 years. In 1953, Canada did not attend. Sweden won their first World Championship that year.
Canada vs. Soviet Union Rivalry (1954–1962)

The 1954 World Championships marked a new era. The Soviet Union played for the first time. They had started their first ice hockey league in 1946. The Soviet team won their first six games. Canada was also undefeated. In the final game, the Soviet Union beat Canada 7–2. This made them the fifth team to win a World Championship.
In 1956, the Soviets went undefeated and won their first Olympic ice hockey gold medal. It took seven more years for them to win another World Championship. The 1957 World Championships were held in Moscow. Canada and the United States did not play to protest the Soviet occupation of Hungary. Sweden won the gold medal that year.
Canada returned in 1958 and won two titles in a row. At the 1960 Winter Olympics, the American team surprised everyone. They beat Canada, the Soviet Union, Czechoslovakia, and Sweden to win their first Olympic gold medal.
In 1961, Canada beat the Soviets 5–1 to win their 19th gold medal. The Trail Smoke Eaters were the last club team to represent Canada. The next year, Canada started a national team program. Canada did not win another World Championship gold until 1994. In 1962, the World Championships were held in North America for the first time, in Denver, USA. Sweden beat Canada for the first time and won their third gold medal.
Soviet Union's Dominance (1963–1976)

At the 1963 World Championships, the Soviet Union won gold. This started a streak of nine gold medals in a row! They were almost unbeatable for four years. Their streak was broken by Czechoslovakia at the 1968 Winter Olympics. Even with that loss, the Soviets still won gold. This was the last time the Olympics also counted as the World Championships.
In 1969, the Soviet Union and Czechoslovakia played very emotional games. Czechoslovakia had to give up hosting the tournament because of the Soviet invasion of their country. The tournament was held in Sweden. The Czechoslovak team was determined to beat the Soviets, and they did, winning both games against them. However, they lost to Sweden and won bronze.

Canada felt their amateur players could no longer compete with the European teams, who were using their best players. Canada wanted to use professional players. The IIHF first agreed to let Canada use some professional players in 1970. The tournament was even supposed to be held in Canada for the first time. But this decision was changed. The Olympic Committee president was against it. So, Canada pulled out of international ice hockey for a few years.
The Soviet Union, led by amazing players like Vladislav Tretiak, won gold in 1970, 1971, and the 1972 Winter Olympics. In 1972, Czechoslovakia ended the Soviet streak at the World Championships. But the Soviets quickly returned to winning ways in 1973 and 1974. In 1976, Poland pulled off a huge upset, beating the Soviet Union 6–4. Czechoslovakia won gold that year.
Open Competition Begins (1976–1987)
In 1975, Günther Sabetzki became IIHF president. He helped solve the problem with Canada. The IIHF agreed to let all players, professionals included, play in the World Championships. The tournament was moved later in the season so NHL players whose teams were out of the playoffs could join.
The 1976 World Ice Hockey Championships were the first to allow professionals. The United States was the only team to use this new rule. The first fully "open" World Championship was in 1977. Active Canadian NHL players joined for the first time. Many Canadian players were not used to the international game. The team finished fourth. Czechoslovakia won gold.
The IIHF World Junior Championship (for players under 20) became an official world championship. The IIHF World U18 Championship (for players under 18) started in 1999.
From 1978, the Soviet team won five World Championships in a row. They had a long winning streak that lasted until 1985. Canada was still competitive, winning three bronze medals during this time. World Championship tournaments were not held in Olympic years (1980, 1984, 1988).
The 1987 World Ice Hockey Championships had some arguments. A player on the West German team had played for Poland before. The IIHF said he couldn't switch countries and took away West Germany's points. But a court in Austria disagreed. This caused some confusion in the final standings. Sweden won their first gold medal since 1962.
Changes in Hockey (1989–1992)

Before 1989, players in the Soviet Union and other Eastern European countries could not leave to play in the NHL. In 1989, this changed. Sergei Pryakhin was the first Soviet player allowed to play for a non-Soviet team. Many top Soviet players then moved to the NHL. The Soviet Union won its 21st World Championship that year.
The Soviet team won their last title in 1990. In 1991, Sweden won gold. The Soviets won bronze, which was their last medal.
The Soviet Union broke up in December 1991. Many new countries, like Belarus and Kazakhstan, joined the IIHF. Russia took over from the USSR. The IIHF increased the number of teams in the top division. From 1963 to 1991, only four teams won medals: the Soviet Union, Czechoslovakia, Sweden, and Canada. In 1992, Sweden won gold again. Finland won silver, their first World Championship medal ever!
Modern Era (1993–Present)
Czechoslovakia split into the Czech Republic and Slovakia in 1993. The Czech Republic kept its spot in the top division. Slovakia started in the lowest division and worked its way up.
The next ten years were dominated by the "Big Six" teams: Canada, Czech Republic, Finland, Russia, Sweden, and the United States. From 1992 to 1996, five different teams won the World Championship. In 1993, Russia won its first title as an independent country. The Czech Republic won its first medal.
In 1994, Canada won its first World Championship since 1961. The next year, Finland won its first World Championship, beating rival Sweden. In 1996, the Czech Republic won its first title as a separate country. The United States won bronze, their first medal since 1962. The IIHF increased the number of teams to 16 in the top division starting in 1998.

From 1996 to 2001, the Czech Republic won six medals in a row, including three gold medals from 1999 to 2001. In 2002, Slovakia won its first World Championship, beating Russia in the final. In 2003, Canada won gold in overtime against Sweden. Canada won again in 2004.
The 2004–05 NHL season was cancelled due to a player dispute. This meant more top players were available for the 2005 World Championships, which the Czech Republic won. In 2006, Sweden won Olympic gold. Three months later, Sweden also won the 2006 World Championships. They were the first team to win both in the same year.
In 2007, Canada won gold. The next year, the tournament was held in Canada for the first time. Russia beat Canada to win gold. Russia won again in 2009.
The 2010 tournament in Germany set a new attendance record for a single game. Germany beat the United States in front of 77,803 people! The tournament had many surprises. Switzerland beat Canada for the first time. Denmark reached the quarterfinals for the first time. The Czech Republic won gold, beating Russia.
The 2011 tournament was held in Slovakia. Finland won its second world championship. The Czech Republic won bronze. In 2012, Russia beat Slovakia in the final.
In 2013, Switzerland had a great run, finishing the first round undefeated. They lost the gold medal game to Sweden. Sweden became the first team to win the tournament at home since 1986.
The 2014 tournament was held in Belarus. France beat Canada, which was a big upset. Russia won the tournament. Finland won silver, and Sweden won bronze.
The 2015 tournament in Czechia was the most attended championship ever. Canada had an excellent team and went undefeated. They beat Russia 6–1 in the gold medal game. Their captain, Sidney Crosby, became the first player to win the Stanley Cup, Olympic gold, and World Championship gold as captain of each team. The United States won bronze.
The 2020 tournament was cancelled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
How the Tournament Works
Tournament Formats Over Time

The first World Championship held as its own event was in 1930. Canada got a direct pass to the gold medal game. Other countries played an elimination tournament to see who would play Canada for gold.
In 1931, the format changed. Teams played in qualifying rounds. Medals were given based on how teams finished in the final round. The format changed a few times in the 1930s. Sometimes there was a gold medal game, other times medals were given based on points.
In 1951, teams were split into two groups. The top group (Pool A) played for the World Championship. The other group (Pool B) played for ranking. This basic setup was used until 1992. People sometimes criticized this format because the gold medal winner was often known before the final game.
In 1990, the IIHF added a playoff system. As more teams joined, more groups (now called divisions) were added. Pool C games started in 1961, and Pool D in 1987. In 2001, these pools were renamed Division I, Division II, and Division III.
Modern Championship Group Format (Since 2012)
The main World Championship group has 16 teams. These teams are split into two groups of eight. This is based on their world ranking. Each team plays seven games in the first round.
The top four teams from each group move on to the playoff stage. In the quarterfinals, the first-place team from one group plays the fourth-place team from the other group. The second-place team plays the third-place team. The winners go to the semi-finals. The winners of the semi-finals play for the gold medal. The losers play for the bronze medal.
Also, since 2012, the two teams that finish last in their groups are moved down to Division I for the next year.
Division I, II, and III Formats (Since 2012)
Division I has two groups of six teams. The top two teams from Group A move up to the main championship group. The last-place team in Group A switches with the winner of Group B. The last-place team in Group B moves down to Division II.
Division II works similarly. Group A promotes one team to Division I. Group B's last-place team moves down to Division III. Division III has one group of six teams. If more than six countries want to play, a special qualifying tournament is held.
Division IV (Since 2020)
The IIHF added Division IV, which started in 2022. Teams in this division play for a chance to move up to Division III.
Game Rules
How the Game is Played
At the first tournament in 1920, hockey was quite different. Games were played outside on natural ice. Players could not pass the puck forward. There were seven players on each side, including an extra player called a "rover." After that tournament, the IIHF decided to use "Canadian rules." This meant six players per side and three periods of play.
In 1969, a big rule change happened. Officials allowed body-checking in all three zones of the rink, just like in the NHL. Before this, body-checking was only allowed in the defending zone. This made the game more aggressive. Also, players had to wear helmets starting in 1970, and goaltender masks became required in 1972.
In 1992, the IIHF started using a playoff system for medals. They also decided that tied games in the medal round would be decided by a shootout. In 1997, a new rule was tested to allow two-line passes. This helped speed up the game and create more scoring chances. The IIHF said this rule "changed the game for the better."
The current IIHF rules are a bit different from the rules used in the NHL. One difference is the size of the rink. NHL rinks are narrower. Another difference is how icings are called. The NHL uses "hybrid icing," while the IIHF uses "no-touch" icing. Also, the NHL has "major penalties" for more serious rule breaks, like fighting. In IIHF games, players who fight are usually ejected.
Since the 2005–06 season, the NHL added new rules. Some, like the shootout and two-line passes, were already used by the IIHF. In 2006, the IIHF voted to get rid of tied games. They also started a three-point system for wins. A win in regular time is worth three points. An overtime win is two points, and an overtime loss is one point.
As of 2019, all overtime periods use a 3-on-3 format, where the first team to score wins. For preliminary games, overtime is 5 minutes, followed by a shootout if needed. For quarterfinals and beyond, overtime is 10 minutes. In the gold medal game, there is no shootout. Instead, 20-minute 3-on-3 periods are played until a goal is scored.
Player Requirements
The World Championships have been open to all players, both professional and amateur, since 1977. Here are some main rules for players:
- Each player must be under the rules of an IIHF member country.
- Each player must be a citizen of the country they play for.
- Players must be at least 18 years old when the championship starts. Players who are 16 or 17 can play with special permission.
If a player changes their citizenship and has never played in an IIHF competition before, they must play in their new country's national games for at least two years. If a player has played for one country and wants to switch to another, they must have played in their new country for four years. A player can only switch national teams once.
Because the tournament happens during the NHL playoffs, many NHL players can only join if their team misses the playoffs or is eliminated. So, it's common for NHL players to join the World Championships after it has already started.
Divisions
As of 2020, the IIHF World Championships are split into five different divisions. This is how the divisions are set up, based on the 2018 IIHF World Ranking.
Keys:
 Promoted (moved up a division)
Promoted (moved up a division) Never been promoted/relegated (started in that division/group)
Never been promoted/relegated (started in that division/group) Relegated (moved down a division)
Relegated (moved down a division)
Championship Division
This is the top division with the best sixteen hockey nations. The 89th championship will be held in Switzerland in 2026.
| Nation | Group (as of 2026) |
IIHF Ranking (as of May 2025) |
Member of IIHF since |
Member of division since |
Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group B | 12 | 1912 | |||
| Group B | 4 | 1920 | |||
| Group A | 6 | 1908 | |||
| Group A | 9 | 1946 | |||
| Group B | 7 | 1928 | |||
| Group B | 8 | 1909 | |||
| Group B | 19 | 1908 | |||
| Group B | 18 | 1927 | |||
| Group A | 20 | 1924 | |||
| Group B | 11 | 1931 | |||
| Group A | 13 | 1935 | |||
| Group A | 10 | 1993 | |||
| Group A | 17 | 1992 | |||
| Group A | 5 | 1912 | |||
| Group B | 3 | 1908 | |||
| Group A | 2 | 1920 | |||
| Suspended | 16 | 1992 | |||
| Suspended | 1 | 1952 |
A. The IIHF sees Bohemia (joined 1908) and Czechoslovakia as the teams that came before the Czech Republic (joined 1993).
B. The IIHF sees the Soviet Union (joined 1952) as the team that came before Russia (joined 1992).
C. On February 28, 2022, the IIHF decided to remove Russia and Belarus from the tournament. This was due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
Player Achievements
All records are from the IIHF and are up to 2025.
| Record | Number | Held by | Team |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top division records | |||
| Most tournaments played | 20 | Andres Ambühl | |
| Most games played | 151 | Andres Ambühl | |
| Most points (goals + assists) | 164 | Boris Mikhailov | |
| Most gold medals | 10 | Alexander Ragulin | |
| Vladislav Tretiak | |||
| Most medals in total | 13 | Jiří Holík | |
| Vladislav Tretiak | |||
Tournament Attendance
The highest number of people to attend a championship was 797,727 in 2024. The second highest was 741,690 in 2015. Both of these tournaments were held in the Czech Republic. The 2024 event also had the most fans per game, with an average of 12,464 people.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Campeonato Mundial de Hockey sobre Hielo Masculino para niños
In Spanish: Campeonato Mundial de Hockey sobre Hielo Masculino para niños