Ionia facts for kids
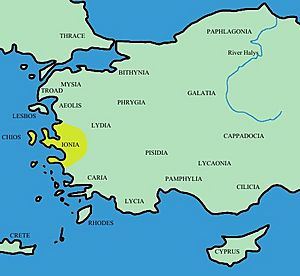
Ionia was an important region in Ancient Greece. It was located on the western coast of Asia Minor, which is now part of Turkey. Many people believe Ionia was the birthplace of Greek civilization.
Contents
Early History of Ionia
Around 1000 to 900 BCE, many Greeks moved from the Peloponnese (a part of Greece) across the Aegean Sea to Anatolia. They were looking for new places to live. At first, there were many small Greek settlements in Ionia.
The Twelve Cities
By the 8th century BCE, these small settlements grew into 12 major cities. These cities became very powerful and wealthy.
The main cities on the mainland were:
- Phocaea
- Erythrae
- Clazomenae
- Teos
- Lebedus
- Colophon
- Ephesus
- Priene
- Myus
- Miletus
The important islands that were part of Ionia were:
- Chios
- Samos
Ionian Prosperity
By the end of the 7th century BCE, the Ionian cities were very successful. They became rich through trading with other regions. They also started new colonies and made many goods. These goods included ceramics (pottery), textiles (cloth), and metalware.
Ionia in Modern Times
After World War I, Ionia was given to Greece from Turkey. This happened as part of the Treaty of Sèvres. Most of the islands in the Aegean Sea, Thrace, and Istanbul were also given to Greece.
However, the Turkish army soon drove the Greek people out of Ionia. Many Greeks had to leave the region. The Turkish army did not challenge the Greeks on the Aegean Islands.
Images for kids
-
One of the earliest electrum coins struck in Ephesus, 620–600 BC. Obverse: Forepart of stag. Reverse: Square incuse punch.
-
The site of Miletus, once coastal, now inland. The plain was a bay in Classical Greece.
-
The temple of Artemis in Sardis.
-
The Library of Celsus in Ephesus was built by the Romans in 114–117. The Temple of Artemis in Ephesus, built by king Croesus of Lydia in the 6th century BC, was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
See also
 In Spanish: Jonia para niños
In Spanish: Jonia para niños