Orbital inclination facts for kids
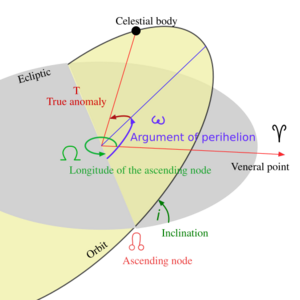
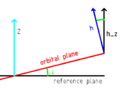
Orbital inclination is a way to describe the angle between two orbital planes. Think of an orbital plane as an imaginary flat surface that an object travels on as it orbits something else. This angle helps us understand how different objects move in space.
We often use orbital inclination to talk about how stars, planets, and moons move. To measure this angle, we pick one plane as a standard, or "reference" plane.
For example, when we talk about stars, the reference plane might be the flat disk of their galaxy. For a planet orbiting a star, like Earth orbiting the Sun, the reference plane is usually the ecliptic plane. This is the imaginary flat surface where Earth's orbit lies.
If a moon orbits a planet with an inclination of 0 degrees, it means the moon is orbiting exactly above the planet's equator. It also moves in the same direction as the planet spins.
Contents
What is an Orbital Plane?
An orbital plane is like an invisible, flat sheet of glass that an object moves along as it orbits another object. Imagine a planet orbiting the Sun. Its path creates a flat circle or oval in space. This flat area is its orbital plane.
Every object that orbits another has its own orbital plane. These planes can be tilted at different angles compared to each other. Orbital inclination measures this tilt.
Why is Orbital Inclination Important?
Understanding orbital inclination is very important for astronomy and space exploration. It helps scientists:
- Predict where spacecraft will go.
- Plan missions to other planets or moons.
- Understand how solar systems formed.
- Find new exoplanets (planets outside our solar system).
For example, if a satellite is launched into space, its orbital inclination decides which parts of Earth it can see. A satellite with a high inclination can pass over many different latitudes, including the poles.
Examples of Inclination
Different objects in space have different orbital inclinations.
Planets in Our Solar System
Most of the major planets in our Solar System orbit the Sun in planes that are very close to the ecliptic plane. This means their inclinations are quite small, usually less than a few degrees. For instance, Jupiter has an inclination of about 1.3 degrees. This shows that our solar system is mostly flat, like a disk.
However, some dwarf planets or smaller objects can have much larger inclinations. For example, Pluto's orbit is tilted by about 17 degrees compared to the ecliptic plane.
Moons and Satellites
For moons orbiting a planet, the inclination is often measured relative to the planet's equator.
- A moon with 0 degrees inclination orbits right over the planet's equator.
- Many of the large moons of Jupiter and Saturn have very low inclinations. This suggests they formed from the same spinning disk of gas and dust that created their parent planet.
Artificial satellites launched from Earth can have a wide range of inclinations.
- A satellite in a geostationary orbit has an inclination of 0 degrees. It stays above the Earth's equator.
- Weather satellites or spy satellites often have high inclinations. This allows them to observe almost the entire surface of the Earth as the planet rotates beneath them.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Inclinación orbital para niños
In Spanish: Inclinación orbital para niños
 | Ernest Everett Just |
 | Mary Jackson |
 | Emmett Chappelle |
 | Marie Maynard Daly |